Papules: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment
About the symptom
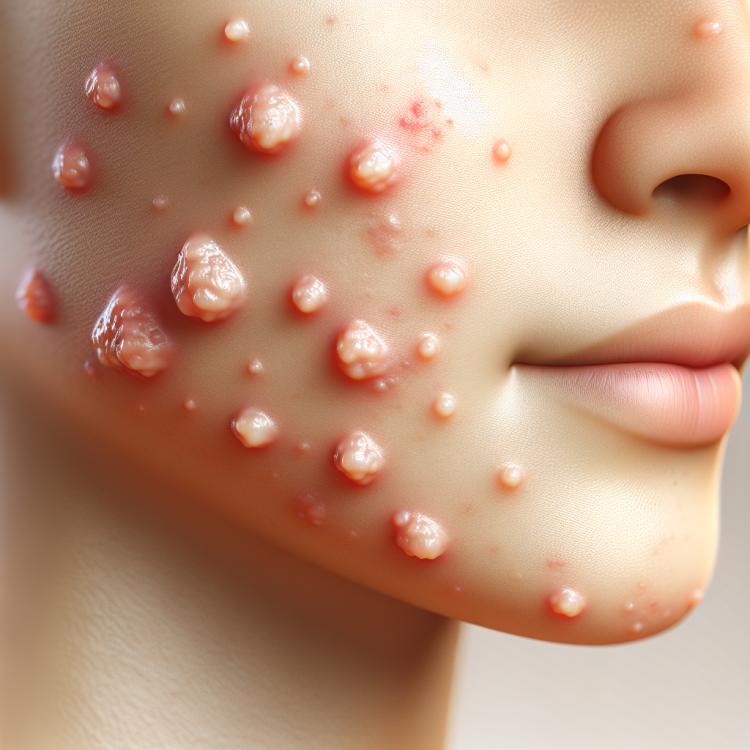
Papules are small, firm lesions on the skin that can vary in size and shape. They can occur as isolated manifestations or in conjunction with other dermatological symptoms. Their size typically ranges from a few millimeters to a centimeter, and they can be colored in various shades—from flesh-toned to bright red. Papules are often a sign of inflammatory processes and can be associated with various conditions, including dermatitis, eczema, psoriasis, and even infectious diseases.
The main symptoms accompanying papules may include itching, burning, or a feeling of discomfort. They may develop crusts, cracks, or flaking, depending on the cause of their appearance. Papules can occur on any part of the body, including the face, torso, and limbs, and their localization generally depends on the specific condition. If you notice the appearance of papules, it is important to consult a doctor to determine the cause of their occurrence and to prescribe appropriate treatment, as some of them may require immediate intervention.
Diseases
Papules are a persistent and varied symptom that can manifest in various diseases. These small, elevated skin formations can have different colors, textures, and diameters, and may also be accompanied by other skin manifestations. Papules can occur as a standalone phenomenon or as part of a broader range of dermatological and infectious diseases. Their appearance requires careful attention from specialists, as they may indicate serious conditions that require medical intervention.
There are numerous diseases that manifest with the formation of papules. These can range from simple dermatitis to more complex infectious or allergic reactions. It is important to understand that diagnosing the cause of papule appearance can be challenging and may require a comprehensive analysis, including medical history, examination, and additional laboratory studies.
- Allergic dermatitis
- Psoriasis
- Skin appearance
- Viral infections (e.g., chickenpox)
- Bacterial infections (e.g., impetigo)
- Simple lupus
- Folliculitis
- Streptoderma
- Dermatophytoses
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of papular rashes begins with a thorough visual examination of the patient’s skin. A specialist, either a dermatologist or a general practitioner, assesses the character, size, color, and location of the papules. These fluid-filled or solid formations may be symptoms of various diseases, so it is important to consider accompanying symptoms such as itching, inflammation, or discharge. In some cases, additional diagnostic methods may be required to confirm the diagnosis, such as dermatoscopy, which allows for a detailed study of the structure of the formation.
Additionally, laboratory tests may be recommended to help exclude allergies or infectious diseases. Depending on the results obtained, the doctor may prescribe the necessary tests to determine the nature of the papules, such as microbiological or allergological examinations. Timely and accurate diagnosis is the key to successful treatment and prevention of complications associated with the underlying disease.
- Visual examination by a dermatologist
- Dermatoscopy
- Laboratory tests for infections
- Allergy tests
- Skin biopsy (in some cases)
Which doctor to consult
Upon discovering papules, which is an important symptom, it is advisable to promptly consult a doctor for qualified assistance. Papules may be manifestations of various dermatological conditions and diseases, thus accurate diagnosis and timely treatment play a crucial role. Depending on the nature of the formation and the suspected cause, consultations with various specialists may be required.
Most often, one should seek help from a dermatologist who can conduct a visual examination and prescribe additional tests. If the papules are related to internal diseases or allergic reactions, a consultation with an allergist, endocrinologist, or infectious disease specialist may also be necessary. A comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment can provide effective resolution of the problem and prevent its recurrence.
- Dermatologist
- Allergist
- Infectious Disease Specialist
- Endocrinologist
- Therapist
Types of Papules
Papules are small, firm, raised lesions on the skin that can manifest in various shapes and have diverse color shades. Depending on the causes of their occurrence, papules can be classified into several types. One of the most common are inflammatory papules, which arise as a result of allergic reactions, infections, or inflammatory processes. These papules are often accompanied by redness and itching.
Additionally, there are papules associated with skin diseases such as acne, psoriasis, or eczema. These papules can be painful and hinder patients’ daily lives. It is important to note that papules can vary in size, shape, and color spectrum, making their manifestations individual to each case. There are also papules that arise from insect bites or in response to physical irritation, such as comedones or brown papules that occur with aging skin.
- Inflammatory papules
- Acne papules
- Psoriasis papules
- eczema papules
- Insect bite papules
- Comedones
- Brown papules with skin aging
Causes of Papule Formation
Papules are small raised areas of skin that can arise for various reasons. One of the main causes of their appearance is inflammation of the skin, which can be triggered by infectious diseases, allergic reactions, or dermatitis. Papules can occur as manifestations of acne, psoriasis, eczema, or other skin conditions, making them an important symptom for diagnosing and treating various disorders.
Additionally, papules can arise as a result of mechanical irritation of the skin, for example, due to friction or injury. Some individuals may also develop papules in response to the use of cosmetic products containing irritating ingredients. When noticing the appearance of papules, it is important to consider not only their appearance but also possible accompanying symptoms, as this will assist the doctor in establishing the correct diagnosis and prescribing appropriate treatment.
- Acne
- Psoriasis
- Eczema
- Contact dermatitis
- Molluscum contagiosum
- Viral infections (e.g., chickenpox)
Common Related Pathologies
Papules can be a symptom of various diseases, and their appearance is often associated with a number of related pathologies. One of the most common is eczema, which is accompanied by inflammatory changes in the skin, often manifested in the form of papules. Dermatitis can also cause the formation of papules, indicating the body’s reaction to external irritants or allergens.
Additionally, papules can be a sign of acne, especially in adolescence, when sebaceous glands produce more sebum, leading to the formation of inflammatory elements. Papules can also appear in infectious diseases such as chickenpox or measles, when the virus causes rashes on the skin, including papular elements.
- Eczema
- Dermatitis
- Acne
- Chickenpox
- Measles
- Psoriasis
- Tinea
Expert Opinion
Papules are a common skin formation that can occur for a variety of reasons. It is important to understand that papules can be a symptom of both benign and malignant diseases, so they should not be ignored. Many patients make the mistake of trying to self-diagnose and treat this issue, which can lead to a deterioration of the skin condition. Therefore, as with other skin manifestations, consulting a dermatologist is the first and mandatory step.
Experts emphasize that in order to correctly identify the cause of papule appearance, it is important to consider not only the appearance of the formation but also accompanying symptoms. For example, itching, redness, or swelling can also provide the doctor with important diagnostic clues. A proper understanding of the characteristics of papules, such as their size, shape, color, and localization, allows the doctor to determine the most likely causes for their appearance and, accordingly, choose the appropriate treatment method.

Treatment of Papules
The treatment of papules depends on their cause and the underlying condition that led to their appearance. It is important that the therapy is conducted by a qualified dermatologist or another specialist, as self-treatment may worsen the condition. In some cases, observation and preventive measures are sufficient if the papules do not cause discomfort and do not increase in size.
In the presence of inflammatory processes, anti-inflammatory ointments, corticosteroids, or antibiotics may be prescribed. If the papules are associated with an allergic reaction, it is important to identify the allergen and, if possible, eliminate contact with it. In advanced cases, systemic medications may be required to control the condition.
- Anti-inflammatory ointments
- Corticosteroid medications
- Antibiotics (if there is an infection)
- Antihistamines (in case of allergy)
- Treatment of the underlying condition (psoriasis, eczema, etc.)
Complications
Papules can lead to various complications if adequate treatment and diagnosis are not conducted. One of the most common problems is that papules can become a source of infection. Due to constant itching or skin irritation, a patient may accidentally damage the papules, creating favorable conditions for bacteria to penetrate, which may result in dermatitis or an abscess. Additionally, untimely or incorrect treatment of papules may provoke the spread of skin diseases.
Another possible complication is related to the psycho-emotional state of the patient. The presence of papules on visible areas of the body can cause discomfort, shame, and lower self-esteem, often leading to the development of anxiety disorders and depression. It is important to note that insufficient attention to the condition of the skin can lead to more serious skin diseases such as psoriasis or eczema.
- Skin infections
- Dermatitis
- Psoriasis
- Eczema
- Clinical depression and anxiety disorders