White spots on the oral mucosa: causes, symptoms, and treatment
About the Symptom
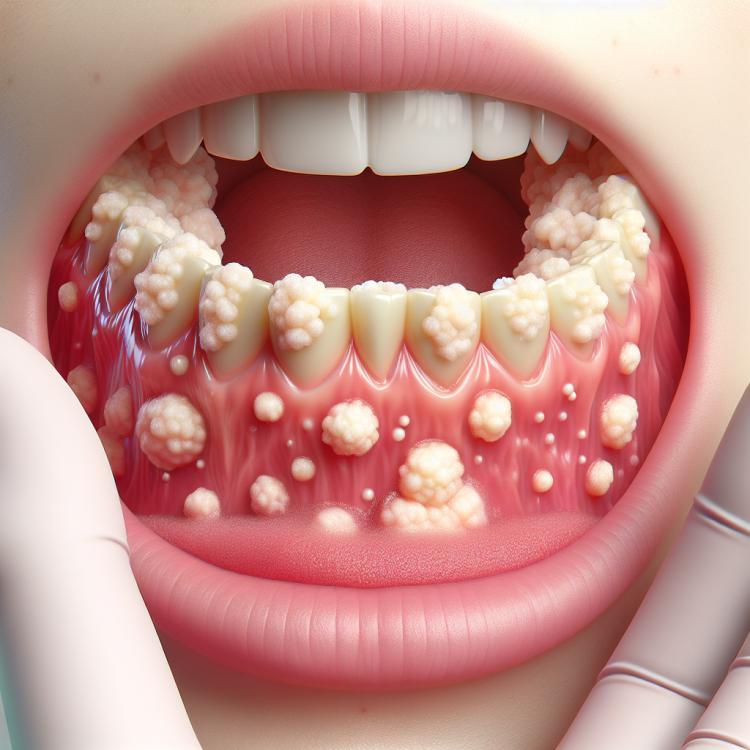
White patches on the mucous membrane of the mouth are a phenomenon that can cause concern for both patients and dentists. These formations can occur on the cheeks, tongue, gums, and even on the lips, and can vary in size and shape. White patches may indicate various conditions and diseases, such as candidiasis (thrush), leukoplakia, or even more serious pathologies that require immediate medical intervention. Additionally, such formations may be caused by mechanical injuries, allergic reactions, or a deficiency of vitamins and minerals in the body.
When white patches appear on the mucous membrane of the mouth, it is important not to ignore this symptom and to consult a doctor for diagnosis. A dentist or an otolaryngologist can perform the necessary tests and assess the condition of the oral cavity to determine the cause of the white patches. It is important to remember that some of these formations may be harmless and not requiring treatment, while others may indicate the presence of serious diseases that require timely therapy. Therefore, early diagnosis and proper treatment play a key role in maintaining oral health and overall well-being.
Diseases
White spots on the oral mucosa can be a sign of various diseases, affecting both the oral cavity itself and the systemic condition of the body. These formations can arise due to infections, inflammatory processes, or even autoimmune diseases. It is important to remember that regardless of the size or number of white spots, one should consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Among the diseases that manifest as white spots on the oral mucosa, the following can be highlighted:
- Oral candidiasis (thrush) caused by fungi of the genus Candida;
- Leukoplakia, characterized by the appearance of white spots on the mucosa and may be a precursor to cancer;
- Acute or chronic stomatitis, accompanied by inflammation of the oral mucosa;
- Viral herpes, which can manifest as white blisters and spots;
- Mucosal lesions in syphilis, including palatal leukoplakia;
- Aphthous stomatitis, characterized by painful ulcers and white spots on the mucosa.
Each of these diseases requires an individualized approach to treatment, so it is important not to delay a visit to a specialist upon discovering such symptoms.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of white spots on the oral mucosa is an important step in establishing their nature and determining the appropriate treatment. If such spots appear, it is necessary to consult a dentist or an otolaryngologist, who will conduct a visual examination and, if necessary, prescribe additional tests. It is important to note that white formations can be either harmless or symptoms of serious diseases, so timely diagnosis will help prevent complications.
To more accurately determine the causes of white spots on the oral mucosa, doctors may use various diagnostic methods. This may include laboratory tests, biopsy, as well as consultations with narrow specialists if necessary. Establishing an accurate diagnosis is extremely important for prescribing adequate and effective treatment.
- Visual examination of the oral mucosa
- Laboratory tests (smears, blood tests)
- Biopsy
- Consultation with a dermatologist
- Endoscopy if necessary
- Clinical tests for infections
Which doctor to consult
When white spots appear on the mucous membrane of the mouth, it is important not to ignore this symptom and seek medical help. This may be a sign of various diseases, and only a qualified specialist can establish an accurate diagnosis. The first step in diagnosis should be a visit to the dentist, who will conduct an examination and assess the condition of your oral cavity. If the dentist suspects a more serious pathology, they may refer you to other specialists.
In addition to the dentist, depending on the nature and accompanying symptoms, you may need a consultation with an otolaryngologist (ENT) or dermatologist. These doctors will be able to carry out the necessary examinations and determine whether the formation of white spots is related to diseases of other organs. However, it is important to remember that prompt medical attention significantly increases the chances of successful treatment.
- Dentist
- Otolaryngologist
- Dermatologist
- Immunologist
- Allergist
Types of White Spots on the Oral Mucosa
White spots on the oral mucosa can manifest in various forms and have their own characteristics, which may indicate different pathologies. One of the most common types of white spots is leukoplakia and candidiasis, each of which has its own causes and treatment methods. Leukoplakia most often occurs as a result of chronic irritation of the mucosa, which can be caused by smoking, alcohol dependence, or mechanical trauma. Candidiasis, on the other hand, is caused by a fungal infection that can develop against a background of decreased immunity or prolonged use of antibiotics.
Additionally, white spots may be associated with other diseases, such as vitiligo or even precancerous conditions. They can be flat, waxy, or red in appearance, depending on the cause of their occurrence. It is very important to correctly identify the type of white spots in order to prescribe appropriate treatment and prevent possible complications. The assessment of the condition of white spots should be carried out by a qualified specialist based on a visual examination and additional studies.
- Leukoplakia
- Candidiasis (thrush)
- Vitiligo
- Aphthous stomatitis
- Psoriasis of the mucosa
- Saline pairs (saliva ionization)
Causes of White Spots on the Oral Mucosa
White spots on the oral mucosa can occur for various reasons, and their appearance often signals that certain changes are happening in the body. One of the most common causes is candidiasis, or thrush, caused by the Candida fungus. This condition most often manifests in individuals with weakened immune systems, such as newborns, the elderly, and patients taking antibiotics or steroids. Candidiasis can cause itching, discomfort, and painful sensations when eating.
Other common causes of white spots may include viral infections, such as herpes, or various autoimmune diseases, for example, leukoplakia. In the latter case, the spots may be precursors to more serious conditions, such as oral cancer. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also contribute to the appearance of white spots, as they irritate the mucosa. It is important to understand that the exact cause requires qualified diagnosis and may vary depending on the patient’s specific situation.
- Candidiasis (thrush)
- Viral infections (herpes)
- Leukoplakia
- Autoimmune diseases
- Injuries or irritation of the mucosa
- Smoking and alcohol consumption
- Vitamin deficiencies, especially B vitamins and C
Common Associated Pathologies
White spots on the mucous membrane of the mouth can be manifestations of various pathologies that require careful diagnosis and, in some cases, treatment. One common cause of such changes is candidiasis, or thrush, caused by the fungus Candida. This infection leads to the formation of a white coating that can be painful and cause discomfort when eating or speaking.
Other common diseases accompanied by white spots include leukoplakia and HIV infection. Leukoplakia is a chronic condition characterized by the formation of white patches on the mucosa, which can evolve into precancerous changes over time. HIV infection can also cause various changes in the oral cavity, including white spots, which is associated with a weakened immune system.
- Candidiasis (thrush)
- Leukoplakia
- HIV infection
- Human papillomavirus infection
- Stomatitis
- Herpes
Expert Opinion
White spots on the mucous membrane of the mouth can have various origins and may indicate different diseases, some of which require immediate medical intervention. A dentist or therapist can perform a preliminary diagnosis and refer the patient to a specialist if necessary. Experts emphasize the importance of timely medical consultation, as not all white formations are safe. Upon discovering white spots, one should not panic, but delaying a visit to a specialist is also not recommended.
Some white spots may be associated with conditions such as candidiasis, leukoplakia, or mucosal changes, which may signal systemic issues, for example, with the immune system. It is important to note that such changes in the oral cavity can also be symptoms of an allergic reaction to food products or medications. Therefore, a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s condition, including an analysis of their health and lifestyle data, plays a key role in accurately interpreting the cause of white spots in the mucosa.

Treatment of white spots on the oral mucosa
The treatment of white spots on the oral mucosa depends on the underlying disease that causes this symptom. However, before starting any therapeutic actions, it is important to undergo a complete examination and obtain an accurate diagnosis from a dentist or therapist. The doctor may recommend anti-inflammatory gels, antiseptics, as well as topical agents if the cause is an infectious process.
In addition, sometimes systemic therapy is necessary, especially if the white spots are a symptom of a more serious disease, such as candidiasis or leukoplakia. In such cases, antifungal medications or immunostimulants may be prescribed. It is also important to consider lifestyle factors, so the doctor may recommend dietary changes, quitting bad habits, and mandatory preventive measures to improve the condition of the oral mucosa.
- Antifungal medications
- Antiseptics and anti-inflammatory gels
- Immunostimulants
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections
- Dietary and lifestyle changes
Complications
White spots on the oral mucosa can be a sign of various diseases, and ignoring this symptom can lead to serious consequences. One of the main complications is the possibility of infections developing, which can spread to adjacent areas of the mucosa. For example, candidiasis can lead not only to white spots but also to painful sensations and difficulties in swallowing. In some cases, in the absence of appropriate treatment, the infection can become chronic, negatively affecting the patient’s quality of life.
Moreover, white spots may indicate precancerous conditions such as leukoplakia, which is characterized by the formation of white patches on the oral mucosa and can progress to cancer. Therefore, it is important to conduct timely diagnostics and follow the doctor’s recommendations. Taking action at an early stage of the disease helps to avoid serious complications and provides a more favorable prognosis for health.
- Development of infections (candidiasis, herpes, staphylococcus)
- Chronic diseases of the oral mucosa
- Precancerous conditions (leukoplakia)
- Deterioration of quality of life (pain, swallowing difficulties)
- Psychological problems due to altered appearance
FAQ
What to do if white spots have appeared on the mucous membrane of the mouth?
What causes white spots on the mucous membrane of the mouth?
Complications
The appearance of white spots on the oral mucosa may be associated not only with visual discomfort but also with potential complications that can arise in the absence of adequate treatment. One of the most common complications is the development of a chronic inflammatory process, which can lead to pain, difficulty in speaking and chewing, as well as a deterioration in the overall condition of the patient. Additionally, some conditions that manifest as white spots may increase the risk of developing infectious diseases, such as candidiasis or herpes, which also requires timely medical assistance to prevent more serious consequences.
Ignoring white spots, especially if they are accompanied by other symptoms such as itching, burning, or bleeding, can lead to the spread of infection to other areas of the oral cavity or even to systemic infections. Chronic changes in the mucous membrane may also become precancerous or cancerous formations, emphasizing the need for timely diagnosis and therapy.