Pain in the scrotum: causes, symptoms, and treatment of diseases
About the Symptom
Testicular pain is a symptom that can arise for various reasons and can vary significantly in intensity. It can present both acutely and chronically, and is often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations in the genital area. Painful sensations may be triggered by injuries, inflammatory processes, or infections, which may indicate serious medical conditions that require immediate intervention. When experiencing pain in the testicles, it is important to seek medical attention promptly to determine the cause and select appropriate treatment.
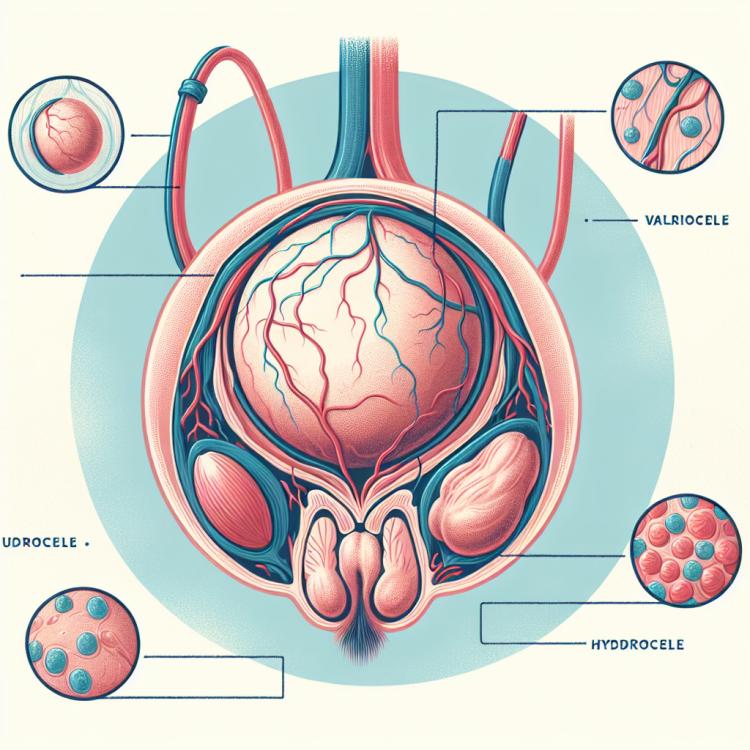
The causes of testicular pain can be diverse. The most common include epididymitis, orchitis, varicocele, and injuries. Epididymitis is accompanied by inflammation of the epididymis, which can cause sharp pain and swelling. Orchitis is inflammation of the testicle, which can also lead to severe pain. Varicocele is the enlargement of veins in the spermatic cord, which can result in discomfort and persistent pain. Regardless of the cause, testicular pain should never be ignored, as in some cases it may be a sign of more serious conditions, such as testicular torsion, which should not be overlooked.
Diseases
Pain in the scrotum can be caused by various diseases, each of which requires special attention and diagnosis. One of the most common causes of pain in this area is epididymitis— inflammation of the epididymis, which can be caused by infections or injuries. This condition is usually accompanied by swelling, redness, and an increase in temperature. Another common disease is orchitis, inflammation of the testicle, which can also be related to infections, viruses, or bacterial agents.
Among the less common but potentially serious conditions are varicocele— enlargement of the veins of the testicle, which can cause discomfort and develop infertility. Testicular torsion— another dangerous pathology, during which the spermatic cord twists, which can lead to tissue necrosis if help is not provided in time. It is also worth mentioning hydrocele— accumulation of fluid in the testicular sac, which can cause a feeling of heaviness and pain in the scrotum.
- Epididymitis
- Orchitis
- Varicocele
- Testicular torsion
- Hydrocele
- Scrotal injuries
- Spermatic cord cyst
- Testicular cancer
Diagnosis
When a patient visits a medical clinic with complaints of testicular pain, the first step in the diagnostic process is a thorough collection of medical history. The doctor asks questions about the nature of the pain, its duration, possible triggers, and accompanying symptoms. This information helps determine what further tests may be needed to clarify the cause of the pain. It is also important to consider whether there have been any previous injuries or surgeries, as well as a history of diseases in the urogenital area.
Among the diagnostic procedures that may be recommended by the doctor are ultrasound of the scrotum and pelvic organs, tests for infectious diseases, and a complete blood count. If necessary, more complex imaging methods, such as CT or MRI, may be prescribed. By conducting these studies, the doctor can identify conditions that cause discomfort, such as varicocele, infectious processes, or tumor formations.
- Ultrasound of the scrotum
- Tests for infections (e.g., PCR for chlamydia and gonococci)
- Complete blood count
- Semen analysis
- CT or MRI of the pelvic organs
Which doctor to consult
If you experience pain in the scrotum, it is important not to delay your visit to a specialist. This symptom may indicate various conditions that require timely diagnosis and treatment. Initially, it is advisable to consult a urologist, as this doctor deals with men’s health issues and can conduct the necessary examinations to determine the cause of the pain.
If the urologist finds the need for a more specialized approach, he may refer you to other specialists. For instance, if the cause of the pain is related to an infection or inflammation, a consultation with an infectious disease specialist may be necessary. If there are suspicions of oncological diseases, a referral to an oncologist will be recommended. It is important to remember that early diagnosis and timely consultation with specialists play a key role in the success of treatment.
- Urologist
- Infectious disease specialist
- Oncologist
- Surgeon
- Therapist
Types of Pain in the Scrotum
Pain in the scrotum can manifest in various ways, and understanding its types is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Depending on the nature and intensity of the pain, several main categories can be identified. Acute pain usually occurs suddenly and may be associated with injuries, infections, or overloads. Chronic pain is present for a long time and often requires more thorough medical examination to determine its causes.
Additionally, the pain may be unilateral or bilateral, which is important for understanding its source. Unilateral pain typically indicates problems with one of the testes or the spermatic cord, while bilateral pain may signal broader issues such as inflammation or infection in the scrotal area. Considering these signs, it is important to clearly describe the symptoms to the doctor for a more accurate diagnosis.
- Acute pain
- Chronic pain
- Unilateral pain
- Bilateral pain
- Dull pain
- Multiplicative pain
Causes of Pain in the Scrotum
Pain in the scrotum can be caused by a variety of factors, and its nature ranges from minor issues to serious medical conditions. One of the most common causes is trauma, which can occur due to physical impact or even excessive physical activity. Injuries can cause inflammation and swelling, leading to painful sensations. Additionally, many men may encounter functional anomalies related to the reproductive system, which can also cause discomfort.
Another frequently encountered cause of scrotal pain is infectious processes. Inflammation of the testicles (orchitis), epididymitis, or urinary tract infections can lead to significant pain and require immediate medical attention. It is also worth noting that some more serious diseases, such as varicocele or cryptorchidism, can also be a source of chronic discomfort. Understanding the causes of scrotal pain will aid in timely diagnosis and treatment, which is a key aspect of maintaining men’s health.
- Scrotal injuries
- Testicle infection (orchitis)
- Epididymitis
- Urinary tract infection
- Varicocele
- Cryptorchidism
- Hernia
- Testicular tumors
Common Associated Pathologies
Scrotal pain can be a symptom of various diseases and pathologies that require attention and professional diagnosis. Among the most common conditions associated with pain in this area are epididymitis, varicocele, orchitis (inflammation of the testicle), and various injuries. Each of these diagnoses has its own characteristics, but all can cause discomfort and serious complications if medical help is not sought in a timely manner.
Epididymitis, for example, is an inflammation of the epididymis, which is often caused by an infection. Varicocele is the dilation of veins, which is accompanied by pain, especially during physical activity, and can lead to infertility. Orchitis often occurs after viral infections such as mumps and also requires medical intervention. Mechanical injuries can also cause acute discomfort, and in such cases, a rapid examination is necessary to prevent serious consequences.
- Epididymitis
- Varicocele
- Orchitis (inflammation of the testicle)
- Injuries to the scrotum and testicles
- Testicular torsion
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
Expert Opinion
Pain in the scrotum is a symptom that may indicate a variety of different diseases and conditions. According to experienced urologists, it is important not to ignore even mild discomfort, as it may be a sign of serious diseases such as orchitis or cryptorchidism. Doctors strongly recommend seeking medical help at the onset of pain in order to conduct necessary diagnostics and rule out more dangerous pathologies such as testicular rupture or spermatic cord torsion.
Experts emphasize that pain in the scrotum can be caused by both infectious and non-infectious factors. For example, infections may arise as a result of sexually transmitted diseases, while injuries may occur due to physical activity. Thus, comprehensive examinations are often ordered to determine the exact cause and choose the most effective treatment method. Combination therapy may include both medications and surgical interventions depending on the diagnosis.

Treatment of Testicular Pain
The treatment of testicular pain depends on the cause of this symptom. It is important to conduct a thorough diagnosis and determine the exact source of discomfort, as it may be related to various conditions, including infections, injuries, and tumors. In some cases, if the cause is related to an infection, a course of antibiotics may be required. In other conditions, such as varicocele, surgical intervention may be necessary to resolve the issue.
In addition to medication therapy, an important aspect of treatment is following the doctor’s recommendations regarding lifestyle. This may include limiting physical activity, using supportive underwear, and changing the diet. It is also essential to monitor your condition and seek medical attention if new symptoms arise.
Now let’s consider some treatment methods:
- Medication therapy (antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs);
- Surgical interventions (e.g., for varicocele);
- Physiotherapy and therapeutic procedures;
- Lifestyle and dietary adjustments;
- Use of supportive underwear to reduce discomfort.
Complications
Pain in the scrotum can indicate a variety of problems in the body, and if medical assistance is not sought in time, it can lead to serious complications. One of the most common consequences is the development of chronic pain, which significantly worsens the patient’s quality of life. Chronic pain can be not only a physical but also a psychological burden, leading to decreased work capacity and social activity.
In addition, some conditions that cause pain in the scrotum can lead to more serious diseases, such as infertility or tissue necrosis. For example, in the presence of an infection or inflammatory process in the testes or epididymis, testicular necrosis may develop, which requires surgical intervention. A real threat is also associated with varicose veins of the spermatic cord, which can disrupt blood flow and complicate recovery.
- Chronic pain in the scrotal area
- Infertility
- Tissue necrosis of the testes
- Urinary tract infections
- Varicose veins of the spermatic cord