Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of Skin Ulcers: A Complete Guide
About the Symptom
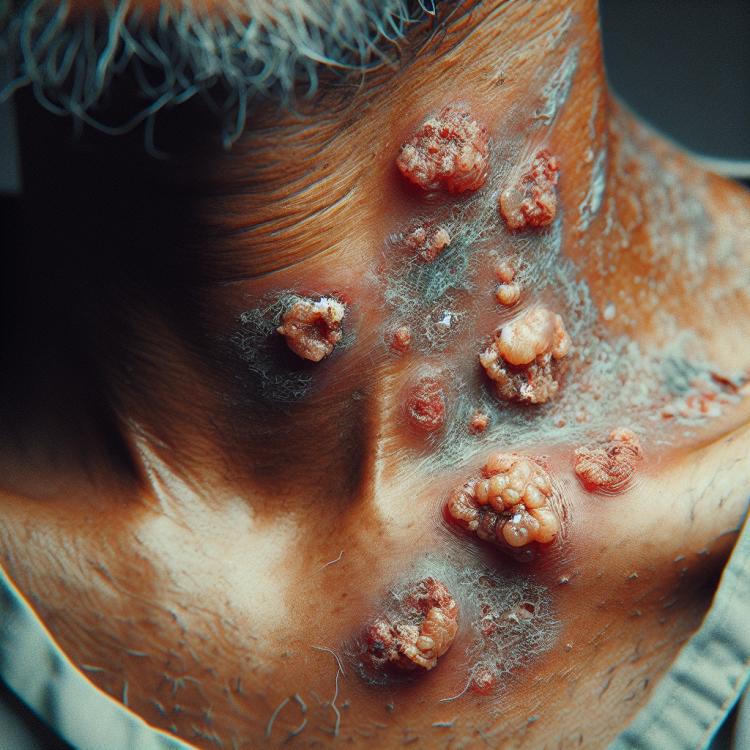
Skin ulcers are a serious symptom that can indicate a variety of diseases or conditions requiring careful attention and proper diagnosis. Ulcers are generally characterized by a disruption of the skin’s integrity, leading to the formation of open wounds and often the discharge of exudate. These formations may be accompanied by itching, burning, or painful sensations, making them not only visually unpleasant but also physically uncomfortable for the patient.
Depending on the causes that led to the appearance of ulcers, they can vary in size, shape, and depth. For example, infectious diseases such as infectious dermatitis or herpes can lead to the formation of small but painful ulcers. At the same time, chronic conditions such as trophic ulcers or diabetic foot can cause the appearance of more extensive and deeper skin lesions, which require prolonged treatment and constant monitoring. Therefore, it is important not to ignore such symptoms and to seek medical help to establish the cause of the ulcers and receive appropriate treatment.
Diseases
The appearance of ulcers on the skin can be a symptom of various diseases that require careful diagnosis and appropriate treatment. One of the most well-known diseases accompanied by ulcers is a venereal disease, specifically syphilis, where ulcers can form on the genitals. Ulcers can also be the result of infectious processes, such as cutaneous tuberculosis or streptococcal infection. In these cases, the ulcers may be accompanied by additional signs of inflammation, such as redness and swelling.
Some skin diseases, such as psoriasis or eczema, can also manifest as ulcers. It is important to note that ulcers can arise from improper skin care or trauma, leading to infection. No less important is the consideration that the appearance of ulcers may be associated with systemic diseases, such as diabetes, where even minor skin injuries can lead to serious complications.
- Syphilis
- Cutaneous tuberculosis
- Streptococcal infection
- Psoriasis
- Eczema
- Diabetic ulcer
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Skin cancer
- Furunclosis
- Dermatitis
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of skin ulcers is a key step in determining the cause of their appearance and prescribing appropriate treatment. A dermatologist conducts a detailed examination of the affected areas of skin and gathers the patient’s history to identify possible factors contributing to the formation of ulcers. It is important to consider all accompanying symptoms, such as itching, swelling, redness, and discharge from the ulcer, as they may provide additional clues about the underlying disease.
For more accurate diagnosis, additional tests may be ordered. This may include laboratory analyses, such as complete blood count and biochemical blood tests, as well as special studies aimed at identifying infectious agents. In some cases, a biopsy of the ulcer may be necessary, which allows for histological examination to determine whether the ulcers are the result of skin disease, an infectious process, or even a malignant tumor.
- Complete blood count
- Biochemical blood test
- Culture from the ulcer for flora and sensitivity to antibiotics
- Pathological biopsy
- Allergy tests
- Ultrasound diagnosis of soft tissues
Which doctor to contact
When ulcers appear on the skin, it is very important to consult a doctor for timely diagnosis and adequate treatment. Ulcers can be a symptom of various diseases, and misunderstanding their nature can lead to serious health consequences. The most appropriate specialist for the initial consultation is a dermatologist, who can conduct a comprehensive examination of the skin manifestations and prescribe necessary tests to clarify the diagnosis.
If deeper diagnostics or monitoring of the condition is needed, the dermatologist may refer you to other specialists. For example, if the ulcers stem from internal pathologies, you may require a consultation with a gastroenterologist or an infectious disease specialist. In some cases, the intervention of an allergist may be necessary, especially if the ulcers are related to allergic reactions. It is important to remember that timely consultation with a doctor can significantly accelerate the healing process and increase the chances of a full recovery.
List of medical specialties for treatment
- Dermatology
- Infectious diseases
- Allergology
- Gastroenterology
- Immunology
- Endocrinology
Types of Skin Ulcers
Skin ulcers can have various causes and may differ in their appearance, depth, and characteristics. In nature, ulcers are divided into primary and secondary. Primary ulcers appear directly as a result of skin damage or inflammation. This can include wounds, erysipelas, or allergic reactions. Secondary ulcers occur against the background of pre-existing diseases and may signal systemic disorders in the body.
Moreover, skin ulcers can be classified by their nature. For example, they can be infectious, venous, or neurotrophic. Infectious ulcers are often caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses, while venous ulcers typically develop due to impaired venous drainage and are commonly found in people with chronic venous insufficiency. Neurotrophic ulcers, on the other hand, may arise from damage to nerve endings and reduced sensitivity in a specific area of the skin, which also requires special attention during diagnosis and treatment.
- Infectious ulcers
- Venous ulcers
- Neurotrophic ulcers
- Trophic ulcers
- Ulcers caused by allergic reactions
Causes of Skin Ulcers
Skin ulcers can occur for a number of reasons, ranging from mechanical injuries to serious illnesses. One of the most common causes is an infection caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi that penetrate the skin. These infectious agents can cause inflammation, a destructive process, and eventually lead to the formation of ulcers. It is important to note that some ulcers may be the result of chronic diseases, such as diabetes or venous insufficiency, highlighting the need for timely diagnosis.
In addition to infections, skin ulcers can be caused by autoimmune diseases such as psoriasis or dermatological conditions like eczema. Other factors, such as allergic reactions, burns, or frostbite, can also be the cause of ulcers. Furthermore, circulatory disorders or injuries can contribute to the formation of ulcers, especially in individuals predisposed to skin diseases.
- Infections (bacterial, viral, fungal)
- Chronic diseases (diabetes, venous insufficiency)
- Autoimmune diseases (psoriasis, eczema)
- Allergic reactions
- Burns and frostbite
- Injuries and circulatory disorders
Common Related Pathologies
Skin ulcers can serve as a symptom of various diseases and conditions that affect not only dermatology but also other areas of medicine. Often, ulcers are markers of more serious systemic diseases. Their appearance may indicate infection, inflammation, or even pathology of internal organs. Proper diagnosis and timely consultation with a specialist can help determine the underlying disease and initiate timely treatment.
Among the common pathologies associated with the appearance of ulcers on the skin, one can note diseases such as diabetic foot, which is a consequence of diabetes and contributes to the formation of ulcers on the legs. In addition, ulcers can occur due to trophic changes resulting from inadequate blood supply to the tissues, which often happens with varicose disease. It is also worth mentioning infectious diseases such as syphilis or impetigo, which can also manifest as ulcers on the skin.
- Diabetic foot
- Trophic ulcers
- Varicose disease
- Syphilis
- Impetigo
- eczema
- Psoriasis
- Necrotizing fasciitis
Expert Opinion
The appearance of ulcers on the skin is a serious signal that should not be ignored. Such changes can be caused by various factors, ranging from infectious diseases to chronic disorders. It is important to understand that ulcers can be simple manifestations of skin diseases as well as symptoms of more complex pathologies. At the first sign of an ulcer on the skin, it is recommended to consult a doctor to determine the exact cause and prescribe appropriate treatment.
From a dermatologist’s perspective, timely diagnosis and treatment of ulcers are crucial to avoid complications. Ulcers can lead to secondary infections, adversely affect the overall health of the patient, and may even require surgical intervention in advanced cases. Therefore, experts emphasize the need for a careful approach to monitoring and treating such manifestations, which will enable effective management of skin problems and prevent their further progression.

Treatment of skin ulcers
Treatment of skin ulcers is a multi-step process that depends on the cause of their appearance. Initially, it is necessary to identify the factor contributing to the formation of ulcers, whether it is an infection, an allergic reaction, or a chronic disease. The doctor may prescribe various diagnostics to identify the underlying pathology and suggest appropriate treatment. This may involve either local therapy or systemic medications, depending on the severity of the condition.
One of the main treatment methods is the use of antiseptics and ointments that promote tissue healing. In some cases, antibiotics may be required, especially if the ulcers have an infectious nature. Proper care for the ulcers is also essential: regular dressing changes and keeping the affected area clean can significantly improve the healing process and reduce the risk of complications.
- Local therapy (ointments, creams, dressings)
- Antibiotics (for bacterial infections)
- Medications to improve microcirculation
- Physiotherapy procedures
- Immunomodulators (for autoimmune diseases)
Complications
The appearance of ulcers on the skin can lead to various complications that can significantly worsen the overall condition of the patient and their quality of life. One of the most common complications is ulcer infection. This can occur if bacteria penetrate the damaged area of the skin, leading to the development of an inflammatory process and even purulent inflammation. Infected ulcers require immediate medical intervention, as they can lead to more serious consequences, including sepsis.
Additionally, patients with ulcers on the skin may develop localized swelling, which restricts mobility and can cause chronic pain. The prolonged existence of ulcers can also lead to depression, as patients may experience embarrassment due to cosmetic defects and physical discomfort. In rare cases, some types of ulcers may have precancerous characteristics, which requires careful monitoring and further investigation by medical professionals.
- Ulcer infection
- Localized swelling
- Chronic pain
- Depression and psychological disorders
- Risk of developing oncological diseases