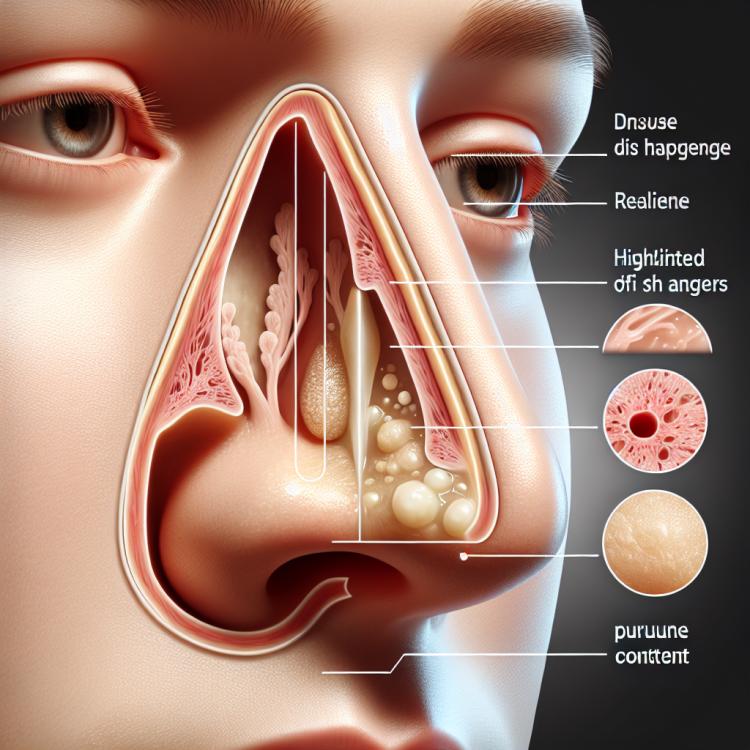
Pus-like nasal discharge: causes, symptoms, and treatment
About the Symptom
Purulent nasal discharge is a common symptom that can indicate various respiratory diseases. This discharge is often accompanied by inflammation of the nasal mucosa, leading to nasal congestion, pain in the sinus area, and general malaise. The appearance of pus in the discharge usually signals a bacterial infection, such as sinusitis or rhinitis, especially when the discharge is yellow-green and has an unpleasant odor.
It is important to understand that purulent nasal discharge can result from not only an infection but also other factors, such as allergies, the presence of polyps, or even foreign bodies in the nasal passages. Symptoms accompanying purulent discharge may range from mild congestion and sneezing to high fever and severe headache, highlighting the necessity of consulting a doctor to determine the precise cause and to prescribe appropriate treatment.
Diseases
Purulent nasal discharge can be a symptom of various diseases related to inflammation of the nasal passages and sinuses. The most common causes of this condition include sinusitis, rhinitis, and adenoiditis. In sinusitis, inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, the purulent discharge may have a greenish-yellow color and be accompanied by headache, fever, and general weakness. Chronic rhinitis (inflammation of the nasal mucosa) can also lead to the appearance of pus, especially if there is an infection.
Additionally, adenoiditis is often seen in children, characterized by an increase in adenoid tissue and, as a consequence, difficulty breathing and purulent nasal discharge. Any of these diseases requires timely consultation with a doctor to obtain an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Ignoring symptoms can lead to complications and a worsening of health.
- Sinusitis
- Rhinitis
- Adenoiditis
- Tonsillitis
- Bacterial infection of the upper respiratory tract
- Nasal polyps
- Other chronic respiratory infection
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of purulent nasal discharge is an important step in determining the cause of the disease and prescribing effective treatment. The ENT doctor examines the patient, collecting medical history and assessing the overall health condition. Often, additional tests are required for more accurate diagnosis to identify the source of the problem, such as a bacterial or viral infection, irritation, or an allergic reaction.
The main diagnostic methods include visual examination, rhinoscopy, and, if necessary, laboratory tests. This may include culture of nasal discharge to determine the type of microorganisms, as well as sensitivity tests for antibiotics. In some cases, special imaging may be required, such as X-rays or CT scans of the nasal cavity and sinuses.
- Visual examination of the nasal cavity
- Rhinoscopy
- Culture of nasal discharge
- Sensitivity test for antibiotics
- X-ray of the sinus cavities
- Computed tomography (CT) of the nasal cavity
Which doctor to consult
Purulent nasal discharge can be a symptom of various diseases, and for effective treatment, it is crucial to consult the right specialist. Usually, in such cases, the first doctor to consult is an otolaryngologist (ENT). He will conduct a complete examination, determine the cause of the purulent discharge, and prescribe the appropriate treatment. The specialist will focus on your symptoms, medical history, and diagnostic results.
Additionally, in some cases, it may be necessary to consult other specialists, such as an allergist or immunologist, especially if the discharge is related to allergic reactions. It is important to understand that self-examination and self-treatment can lead to complications, so you should not delay visiting a doctor if this symptom manifests.
- Otolaryngologist (ENT)
- Allergist
- Immunologist
- Pediatrician (for children)
- Therapist
Types of Purulent Nasal Discharge
Purulent nasal discharges can have various characteristics that help doctors diagnose the underlying cause. The main types of discharge may include thick, yellow, or green pus, which often indicates the presence of an infection. The thickness and color of the discharge can vary depending on the stage of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient.
It is important to note that the discharge can be unilateral or bilateral. Unilateral purulent discharge often indicates a local infection, such as sinusitis, while bilateral discharge may point to more extensive inflammation affecting both sides of the nasal cavities. Understanding these features can aid in the quick and accurate diagnosis of the problem.
- Yellow purulent discharge
- Green purulent discharge
- Thick discharge
- Thin, watery discharge with admixture of pus
- Profuse discharge
Causes of purulent discharge from the nose
Purulent discharge from the nose can be the result of various diseases and pathological conditions. The most common causes of the appearance of pus are infections caused by bacteria or viruses. Viral infections, such as influenza or the common cold, can lead to inflammation of the nasal mucosa, which in turn creates favorable conditions for the growth of bacteria and the development of bacterial sinusitis. This condition is characterized by an increase in discharge, its cloudy color, and odor.
In addition, purulent discharge may occur as a result of allergic reactions or injuries that facilitate the invasion of microbes into the nasal cavity. Chronic diseases such as allergic rhinitis or nasal polyps can also influence the appearance of such symptoms. An important aspect of diagnosis is that the state of the patient’s immune system can significantly increase the likelihood of purulent discharge in the presence of other predisposing factors.
- Acute and chronic sinusitis;
- Viral infections (influenza, ARI);
- Allergic rhinitis;
- Nasal cavity injuries;
- Nasal polyps;
- The presence of foreign bodies in the nose.
Common Related Pathologies
Purulent nasal discharge often signals the presence of more serious diseases that require the attention of a specialist. These discharges can be a symptom of various infections and inflammatory processes affecting the upper respiratory tract. One of the most common pathologies is sinusitis, which can occur in both acute and chronic forms. In sinusitis, the nasal sinuses become inflamed, leading to the accumulation of purulent content and, consequently, to purulent discharge.
Another common pathology is rhinitis, which can be of either allergic or infectious origin. Allergic rhinitis causes inflammation and swelling of the nasal mucosa, which can lead to discharge, including purulent. Viral and bacterial infections, such as influenza and the common cold, can also cause similar symptoms. The addition of a secondary bacterial infection often complicates the course of the disease and worsens the patient’s condition.
- Sinusitis (acute and chronic)
- Allergic rhinitis
- Viral and bacterial infections of the upper respiratory tract
- Nasal polyposis
- Inhalation of foreign bodies
Expert Opinion
Purulent nasal discharge is a symptom that may indicate various infectious and inflammatory processes in the body. In most cases, this phenomenon is associated with respiratory diseases such as sinusitis or rhinitis. When visiting a doctor, it is important to mention all accompanying symptoms, as this can significantly influence the final diagnosis and, accordingly, the treatment methods.
Experts note that self-diagnosing and prescribing treatment based on purulent nasal discharge is impractical. Many patients decide to use antibacterial medications without consulting a doctor, which can lead to a worsening of the condition and the development of resistant strains of bacteria. A qualified doctor will perform the necessary examinations to identify the true cause of the purulent discharge and prescribe effective treatment.
It is important to remember that prolonged or especially abundant purulent discharge may indicate more serious diseases. Therefore, when symptoms persist for a long time, it is advisable not to postpone a visit to a specialist to avoid possible complications.

Treatment of purulent nasal discharge
The treatment of purulent nasal discharge primarily depends on the cause of its occurrence. In most cases, it is associated with infectious diseases such as sinusitis or rhinitis, which require a comprehensive approach to therapy. An important aspect is the diagnosis and determination of the type of infection, which helps doctors prescribe adequate treatment, including antibiotics if a bacterial infection is present. Anti-inflammatory medications and decongestants may also be prescribed to relieve symptoms and reduce swelling of the nasal passages.
In addition to medication treatment, in some cases, physiotherapeutic procedures are recommended, such as rinsing the nose with saline solutions, inhalations, or UHF therapy. These methods help clear the nasal passages of pus and facilitate breathing. Emergency cases, where conservative methods do not yield results, may require surgical intervention to drain the nasal sinuses.
- Antibiotics (in case of bacterial infection)
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Decongestants
- Saline solutions for nasal rinsing
- Physiotherapy
- Surgical intervention (in extreme cases)
Complications
Purulent discharge from the nose can be a manifestation of various diseases, including sinusitis, rhinitis, and other upper respiratory tract infections. In the absence of timely and proper treatment, these conditions can lead to serious complications. One of the most common consequences is the spread of infection to neighboring organs, such as the ears (otitis) and throat (pharyngitis). In some cases, inflammatory processes can also affect the eyes, threatening the development of conjunctivitis or even infections that can cause vision loss.
Another significant complication is the possible development of chronic sinusitis, in which inflammation of the nasal cavities becomes prolonged and difficult to treat. This can lead to recurrent episodes of purulent discharge and deterioration of the patient’s overall condition. Long-term consequences may include loss of smell and allergic reactions, significantly reducing the quality of life.
- Spread of infection to the ears (otitis)
- Development of chronic sinusitis
- Loss of smell
- Eye infections (conjunctivitis)
- Allergic reactions