Glossitis: symptoms, types, causes, and treatment of the disease
About the Symptom
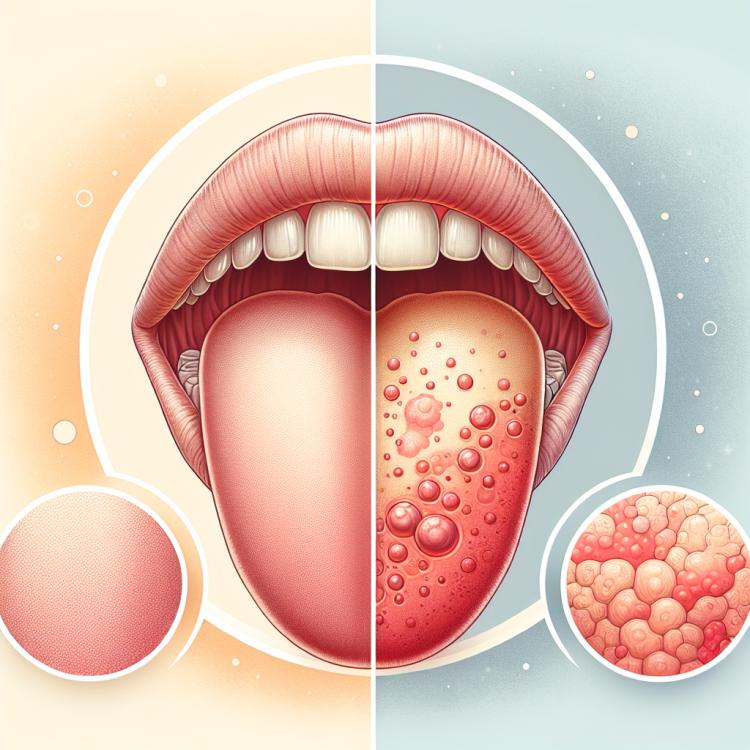
Glossitis is an inflammation of the tongue that can manifest with various symptoms. The main sign of this condition is a change in the appearance of the tongue: it may become swollen, smooth, or red. A change in the color of the tongue’s surface is often observed, which can take on a bright red or even purple hue. Other characteristic symptoms include pain, burning, and a decreased perception of taste. In some cases, cracks or sores may appear on the surface of the tongue, leading to additional discomfort.
Among the possible causes of glossitis are allergic reactions, infections, trauma, or poor nutrition. Glossitis may also be associated with chronic diseases such as diabetes or vitamin deficiencies, especially B12. Fluctuations in stress levels or hormonal changes can also contribute to the development of this condition. If symptoms of glossitis are present, it is important to consult a doctor for timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Diseases
Glossitis is an inflammatory disease of the tongue that can be caused by a variety of factors, including infectious agents, allergic reactions, and vitamin deficiencies. Symptoms of glossitis can range from mild itching and redness to painful sensations and swelling. It is important to remember that glossitis may not be a separate disease, but rather a symptom of underlying pathologies that require mandatory medical examination and treatment.
There are several diseases that can lead to the development of glossitis, and it is important to recognize them for timely diagnosis. Among the diseases associated with glossitis, we can note:
- Anemia (deficiency of vitamins B12 and iron)
- Fungal infections (e.g., candidiasis)
- Viral infections (herpetic infection)
- Allergic reactions to food or dental products
- Autoimmune diseases (such as systemic lupus erythematosus)
- Sexually transmitted diseases (e.g., syphilis)
- Nutrient deficiencies (vitamins B2, B3, and B6)
Correct diagnosis of the underlying disease is a key step in the effective treatment of glossitis, highlighting the importance of consulting a specialist upon the appearance of its first symptoms.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of glossitis begins with a thorough interview of the patient regarding their symptoms and lifestyle. The dentist or therapist pays attention to the presence or absence of pain, changes in the color and texture of the tongue, as well as accompanying symptoms such as dryness in the mouth or difficulty swallowing. This information allows the doctor to suggest possible causes of the inflammation of the tongue and to choose the most effective methods for further examination.
A clinical examination of the tongue is an important stage in diagnosing glossitis. The specialist assesses the condition of the mucous membrane, its color, and the presence of swelling or ulcers. Additional laboratory tests may be prescribed, such as a complete blood count or streptosensitization, to determine the presence of infectious processes or allergic reactions. In some cases, a biopsy may be required to rule out more serious pathologies.
- Complete blood count
- Clinical urine analysis
- Laboratory tests for infections (e.g., culture for fungal infections)
- Allergy testing
- Biopsy of the tongue (if necessary)
Which doctor to consult
When symptoms of glossitis occur, such as redness, swelling, pain, or changes in the color of the mucous membrane of the tongue, it is crucial to promptly consult a specialist. Glossitis can be caused by various factors, including infectious processes, allergic reactions, and vitamin deficiencies. Based on these reasons, the best choice may be to consult with several doctors. A primary examination can be conducted by a therapist, who will assess the patient’s condition and refer them to specialists if necessary.
If you suspect an infectious nature of glossitis, you may need assistance from an otolaryngologist or dentist. These specialists can perform a detailed examination and determine whether additional treatment is necessary. Additionally, if the cause of the disease is vitamin deficiency, a consultation with a dietitian or gastroenterologist may be required to prescribe an appropriate diet and therapy.
- Therapist
- Dentist
- Otolaryngologist
- Gastroenterologist
- Dermatologist (in case of skin manifestations)
- Dietitian (for dietary correction)
Types of Glossitis
Glossitis is an inflammatory condition of the tongue that can manifest in various forms. There are several types of glossitis, each with its specific symptoms and causes. The main types of glossitis include atrophic, ulcerative, and geographic glossitis, each requiring an individual approach to treatment and diagnosis.
Atrophic glossitis is characterized by a thinning of the tongue, resulting in redness and smoothness of its surface. This type can occur due to a deficiency of vitamins, especially B12, or due to systemic diseases. Ulcerative glossitis is manifested by the formation of painful ulcers on the tongue, which can hinder the process of eating and speaking. Geographic glossitis, in turn, is marked by the appearance of spots resembling a map and may be related to allergic reactions or stress.
- Atrophic glossitis
- Ulcerative glossitis
- Geographic glossitis
- Hypertrophic glossitis
- Candidal glossitis
Causes of Glossitis
Glossitis is inflammation of the tongue that can occur for a number of reasons. One of the main causes is a deficiency of vitamins and minerals, especially B vitamins, iron, and folic acid. A lack of these substances can lead to changes in the mucous membrane of the tongue, which subsequently causes inflammation. Another important factor is disorders in the digestive system, such as gastritis or stomach ulcers, which can affect the condition of the tongue.
The second common cause of glossitis is infections. Bacterial and viral infections (such as herpes) can cause inflammation of the tongue and are accompanied by a number of symptoms, such as swelling and color changes. Additionally, allergic reactions to certain foods, medications, or toothpaste can also trigger inflammation of the tongue, causing glossitis.
- Vitamin and mineral deficiency
- Infections (bacterial and viral)
- Allergic reactions
- Injuries to the tongue (mechanical or chemical)
- Chronic diseases (such as diabetes)
Common Related Pathologies
Glossitis is inflammation of the tongue that can be associated with various pathologies and conditions. One of the most common causes of glossitis is infections, including viral, bacterial, and fungal. For example, candidiasis (thrush) can lead to inflammation of the tongue, making it painful and difficult to swallow and speak. Infections caused by viruses, such as the herpes virus, can also cause symptoms of glossitis.
Additionally, glossitis can be a consequence of systemic diseases, such as diabetes or anemia. In such conditions, there may be a deficiency of vitamins and minerals, which also affects the health of the tongue. Causes related to a lack of iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid can lead to changes in the structure, color, and texture of the tongue, often resulting in glossitis.
- Candidiasis (thrush)
- Viral infections (herpes virus)
- Systemic diseases (diabetes, anemia)
- Vitamin B deficiencies
- Allergic reactions to foods or substances
Expert Opinion
Glossitis, inflammation of the tongue, is a symptom that may indicate a wider range of diseases and conditions. That is why it is important not to ignore this symptom. Often, patients may underestimate the seriousness of glossitis manifestations, thinking that it is a temporary phenomenon; however, a dentist or therapist can identify more serious pathologies at early stages if the patient seeks help in a timely manner. Typically, the treatment of glossitis requires a comprehensive approach and the elimination of the causes that triggered the condition, which also emphasizes the importance of timely diagnosis.
Experts in the field of dentistry and maxillofacial surgery emphasize that important aspects in the treatment of glossitis are prevention and adherence to hygiene standards. Caution is recommended when choosing oral hygiene products, as some of them may irritate the tongue. Reviews from patients who have undergone glossitis treatment show that an individualized approach and recommendations from specialists significantly contribute to successfully overcoming this condition and preventing its recurrences.

Treatment of Glossitis
The treatment of glossitis usually depends on its cause and severity. Therapy may include both conservative and more complex methods if the disease is associated with more serious pathologies. It is primarily recommended to identify the provoking factor, such as allergy, infection, or trauma, as this will determine the further treatment strategy. If glossitis is caused by a microbial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed, and for fungal infections, antifungal medications may be used.
It is also important to pay attention to improving oral hygiene, including regular cleaning of the tongue and teeth, using mouth rinses, and avoiding irritating foods. In some cases, special diets may be required, excluding spicy, acidic, and salty foods, to relieve discomfort and promote the rapid healing of inflamed tissue.
- Antibacterial therapy (in infectious glossitis)
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Antifungal therapy (in candidal glossitis)
- Topical antiseptics and mouth rinses
- Correction of diet and hygiene regimen
- General supportive therapy to strengthen the immune system
Complications
Glossitis, like any other disease, can lead to various complications if it is not diagnosed and treated in a timely manner. One of the most common consequences is the development of chronic glossitis, which can manifest as periodic exacerbations and constant discomfort. The chronic form of the disease can significantly impair the quality of life, as it is associated with pain during eating and dysfunction of the chewing system.
Another serious complication of glossitis is the risk of developing an infection. The inflamed tissue of the tongue becomes more susceptible to bacterial and fungal infections, which can lead to additional diseases of the oral cavity. It is important to note that the presence of chronic glossitis can indicate other disorders in the body, such as vitamin deficiencies or mucous membrane diseases, which require a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment.
- Chronic glossitis
- Oral infections
- Chewing system dysfunction
- Nutrition and nutrient absorption problems
- Exacerbation of comorbid diseases