Angioedema: causes, symptoms, treatment
About the Symptom
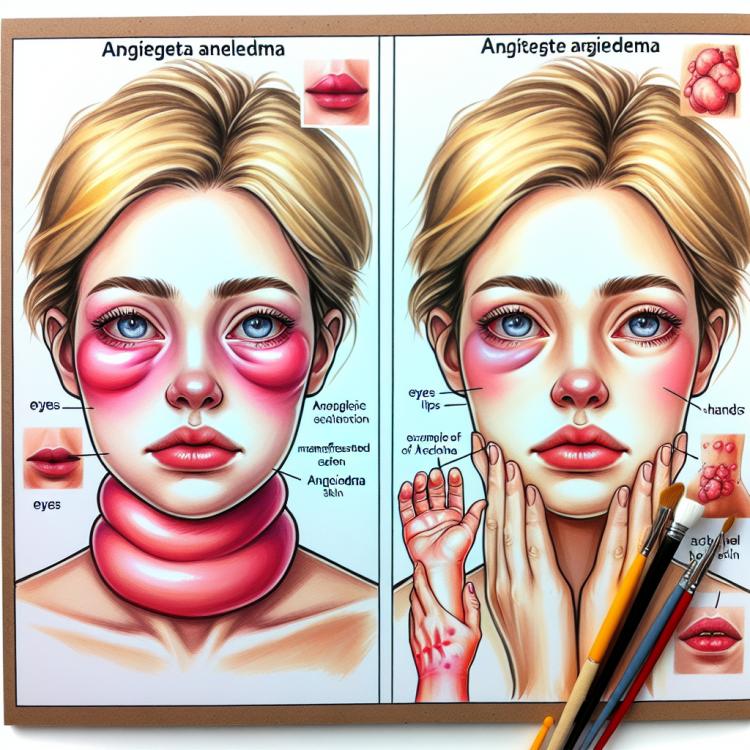
Angioedema is a condition in which swelling occurs in the skin, mucous membranes, or subcutaneous tissue. This swelling occurs due to the engorgement of tissues caused by fluid leakage. It can develop in various areas of the body, such as the face, lips, and larynx, causing significant discomfort for the patient.
The main symptom of angioedema is rapidly increasing swelling that can occur suddenly and worsen over a few minutes or hours. Patients may also experience itching, burning, and redness at the site of swelling. In case of swelling of the larynx, breathing difficulties may arise, necessitating immediate medical attention.
Diseases
Angioedema is a condition in which there is swelling of the skin, mucous membranes, or subcutaneous tissue due to the rapid growth of vascular formations. This swelling usually occurs in the area of the face, lips, tongue, throat, or ears and can lead to serious complications, including respiratory distress.
There are several diseases that can lead to the development of angioedema. Among them:
- Allergic reactions to food, medications, or insect stings;
- Hereditary angioedema caused by defects in the gene that controls the protein regulating fluid permeability in tissues;
- Some autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis;
- Physical factors, such as pressure or trauma to the skin.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of angioneurotic edema plays a crucial role in determining this condition and selecting the appropriate treatment. The main symptom of angioneurotic edema is a sudden swelling of the skin and mucous membranes, most often in the areas of the face, lips, tongue, larynx, and uvula. Diagnosis is typically performed by an allergist or immunologist.
To establish a diagnosis and rule out other possible causes of edema, various clinical and laboratory studies are conducted. These diagnostic methods may include a clinical examination, blood tests for allergic reactions and immunoglobulin levels, as well as allergy tests.
- Clinical examination
- Complete blood count
- Immunochemical analyses
- Allergy tests
Which doctor to consult
If you suspect angioedema, it is important to consult an allergist or immunologist. These specialists have the necessary qualifications and experience to diagnose and treat allergic reactions, including angioedema.
A consultation with a dermatologist or general practitioner is also recommended for an initial assessment of symptoms and referral for appropriate testing.
- Allergist/Immunologist
- Dermatologist
- Therapist/General Practitioner
Angioneurotic edema is a condition in which the skin, mucous membranes, subcutaneous tissue, or the mucous membrane of the pharynx and vocal cords begin to swell due to uncontrolled inflammation in the body. There are various types of angioneurotic edema, each of which may have its own characteristics and causes of development.
1. Idiopathic angioneurotic edema: this form of edema occurs suddenly and is associated with genetic or immunological causes. It can be hereditary or develop on its own.
2. Allergic angioneurotic edema: this variant of edema occurs as a result of the body’s allergic reaction to certain food products, medications, or other substances.
3. Psychogenic angioneurotic edema: this type of edema may arise in response to stress, emotional experiences, or psychosomatic conditions.
These types of angioneurotic edema can be influenced by various factors, so accurately defining the type of edema is crucial for the diagnosis and treatment of this condition.
Angioedema can arise from various factors, both genetic and external. One of the most common causes is an allergy to certain foods, medications, or substances. Angioedema may also be related to uncontrolled stress and prolonged nervous tension. Often, the swelling occurs as a reaction to food intolerance or autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus.
There are other causes that can trigger angioedema, including thyroid dysfunction, infections, insect bites, changes in the blood, and even improper absorption of certain medications. It is important to remember that in each specific case, the causes of the swelling can be unique, so for an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to consult a specialist and undergo the appropriate examination.
Common Associated Pathologies
Angioneurotic edema, while a serious condition in itself, can also be associated with other pathologies and states of the body. This type of edema is often observed in patients with allergic reactions. Allergies can be triggered by food, medications, insects, or other allergens, and this frequently leads to the development of angioneurotic edema.
Additionally, angioneurotic edema may be associated with hereditary angioedema or neuroedema. Some conditions, such as Quincke’s disease, can also cause angioneurotic edema. It is important to identify the underlying condition related to the edema to determine the most effective treatment and prevent further complications.
- Allergic reactions
- Hereditary angioedema
- Neuroedema
- Quincke’s disease
Expert Opinion
Angioedema is a serious condition that requires careful attention and a competent approach from specialists. According to leading experts in the field of allergology and immunology, angioedema occurs as a result of the body’s reaction to various irritants, such as allergens, food products, medications, or physical influences.
Experts also emphasize the importance of timely diagnosis and treatment of angioedema. Delayed consultation with a physician and incorrectly chosen treatment can lead to severe complications, including a threat to the patient’s life. Therefore, it is recommended to consult qualified specialists at the first signs of possible development of angioedema.
- Conducting allergy tests to identify potential allergens.
- Consultation with an allergist or immunologist to develop an individual treatment program.
- Prescribing specialized treatment, including antihistamines or hormonal medications in severe cases.

Treatment of Angioneurotic Edema
The treatment of angioneurotic edema includes several main methods and aims to eliminate the edema, prevent its recurrence, and relieve the patient’s symptoms. In most cases, the treatment is carried out in conjunction with an allergist or immunologist and includes necessary therapy.
The main methods of treating angioneurotic edema are:
- The use of antihistamine medications to reduce the allergic reaction and decrease swelling;
- The use of glucocorticoid medications to reduce inflammation and tissue swelling;
- Taking measures to prevent contact with an identified allergen;
- Sometimes, medications may be required to support respiratory and cardiovascular functions.
Complications
Although angioedema is usually not life-threatening, in some situations this symptom can lead to serious complications. One of the most dangerous types of complications from angioedema is laryngeal edema, where swelling of the larynx leads to breathing difficulties and can cause suffocation.
Another common complication of angioedema is anaphylactic shock — a severe systemic allergic reaction that can lead to decreased blood pressure, heart rhythm disturbances, and in some cases even loss of consciousness and death.
- Laryngeal edema
- Anaphylactic shock
- Shortness of breath and breathing difficulties
- Increased pressure in the eyes
- Swelling of the larynx