Cholesterol plaques: causes, symptoms, and treatment
About the Symptom
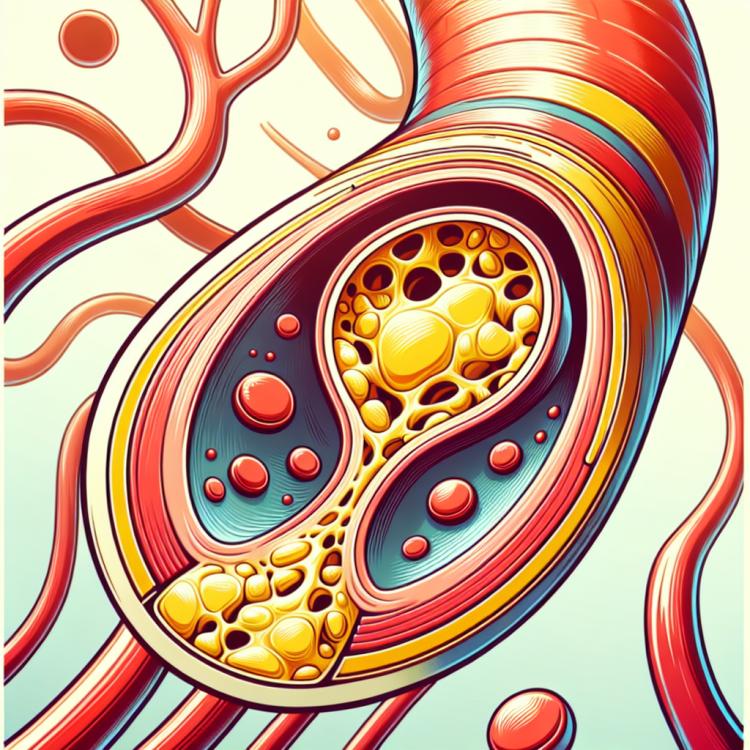
Cholesterol plaques are an important indicator of the state of the cardiovascular system, and their presence may signal the development of atherosclerosis. These plaques consist of accumulations of cholesterol, fats, and other substances that accumulate on the walls of the arteries, narrowing their lumen and hindering blood circulation. Initially, symptoms may be absent; however, as the disease progresses, the clinical picture becomes more pronounced. The main symptoms of cholesterol plaques may include chest pain, fatigue during physical exertion, and a general deterioration of well-being.
It is important to note that cholesterol plaques can lead to more serious complications — ischemic heart disease, stroke, or myocardial infarction. Accordingly, the identification and monitoring of symptoms such as shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, or intermittent pain in the limbs is critically important. Regular medical check-ups, including tests for cholesterol levels, can help in the early detection and treatment of this condition, allowing for the prevention of serious health consequences.
Diseases
Cholesterol plaques, which are accumulations of lipids on the walls of arteries, can lead to many serious diseases. Firstly, they cause narrowing of the vessels, which in turn restricts blood flow to vital organs. Over time, this can manifest as angina, characterized by chest pain during physical exertion or emotional stress. Gradual deterioration can lead to a myocardial infarction, when blood flow to areas of the heart is completely blocked, causing necrosis of the heart muscle.
Moreover, cholesterol plaques can contribute to the development of a stroke, when one of the arteries supplying the brain becomes blocked. This will result in damage to the nerve tissue and impairment of various parts of the brain. It should also be noted that the plaques on the walls of arteries can rupture, forming clots, which significantly increases the risk of an acute vascular event.
- Angina
- Myocardial infarction
- Stroke
- Chronic heart failure
- Atherosclerosis
- Obliterating atherosclerosis
- Peripheral artery disease (PAD)
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of cholesterol plaques is an important step in assessing the condition of the cardiovascular system. In the early stages, there may be no obvious symptoms, but early detection of problems helps to avoid serious complications. The main diagnostic methods include blood tests for cholesterol levels, as well as instrumental methods such as ultrasound (US) and angiography. These procedures allow doctors to assess the extent of atherosclerotic changes in the vessels and make decisions about further actions.
To obtain a more complete picture of the patient’s condition, other diagnostics, such as stress tests, may be used, as they help determine how well the heart copes with exertion. It is important to note that regular medical examinations and monitoring of cholesterol levels are very important, especially for people at risk. Timely consultation with a doctor upon the first signs of illness can significantly enhance the effectiveness of treatment.
- Complete blood count
- Lipid profile (cholesterol level test)
- Ultrasound of the vessels
- Angiography
- ECG (electrocardiogram)
- Stress test
Which doctor to contact
If you suspect the presence of cholesterol plaques and related diseases, it is advisable to consult several specialists. The first doctor you can make an appointment with is a therapist. He will conduct an initial examination, assess your complaints and circumstances, and refer you for the necessary tests to clarify the diagnosis. The therapist plays a key role in the early diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases related to cholesterol levels in the blood.
After receiving the test results and diagnosis, you may need a consultation with a cardiologist. This specialist deals with treating heart and vascular diseases, and his help is essential if serious deviations are identified, such as atherosclerosis or coronary disease. It should also be considered that if you have additional risk factors (for example, diabetes, obesity, or hypertension), you may need a consultation with an endocrinologist or dietitian to adjust your lifestyle and diet.
Directions for specialists for the treatment of cholesterol plaques:
- Therapist
- Cardiologist
- Endocrinologist
- Dietitian
- Vascular surgeon
Types of Cholesterol Plaques
Cholesterol plaques are areas of lipid and cholesterol accumulation in the walls of arteries, which can significantly affect blood circulation and overall human health. There are several types of cholesterol plaques that differ in their characteristics and consequences for the body. Among the main types, stable and unstable plaques can be distinguished. Stable plaques typically have a dense capsule made of connective tissue and grow slowly, reducing the risk of rupture and thrombus formation. Unstable plaques, on the other hand, are more prone to rupture and thrombus formation, potentially leading to acute cardiovascular diseases.
Furthermore, cholesterol plaques can vary in size—from small to large formations. Small plaques, often not visualized in standard examinations, can accumulate over many years, leading to a gradual deterioration of blood flow. Large plaques, however, can cause noticeable symptoms and significantly complicate the body’s functioning. Understanding these differences is important for a competent approach to the diagnosis and treatment of diseases associated with atherosclerosis.
- Stable cholesterol plaques
- Unstable cholesterol plaques
- Small cholesterol plaques
- Large cholesterol plaques
Causes of Cholesterol Plaques
Cholesterol plaques form as a result of a complex process that begins with the accumulation of cholesterol and other fats in the walls of the arteries. One of the main reasons for this process is poorly organized nutrition, rich in saturated fats and trans fats, which leads to an increase in cholesterol levels in the blood. Excessive consumption of fast food, ready-made culinary products, and sweets can be the starting point for the appearance of plaques.
Another important reason is a sedentary lifestyle. Physical inactivity impairs metabolism and the elimination of “bad” cholesterol from the body, which also contributes to the accumulation of cholesterol in the vessels. It is also worth noting that genetic predisposition, smoking, stress, high blood pressure, and diabetes are factors that increase the risk of forming cholesterol plaques.
- Poor nutrition (high content of saturated and trans fats)
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Smoking
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Genetic predisposition
- Stress and psychological factors
Common Related Pathologies
Cholesterol plaques are an important indicator of the state of the cardiovascular system and can lead to a number of serious diseases. The accumulation of plaques in the vessels hinders blood circulation, which can cause various pathologies. The most common related diseases are atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral arterial disease. These conditions develop as a result of damage to the vessel walls and increased cholesterol levels in the blood.
Atherosclerosis, as the primary disease, is characterized by the deposition of cholesterol plaques on the walls of the arteries, which can subsequently lead to stenosis (narrowing) of the vessels. Coronary artery disease, arising from insufficient blood supply to the myocardium, carries a high risk of developing myocardial infarction. Stroke is associated with the cessation of blood supply to the brain, which can have serious health consequences. Peripheral arterial disease affects the blood vessels leading to the limbs, which can result in pain and even gangrene.
- Atherosclerosis
- Coronary artery disease
- Stroke
- Peripheral arterial disease
- Hypertensive disease
- Heart failure
Expert Opinion
Cholesterol plaques pose a serious problem that directly affects the state of the cardiovascular system. According to leading cardiologists, the presence of such formations in the vessels can significantly increase the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases such as myocardial infarction and stroke. These plaques form due to the accumulation of cholesterol, triglycerides, and other fats in the walls of the arteries, leading to their narrowing and reduced blood flow. It is important to understand that over time, this problem can remain asymptomatic, which makes it particularly insidious.
Experts emphasize that prevention and timely diagnosis are the key factors in successfully combating cholesterol plaques. Regular checks of cholesterol levels, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and following the doctor’s recommendations regarding therapeutic diets and physical activity can significantly reduce the risk of plaque formation. Furthermore, an important aspect is patient awareness of risk factors and access to medical care, which will help prevent the development of serious diseases.

Treatment of Cholesterol Plaques
Treatment of cholesterol plaques that form in the arteries requires a comprehensive approach and may include both medication and non-medication methods. At the first stage, it is important to change lifestyle: follow a diet low in saturated fats, increase physical activity, and monitor blood pressure and weight. These changes can significantly lower blood cholesterol levels and slow down the plaque formation process.
Medication therapy often includes statin drugs, which help lower cholesterol levels, as well as medications that affect its absorption and excretion from the body. In some cases, if the plaques have caused complications (such as angina or stroke), surgical intervention may be required, such as angioplasty or stent placement.
- Diet correction
- Increased physical activity
- Statin intake
- Aspirin for preventing thrombosis
- Surgical methods (angioplasty, stenting)
Complications
Cholesterol plaques represent a dangerous condition that can lead to serious complications in the body. One of the most common complications is atherosclerosis, a condition in which plaques accumulate in the arteries, narrowing their lumen and obstructing blood flow. This can cause a wide range of cardiovascular diseases, including coronary artery disease, angina, and myocardial infarction. Additionally, irregular or insufficient blood supply to organs can lead to disability and even death.
Another dangerous complication is the occurrence of a stroke, which happens when blood flow to a part of the brain is blocked either by a thrombus formed due to plaque rupture or by narrowing of blood vessels. A stroke can have serious consequences, including loss of functions, the need for long-term rehabilitation, and the risk of recurrent strokes. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to cholesterol levels and monitor the state of the cardiovascular system to minimize the risks of complications.
Major complications of cholesterol plaques:
- Atherosclerosis
- Coronary artery disease
- Angina
- Myocardial infarction
- Stroke
- Chronic heart failure
- Peripheral arterial disease