Seborrhea: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Methods
About the symptom
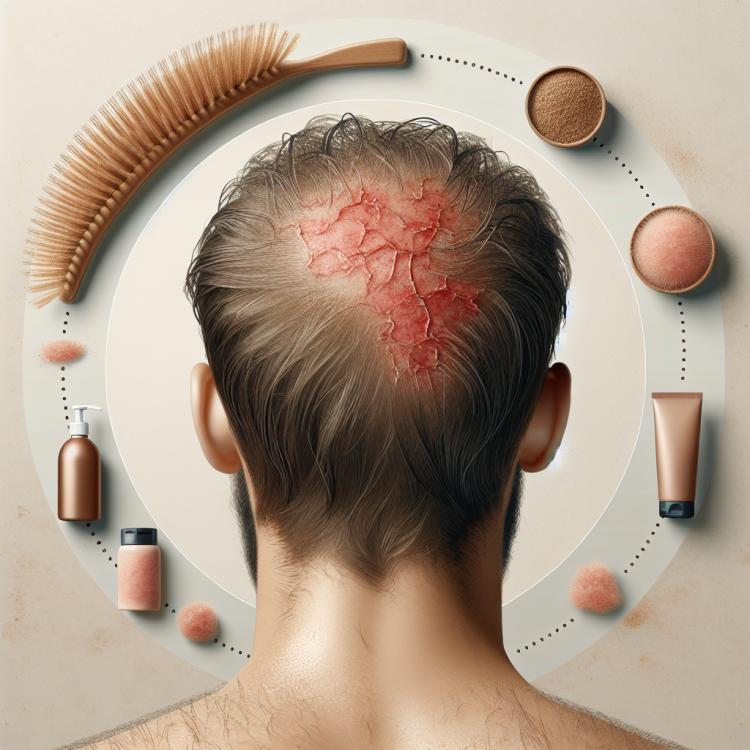
Seborrhea is a skin condition that occurs as a result of dysfunction of the sebaceous glands. It manifests with various symptoms, the most characteristic of which are itching, redness, and flaking of the skin. Seborrhea often affects the scalp but can also manifest on the face, chest area, and back. People with seborrhea may have skin that looks excessively oily or, conversely, dry, depending on the type of seborrhea—oily or dry. It is important to remember that these symptoms can vary depending on individual characteristics of the body and skin condition.
Another common sign of seborrhea is the formation of crusts and scales, which can be yellowish or white. In the case of oily seborrhea, the scales are most often sticky and thickened, while with dry seborrhea, they are smaller and flaky. Inflammatory processes may also occur, which can significantly disturb the patient. Without proper treatment, the symptoms can progress, leading to a significant deterioration in the overall skin condition and quality of life. Therefore, at the first signs of seborrhea, it is recommended to consult a specialist who will prescribe adequate treatment and provide recommendations for skin care.
Diseases
Seborrhea is not just a separate disease, but often serves as a precursor or accompanying condition to a range of dermatological problems. It is characterized by excessive secretion of sebum and disruption of the normal shedding of skin cells. Often, seborrhea can be associated with other skin diseases, leading to a worsening of the patient’s condition and requiring more in-depth medical intervention.
The most common diseases that may be associated with seborrhea include:
- Dermatitis: Inflammation of the skin, manifesting as redness, itching, and peeling.
- Psoriasis: A chronic inflammatory skin disease accompanied by the formation of plaques and itching.
- Trichomycosis: A hair condition, often caused by fungal infections.
- Fungal infections: Infections caused by various microorganisms belonging to fungi that can exacerbate seborrhea.
- Acne: Pimples and inflammatory elements on the skin, often worsening in combination with seborrhea.
Understanding the relationship between seborrhea and other dermatological diseases is important for choosing an effective treatment strategy. Early diagnosis and a comprehensive approach to therapies can significantly improve the quality of life for patients and prevent more serious complications.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of seborrhea includes a set of measures aimed at determining the severity of the disease, its forms, and clarifying possible causes. The dermatologist collects the medical history, specifying when the first symptoms appeared, how they progress, and what factors may contribute to the worsening of the skin condition. It is important to pay attention to preceding disorders such as stress, changes in diet, or hormonal imbalances that may affect the function of the sebaceous glands.
After collecting the medical history, the doctor may conduct a physical examination to assess the condition of the skin and hair. In some cases, additional research may be required to exclude other dermatological diseases that may have similar symptoms, such as fungal infections or psoriasis. For a more accurate diagnosis, a study of the content of sebaceous gland cells and a skin analysis for pathogens may be prescribed.
- Clinical examination by a dermatologist
- Culture of scrape for microorganisms
- Testing for hormonal disorders
- Assessment of hair and scalp condition
- Performing trichoscopy
Which doctor to consult
If you have symptoms of seborrhea, such as itching, skin redness, the appearance of scales or oily crusts, it is crucial to consult a specialist. Seborrhea can manifest not only on the scalp but also on other areas of the body, so do not postpone a visit to the doctor. Initially, it is advisable to consult a dermatologist who has experience in diagnosing and treating skin diseases.
The dermatologist will conduct the necessary examination, assess the clinical picture, and if needed, refer you to other specialists. For example, in cases of secondary seborrhea caused by internal organ diseases, a consultation with an endocrinologist or gastroenterologist may be required. It is important to consider that timely consultation with a doctor can prevent complications and improve the condition of the skin.
- Dermatologist
- Endocrinologist
- Gastroenterologist
- Allergist
- Trichologist
Types of Seborrhea
Seborrhea is a chronic condition that manifests as a dysfunction of the sebaceous glands. There are several types of seborrhea, each with its own characteristics and symptoms. The most common forms are wet (oily) seborrhea and dry seborrhea. Wet seborrhea is characterized by excessive secretion of sebum, leading to oily hair and skin flakes. In this case, inflammatory processes may develop, and the skin can appear unhealthy and shiny.
Dry seborrhea, on the other hand, is accompanied by insufficient oil production, making the skin irritated, itchy, and prone to crust formation. This can lead to flaking, which is often observed on the scalp and in other areas such as the face or chest. Understanding the different types of seborrhea allows for more effective treatment and prevention methods.
- Oily seborrhea
- Dry seborrhea
- Mixed seborrhea
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Focal seborrhea
Causes of seborrhea
Seborrhea is a condition related to the malfunctioning of the sebaceous glands on the skin. It can arise from various reasons, including both internal and external factors. One of the main causes of seborrhea is an imbalance in the skin’s microflora, which can be triggered by stress, hormonal changes, improper nutrition, or the presence of diseases of the endocrine system. Regarding external factors, it is important to mention improper skin care, the use of low-quality cosmetics, and unfavorable environmental conditions.
Furthermore, research shows that heredity plays an important role in the predisposition to seborrhea. Genetic predisposition may make some individuals more susceptible to this condition. It is also necessary to consider the influence of climatic factors, such as high humidity and temperature, which can exacerbate the symptoms of the disease. It is important to understand that seborrhea is not just a cosmetic problem but a serious condition that requires a comprehensive approach to treatment.
- Genetic predisposition
- Hormonal changes
- Stress and psycho-emotional state
- Inadequate skin care
- Poor nutrition
- Endocrine system diseases
- Environmental factors
Common Associated Pathologies
Seborrhea is often associated with a number of accompanying diseases that can exacerbate the manifestations of this dermatological problem. One of the most common associated pathologies is eczema, which can present as inflammatory processes on the skin, causing itching and redness. In the presence of seborrhea, eczema may worsen, as oily skin creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of fungi and bacteria, contributing to the development of inflammatory processes.
Another pathology that often accompanies seborrhea is psoriasis. This chronic disease, characterized by the formation of plaques on the skin, can arise against the background of already existing manifestations of seborrhea. Furthermore, altered microflora and skin conditions can serve as triggers for psoriasis flare-ups, necessitating a comprehensive approach to treatment.
- Eczema
- Psoriasis
- Atopic dermatitis
- Fungal skin infections
- Allergic reactions
Expert Opinion
Seborrhea is a condition that can negatively impact not only the appearance of the skin but also the overall health of the patient. An expert in dermatology emphasizes that seborrhea is often a sign of dysfunction in the sebaceous glands and can be caused by various factors, including stress, poor nutrition, and hormonal changes. Therefore, it is important to not only treat the symptoms but also to identify and eliminate the underlying causes that contribute to the development of this ailment.
According to the specialist, self-isolation and lack of proper skin care often lead to worsening conditions in seborrhea. Proper restorative treatment and the use of suitable cosmetic products can significantly reduce the manifestations of seborrhea. The expert highlights that regular consultations with a dermatologist can help manage the condition and prevent recurrences.
It is important to remember that self-treatment can be ineffective and even dangerous. Any changes in the condition of the skin should be discussed with a qualified specialist who can provide recommendations for treatment and prevention.

Treatment of Seborrhea
Treatment of seborrhea is a complex process that includes both medicinal and non-medicinal methods. It is important to understand that seborrhea is not just a cosmetic problem, but a disease that requires careful attention. Depending on the type and severity of seborrhea, a doctor may prescribe special shampoos, ointments, and even systemic medications to reduce the inflammatory process. Additionally, using products that contain active ingredients such as salicylic acid, ketoconazole, or zinc can be effective. They help regulate sebum production and maintain the balance of skin microflora.
Additionally, treatment of seborrhea may include lifestyle changes. Proper nutrition, regular physical activity, and avoidance of stressful situations contribute to the overall strengthening of the body and reduction of inflammatory processes. Some patients also report a positive impact from physiotherapeutic procedures, such as magnetotherapy or ultraviolet radiation. It is important to remember that self-medication can lead to a worsening of the condition, so it is advisable to seek consultation from a qualified specialist.
- Medications therapy
- Physiotherapeutic procedures
- Cosmetic products
- Diet correction
- Psychological support
Complications
Seborrhea, if left untreated or if its manifestations are ignored, can lead to a number of complications that significantly impair the patient’s quality of life. One of the most common consequences is the development of skin infections. Since seborrhea causes dryness and itching of the skin, constant scratching can damage the skin barrier, allowing pathogenic microorganisms to easily enter and trigger inflammatory processes.
Additionally, people with seborrhea often suffer from dermatological conditions such as eczema and psoriasis. These conditions can exacerbate overall discomfort and require more complex treatment methods. In severe cases, seborrhea can even lead to psychological disorders, such as depression or anxiety, due to low self-esteem and embarrassment about appearance.
- Skin infections
- Dermatitis
- Eczema
- Psoriasis
- Psychological disorders (depression, anxiety)