Swelling of the eyelids in infections: causes, symptoms, and treatment
About the Symptom
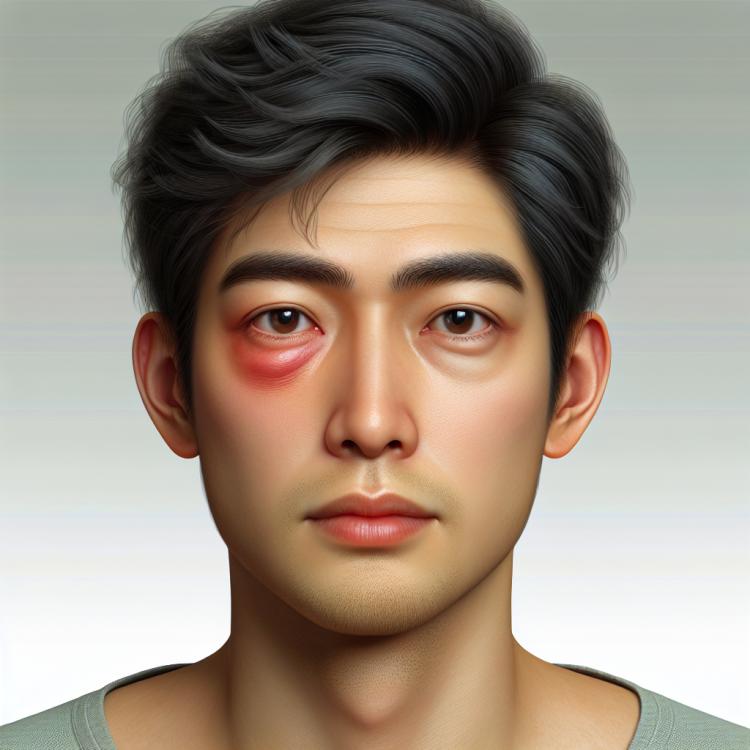
Swelling of the eyelids is a common symptom that can occur with various infections, including viral, bacterial, and fungal. These swellings are often accompanied by redness, itching, and discomfort in the eye area. Infectious processes can be caused by both external and internal factors, such as allergens, upper respiratory infections, or contact inflammation. In this case, eyelid swelling is the body’s reaction to inflammation and increased blood vessel size, leading to fluid retention in the soft tissues.
It is important to note that eyelid swelling due to infection may indicate more serious conditions, such as conjunctivitis, blepharitis, or even sinusitis. In these diseases, the eyes become vulnerable and begin to require special attention. This is especially relevant for young children and the elderly, whose immune systems may be weakened. In the presence of eyelid swelling, especially if accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, purulent discharge from the eyes, or worsening vision, it is necessary to seek medical help for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Diseases
Edema of the eyelids can be a manifestation of various diseases, often of an infectious nature. The most common causes of eyelid edema are conjunctivitis, blepharitis, and stye. These conditions require medical diagnosis and treatment, as they can lead to serious complications if steps are not taken in a timely manner.
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, which is usually caused by viruses or bacteria. The patient may experience watery discharge from the eyes, burning, and a feeling of sand in the eyes. Blepharitis, on the other hand, affects the edges of the eyelids and can be caused by infections or allergic reactions. A stye is an infectious inflammation of the hair follicles of the eyelashes, presenting as painful swelling, redness, and sometimes purulent discharge.
In addition to these diseases, eyelid edema can also be observed in more serious infections, such as orbital cellulitis or herpes infections. It is important to pay attention to accompanying symptoms and consult a doctor to determine the exact cause of the edema, as prompt medical attention can significantly speed up the recovery process.
- Conjunctivitis
- Blepharitis
- Stye
- Orbital cellulitis
- Herpetic eye infections
- Allergic reactions
- Sinusitis
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of eyelid edema in infections requires a comprehensive approach and may include several stages. Unlike some other symptoms, eyelid edema can be a manifestation of various infectious diseases, which necessitates precise identification of their nature. The doctor, during the initial examination, will review the patient’s medical history and pay attention to accompanying symptoms such as redness, itching, and discharge from the eyes. This information will help narrow down the potential causes of the edema.
For a more detailed study of the patient’s condition, various diagnostic procedures may be prescribed. This may include laboratory tests to identify infectious agents, as well as instrumental studies, such as ultrasound diagnostics or imaging using computed tomography, if there is a suspicion of deep or complex infections. Accurate diagnosis is a key step for selecting the optimal treatment method and preventing possible complications.
- Complete blood count
- Bacterial culture
- Conjunctival scraping
- Ultrasound examination
- Computed tomography
- Allergy tests
Which doctor to consult
When swelling of the eyelids occurs due to infection, it’s important not to delay a visit to a specialist. Initially, it is advisable to consult an ophthalmologist who will examine the eyes and assess the degree of swelling, as well as identify possible causes for its occurrence. This specialist is capable of diagnosing various eye diseases, including conjunctivitis, blepharitis, or dacryocystitis, which can lead to eyelid swelling.
If the ophthalmologist does not find specific eye diseases, it is recommended to visit a general practitioner or therapist. They can help determine if you have a general infectious disease affecting the condition of your eyelids. In some cases, a consultation with an allergist may be required if there is a possibility of an allergic reaction as a cause of the swelling.
- Ophthalmologist
- Therapist
- Allergist
- Immunologist
- Dermatologist
Types of Eyelid Swelling in Infections
Eyelid swelling can manifest in various forms depending on the nature and cause of the infection. Each type of swelling has its own characteristics and requires an individual approach to treatment. Initially, acute and chronic swellings are distinguished. Acute eyelid swellings most often occur with viral or bacterial infections, such as conjunctivitis or blepharitis. They are characterized by a sudden appearance of swelling, redness, itching, and discomfort.
Chronic swellings are often a result of a prolonged inflammatory process or an allergic reaction. In such cases, the swellings may have less pronounced symptoms but can persist for a long time. Understanding the different types of swellings is important for determining the appropriate treatment and for timely consultation with a specialist.
- Acute swelling in allergic conjunctivitis
- Viral swelling in herpes infection
- Bacterial swelling in blepharitis
- Chronic swelling in rhinitis
- Swelling in systemic infections, for example, in ornithosis
Causes of Eyelid Swelling in Infections
Eyelid swelling can occur for various reasons, especially in the context of infectious diseases. When our body encounters an infection, the immune system is activated, which can result in inflammation and fluid accumulation in the tissues. This, in turn, leads to swelling that can affect not only the eyelids but also the area around the eyes.
One of the most common causes of eyelid swelling is conjunctivitis, which can be caused by a bacterial or viral infection. Viral infections, such as the flu or cold, can also cause swelling, as the infection is often accompanied by general inflammation and puffiness. Additionally, allergic reactions to various irritants, such as pollen or pet dander, can be perceived by the body as an infection, leading to eyelid swelling as well.
- Conjunctivitis (bacterial and viral)
- Vestibular neuritis
- Orbital sinusitis
- Herpes zoster
- Allergic reactions
- Infections caused by insect bites
- Systemic infections (e.g., flu, ARVI)
Common Associated Pathologies
Swelling of the eyelids due to infection can be a sign of various diseases and conditions related to both infections and other pathologies. One of the most common associated pathologies is blepharitis, an inflammation of the eyelid margins, which often develops under the influence of infectious agents. Blepharitis can cause itching, redness, and swelling of the eyelids, making it a frequent reason for seeking medical attention with such symptoms.
Another common pathology is conjunctivitis, inflammation of the eye’s mucous membrane. It can be caused by viral, bacterial, or allergic infections. Conjunctivitis is often accompanied by eyelid swelling, as well as discharge from the eyes. It is important to note that without adequate treatment, conjunctivitis can lead to more serious complications, highlighting the necessity of diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
- Blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelids)
- Conjunctivitis (inflammation of the eye’s mucous membrane)
- Chalazion (tumor of the eyelid due to blockage of the sebaceous gland)
- Hordeolum (inflammation of the meibomian gland)
- Orbital cellulitis (inflammation of the orbital tissues)
Expert Opinion
Swelling of the eyelids in infections is a symptom that can indicate various pathologies, ranging from conjunctivitis to more serious systemic diseases. It is important to understand that eyelid swelling can be both a primary manifestation of an infection and a consequence of a general inflammatory process in the body. Often, patients consult a doctor with swelling, unaware that the problem may be related not only to the eyes but also to other organs and systems, such as the kidneys or heart.
Specialists recommend not to ignore eyelid swelling, especially if it is accompanied by symptoms such as redness of the eyes, pain, light sensitivity, or discharge from the eyes. It is important to conduct a thorough examination to determine the cause of the swelling. Generally, in such cases, teamwork is necessary: an ophthalmologist can adjust local therapy, while a therapist or neurologist can support the overall health condition of the patient.
Consulting a doctor at the early stages of the disease significantly increases the chances of successful and rapid recovery. Mistakes in treatment can lead to complications, so it is better to consult professionals in advance.

Treatment of Eyelid Swelling Due to Infection
Treatment of eyelid swelling due to infection requires a comprehensive approach and should be carried out under the supervision of an experienced specialist. Before starting therapy, it is important to establish the exact cause of the swelling, which often requires diagnostic studies. Depending on the nature of the infection, the doctor may prescribe antibacterial or antiviral medications. Anti-inflammatory agents and local treatments may also be used to reduce swelling and alleviate symptoms.
It is important to remember that self-treatment can lead to complications, so one should seek medical help at the first signs of eyelid swelling. In some cases, immediate hospitalization may be required for a better effect, especially in the presence of systemic manifestations of the infection, such as high fever and general malaise.
- Antibacterial medications
- Antiviral medications
- Anti-inflammatory agents
- Eye drops with vasoconstrictor effect
- Washing the eyes with antiseptic solutions
- Physiotherapeutic procedures
Complications
Swelling of the eyelids due to infection can be not only an unpleasant symptom but also lead to serious complications if timely measures are not taken. Inflammatory processes occurring in the eye area can spread to nearby tissues, posing a potential threat to health. For example, with the progression of bacterial infection, there is a risk of developing conjunctivitis or keratitis, which can cause vision deterioration or even blindness.
Moreover, eyelid swelling may indicate systemic diseases, such as allergic reactions, which can lead to angioedema and other threatening conditions. Therefore, it is important not only to eliminate visible symptoms but also to conduct a comprehensive examination to identify the underlying cause of the swelling. If such symptoms are ignored, there is a possibility of developing chronic eye diseases and persistent infections requiring long and complicated treatment.
- Conjunctivitis
- Keratitis
- Blepharitis
- Sinusitis
- Allergic reactions (angioedema)
- Thyroid gland diseases
- Infections related to systemic pathological processes