Swelling of the throat: causes, symptoms, and treatment methods
About the symptom
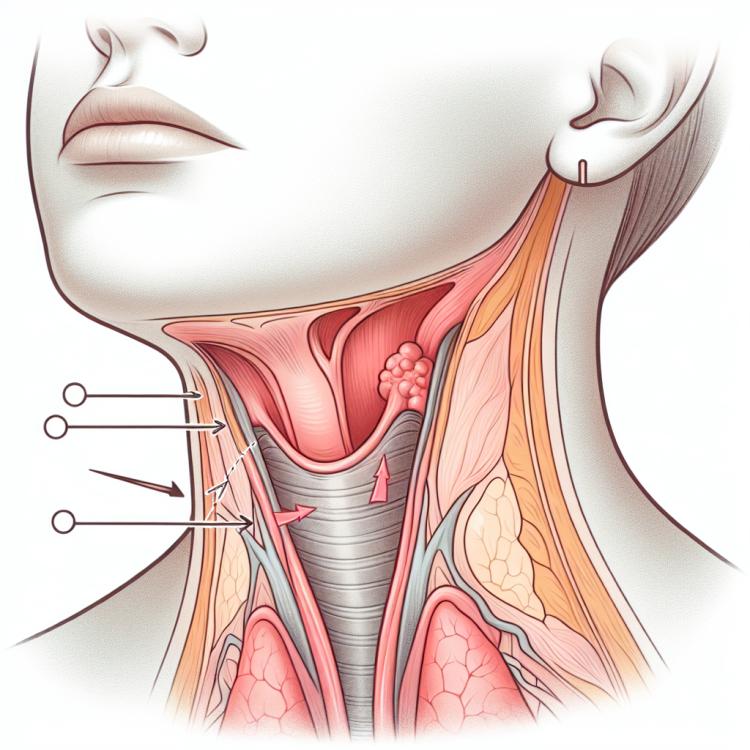
Throat swelling is a condition characterized by an increase in the volume of tissues in the area of the larynx and pharynx, which can cause difficulties in breathing and swallowing. This symptom can be triggered by various factors, including allergic reactions, infections, injuries, or inflammatory processes. It is important to note that throat swelling can develop rapidly and may require emergency medical attention, especially if accompanied by symptoms such as difficulty breathing, hoarseness, or a feeling of choking.
The most common causes of throat swelling include allergic reactions to food, pollen, or insect bites, as well as infectious diseases such as tonsillitis or laryngitis. In some cases, the swelling may be a result of mechanical trauma or burns caused by hot liquids. If throat swelling occurs, it is essential to consult a doctor to determine the cause and prescribe appropriate treatment, as ignoring this symptom can lead to serious complications.
Diseases
Throat swelling can be a symptom of various diseases that require careful and competent diagnosis and treatment. Most often, throat swelling occurs as a result of inflammatory processes, allergic reactions, or infectious diseases. It is important to understand that timely consultation with a doctor will help establish an accurate diagnosis and prevent possible complications.
There are several diseases that can cause throat swelling:
- Acute tonsillitis (angina) — inflammation of the tonsils, which can lead to severe throat pain and swelling.
- Laryngitis — inflammation of the larynx, often accompanied by hoarseness and difficulty breathing.
- Allergic edema — a reaction to various allergens, including pollen, dust, pet dander, and food products.
- Pharyngitis — inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx, leading to discomfort and swelling.
- Infectious mononucleosis — a viral disease that causes inflammation of the tonsils and throat swelling.
When determining the cause of throat swelling, it is important to consider accompanying symptoms and the overall clinical picture for more accurate diagnosis and effective treatment selection.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of throat swelling is an important step in determining the cause of this unpleasant symptom. The doctor will likely start with a detailed questionnaire of the patient about their complaints, medical history, and possible allergies. A physical examination includes a visual inspection of the throat and neck, during which the doctor may notice redness, swelling, or other abnormalities. Such initial manipulations help determine whether further investigation is required.
For accurate diagnosis of throat swelling, various investigative methods may be prescribed. These methods may include laryngoscopy for visualization of the larynx, neck ultrasound to assess the condition of surrounding tissues, as well as dermatological allergy tests in case of suspected allergic reactions. It is important to identify the cause of throat swelling as quickly as possible in order to start appropriate treatment and prevent possible complications.
- Laryngoscopy
- Neck ultrasound
- Allergy tests
- Endoscopy
- Blood tests
- Neck X-ray
- Neck CT scan
Which doctor to consult
If you experience symptoms of throat swelling, such as difficulty breathing, pain, or a feeling of constriction, you should seek medical help immediately. The first specialist you should consult is a therapist. This doctor will conduct an initial examination and will be able to determine the next steps in diagnosis and treatment. The therapist can order necessary tests and, if needed, refer you to a more specialized doctor.
Depending on the cause of the throat swelling, you may need consultations with the following specialists: otolaryngologist, allergist, or even immunologist. An otolaryngologist treats diseases of the throat, nose, and ears and can offer the most appropriate treatment for your situation. An allergist will help if the swelling is caused by an allergic reaction, while an immunologist will address issues related to the immune system and chronic diseases.
- Therapist
- Otolaryngologist (ENT)
- Allergist
- Immunologist
- Pulmonologist (for assessing lung condition)
Types of Throat Swelling
Throat swelling can manifest in various forms, each of which may indicate different causes and require a specific approach to treatment. The most common types of swelling are allergic swelling, caused by reactions to foods, medications, or pollen, as well as swelling associated with infectious diseases, such as tonsillitis or pharyngitis. It is also worth noting angioedema, which can occur suddenly and requires immediate medical attention.
Depending on the severity and localization of the swelling, patients may experience different symptoms. Localized swelling may affect only part of the throat or tonsils, while diffuse swelling can encompass the entire throat and laryngeal area. It is important to understand that some types of throat swelling can be life-threatening if timely measures are not taken.
- Allergic swelling
- Infectious swelling (e.g., in tonsillitis or pharyngitis)
- Traumatic swelling (after surgeries or injuries)
- Angioedema
- Swelling caused by inflammatory processes (tonsillitis, laryngitis)
Causes of Throat Swelling
Throat swelling can occur for a variety of reasons that differ in nature and consequences. One of the most common causes is the body’s reaction to allergens, such as plant pollen, dust, or pet dander. An allergic reaction can cause inflammation and swelling of the tissues in the throat, leading to difficulty in breathing and swallowing.
In addition, throat swelling may be a result of various infections. Viral infections, such as the flu or a cold, are often accompanied by throat inflammation, which can lead to swelling. Bacterial infections, such as angina or tonsillitis, can also cause severe inflammation and swelling that require immediate treatment.
Moreover, there are other factors that contribute to the development of throat swelling, including injuries, exposure to chemicals or irritants, as well as certain chronic diseases, such as obstructive sleep apnea. A consultation with specialists is necessary to determine the exact cause of throat swelling.
- Allergic reactions
- Viral infections (flu, cold)
- Bacterial infections (angina, tonsillitis)
- Neck or throat injuries
- Chemical irritation
- Chronic diseases (obstructive sleep apnea)
Common Related Pathologies
Throat swelling can be a symptom of various diseases, and its occurrence is often associated with a number of pathologies that require careful analysis. One of the most common related conditions is acute laryngitis — inflammation of the larynx, which can cause not only swelling but also sore throat, hoarseness, and difficulties swallowing. Laryngitis can be caused by viral or bacterial infections or even irritation from chemical substances and tobacco smoke.
Another frequent cause of throat swelling is an allergic reaction. Allergens such as pollen, pet dander, or dust can provoke acute allergic swelling, which requires immediate intervention, as it can lead to serious respiratory problems. Additionally, chronic inflammatory diseases, such as tonsillitis or pharyngitis, can also contribute to the development of swelling, as they affect the condition of the throat’s mucous membrane.
- Acute laryngitis
- Allergic swelling
- Chronic tonsillitis
- Pharyngitis
- Adenoiditis
- Injuries and burns of the throat
- Infections caused by streptococci or staphylococci
Expert Opinion
Throat swelling is a symptom that may indicate a number of serious diseases and conditions. It is important to understand that this symptom should not be ignored, and it is best to consult a specialist as soon as possible. Doctors emphasize that throat swelling can lead not only to breathing difficulties but also to more serious complications such as asphyxia or the development of inflammatory processes.
According to experts, the most common causes of throat swelling are allergic reactions, infections, and injuries. ENT specialists note that prompt medical attention can significantly improve the prognosis and relieve the patient’s condition. The choice of treatment method will depend on the cause of the swelling, so it is important to conduct a complete diagnosis and obtain qualified advice.
Moreover, experts recommend avoiding self-treatment, as this can worsen the situation. A doctor’s consultation will help determine not only the causes of throat swelling but also suggest optimal measures for its treatment, contributing to the swift recovery of respiratory functions.

Treatment of Throat Swelling
The treatment of throat swelling depends on its cause and the severity of the condition. It is important to consult a doctor as soon as possible for diagnosis and appropriate treatment. The doctor may recommend antihistamines that help reduce swelling if the cause is an allergic reaction. In cases of viral infections, such as acute pharyngitis, treatment may include anti-inflammatory medications and pain relievers for sore throat.
If the swelling is caused by a bacterial infection, such as tonsillitis, antibacterial therapy may be required. It is also important to monitor hydration by drinking enough fluids, which can reduce discomfort. In some cases, when the swelling is significant and threatens breathing, emergency medical assistance may be needed, including decompression procedures.
- Antihistamines
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Antibiotics (for bacterial infections)
- Hydration (fluid intake)
- Basic methods to ease breathing (if necessary)
Complications
Throat swelling can cause various complications if medical help is not sought in time. One of the most serious consequences is the risk of difficulty in breathing. With significant swelling, airway obstruction may occur, requiring emergency intervention. In such cases, it is important to see a doctor immediately to avoid a life-threatening situation.
Other potential complications may include infections that develop as a result of swelling. Inflamed tissues become more susceptible to bacterial or viral infections, which can lead to conditions such as tonsillitis, pharyngitis, or laryngitis. Additionally, constant swelling can negatively affect the vocal cords, leading to voice problems.
- Difficulty breathing
- Upper respiratory infections
- Vocal cord problems
- Aspiration of food or liquid
- Systemic inflammatory reactions