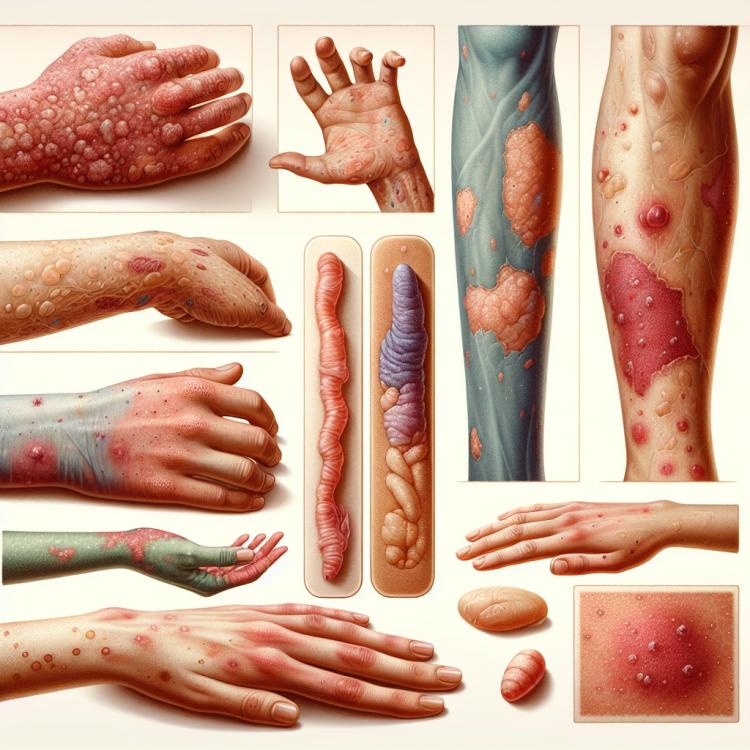
Crusts on the skin: causes, types, and treatment methods
About the symptom
Crusts on the skin are formations that can arise due to various causes, including inflammatory processes, infections, allergic reactions, or even skin diseases. They can vary in size, color, and texture, making them a symptom that requires careful attention. Most often, crusts form as a result of the drying of exudate that is released during skin damage or inflammatory processes. Such layers can cause itching, discomfort, and even pain, especially if there is friction with clothing.
From a diagnostic standpoint, crusts on the skin can indicate a variety of conditions—from eczema, psoriasis, and dermatitis to more serious infections like impetigo. It is important to understand that the presence of crusts is not a separate disease but a symptom that requires a comprehensive analysis. By consulting a medical clinic, a patient can receive recommendations for diagnosis and treatment based on the clinical picture and individual characteristics of the body. Do not ignore crusts on the skin, as they can be a sign of a serious illness that requires medical intervention.
Diseases
Crusts on the skin can be a sign of various diseases that people of different ages experience. Often, crusts form as a result of inflammatory processes, allergic reactions, or infections. Localized or widespread crusty formations may indicate the need for medical consultation for diagnosis and comprehensive treatment.
Some of the diseases that may be accompanied by the formation of crusts on the skin include:
- Psoriasis – a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by red patches with silvery-white crusts.
- Dermatitis – inflammation of the skin that can be triggered by allergies or contact irritants, often leading to the formation of crusts.
- eczema – a condition characterized by itchy rashes and crusts, often associated with allergic reactions.
- Fungal infections – such as mycosis, can cause crusts, peeling, and itching in the affected areas of the skin.
- Contagious molluscum – a viral disease manifested as small crusts or nodules on the skin.
- Scleroderma – an autoimmune disease that leads to thickening and darkening of the skin, which may also be accompanied by crusts.
It is important to remember that if you notice crusts on the skin, especially if they are itchy, bleeding, or do not go away, you should consult a specialist for a thorough examination and appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of skin conditions accompanied by the formation of crusts plays a key role in identifying and treating underlying diseases. First of all, the doctor may conduct a visual examination to assess the extent and nature of the crusts, as well as identify accompanying symptoms such as itching, inflammation, or redness. These observations will help the specialist determine whether the cause of the crusts might be a dermatological disease or an allergic reaction.
After the initial examination, additional diagnostic procedures may be appointed to more accurately determine the cause of the crusts. These may include laboratory tests such as skin scrapings, blood tests for infections or allergens, as well as dermatoscopy for a more detailed study of skin formations. Proper diagnosis will allow for the development of an effective treatment plan and avoid potential complications.
- Visual skin examination
- Laboratory tests (blood, skin scraping)
- Dermoscopy
- Allergological examination
- Clinical tests for infection detection
Which doctor to consult
When crusts appear on the skin, it is important not to ignore this symptom, as it may indicate various diseases and disorders. Initially, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist, who is a specialist in skin diseases. The dermatologist will analyze the condition of the skin, evaluate the nature of the rashes, and order appropriate tests to clarify the diagnosis.
In some cases, crusts on the skin may be related to allergic reactions or internal diseases, which will require consulting other specialists, such as an allergist or a gastroenterologist. Qualified consultation with doctors will help determine the root cause of the crusts and develop an individual treatment plan, as well as prevention of their recurrence.
- Dermatologist
- Allergist
- Gastroenterologist
- Endocrinologist
- Immunologist
Types of Crusts on the Skin
Crusts on the skin can manifest in various forms and represent a symptom of different diseases. Depending on their appearance, color, and texture, crusts can indicate various pathologies, from simple allergic reactions to more serious skin diseases. It is important to understand that a diagnosis can only be made by a qualified specialist after appropriate examination.
Among the main types of crusts on the skin, the following can be highlighted:
- Dry crusts – often occur with dry skin, eczema, or herpes. They can be white or light yellow and form as a result of cell death.
- Wet crusts – usually appear as a result of inflammatory processes or injuries. Their surface may be moist or discharge fluids such as pus.
- Blood crusts – arise after skin injuries, insect bites, or scratching of other types of crusts. They may be a sign of more serious conditions, such as infection.
- Purulent crusts – often found in bacterial infections such as impetigo. They have a yellowish or greenish tint and can be quite painful.
Each of these types requires an individual approach to diagnosis and treatment, so it is necessary to consult a doctor for professional advice and recommendations.
Causes of Scabs on the Skin
Scabs on the skin can arise from a multitude of causes, and understanding them is important for choosing the right treatment. One of the most common reasons for the formation of scabs is skin damage related to injuries, abrasions, or skin diseases. This can be caused either by mechanical impact or by various infections that lead to the formation of scabs and hinder the natural healing process.
It is also worth noting that environmental conditions can have a significant impact on the state of the skin. For example, frequent exposure to water, high or low temperatures can dry out the skin, promoting the formation of scabs. Additionally, allergic reactions to cosmetics, medications, or food can cause inflammation and scab formation, which requires consultation with a doctor to identify the allergen and prescribe appropriate treatment.
- Skin injuries (wounds, abrasions)
- Infectious diseases (herpes, eczema)
- Allergic reactions
- Skin diseases (psoriasis, dermatitis)
- Environmental factors (dry air, temperature)
Common Associated Pathologies
Scabs on the skin can arise for various reasons and are often a symptom of more serious diseases. It is important to understand that scabs do not appear on the skin by themselves, but may be associated with various dermatological or systemic pathologies. For example, eczema, psoriasis, and some infectious diseases, such as fungal infections, can be accompanied by the formation of scabs on the skin’s surface.
If scabs arise as a result of an allergic reaction, this may indicate atopic dermatitis or contact dermatitis. In rare cases, scabs may be a sign of more complex diseases, such as pemphigus vulgaris or leukemia, highlighting the importance of timely diagnosis and consulting a specialist.
- Eczema
- Psoriasis
- Contact dermatitis
- Fungal infections
- Pemphigus vulgaris
- Atopic dermatitis
- Leukemia (in rare cases)
Expert Opinion
Crusts on the skin can arise for various reasons, and their treatment requires a comprehensive approach. A dermatologist, possessing knowledge of different skin diseases, believes that the first step when noticing crusts is to determine their nature. Often, crusts are a result of inflammatory processes, allergic reactions, or fungal infections. Some cases may be associated with more serious conditions such as psoriasis or eczema, which require further investigation and adjustment of treatment.
It is important for the patient not to attempt to remove the crusts on their own, as this may lead to complications of the skin condition. Experts recommend consulting a specialist who will conduct a diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment if necessary. In most cases, the doctor may recommend moisturizing creams, anti-inflammatory medications, or antihistamines depending on the cause of the crusts.
It should also be considered that many skin diseases may be linked to internal problems of the body, including metabolic disorders or hormonal changes. Therefore, to achieve the best results from treatment, it is worth viewing skin health as part of the overall health of the body.

Treatment of crusts on the skin
The treatment of crusts on the skin depends on the initial causes of their appearance, so timely diagnosis is extremely important. It is necessary to see a doctor if crusts appear on large areas of the body or are accompanied by itching, pain, redness, or other symptoms. The doctor will conduct an examination and may order additional tests, such as blood tests, skin samples, or biopsy, to determine the exact cause of the problem.
Depending on the diagnosis, the treatment may vary. For example, in case of infectious diseases, antibacterial or antifungal medications may be prescribed. For skin diseases such as eczema or psoriasis, corticosteroid agents, moisturizing creams, and special ointments may be used. It is also important to revise the skin care regimen, avoiding aggressive cosmetics and caring for delicate skin with gentle, hypoallergenic formulations.
- Medication therapy (antibiotics, antifungal agents)
- Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
- Moisturizing creams and ointments
- Physiotherapy procedures
- Correction of diet and daily routine
Complications
Crusts on the skin can be not just a cosmetic problem, but also a signal of more serious diseases. If attention is not paid to the crusts in time, this can lead to various complications. One of the most common consequences is an infection that can develop against the backdrop of constant scratching and damage to the crusts. Bacteria can penetrate the deeper layers of the skin, causing inflammatory processes and requiring more serious treatment, including the prescription of antibiotics.
In addition, the presence of crusts can cause allergic reactions and discomfort, which, in turn, negatively affects a person’s overall psycho-emotional state. Stress and anxiety can exacerbate the problem, as nervous tension often leads to new rashes. Finally, if the crusts are associated with chronic skin diseases such as eczema or psoriasis, this may lead to further deterioration of the skin condition and the need for more comprehensive therapy.
- Skin infections.
- Allergic reactions.
- Chronic skin diseases (eczema, psoriasis).
- Psycho-emotional tension and stress.
- Deterioration of the skin’s appearance.