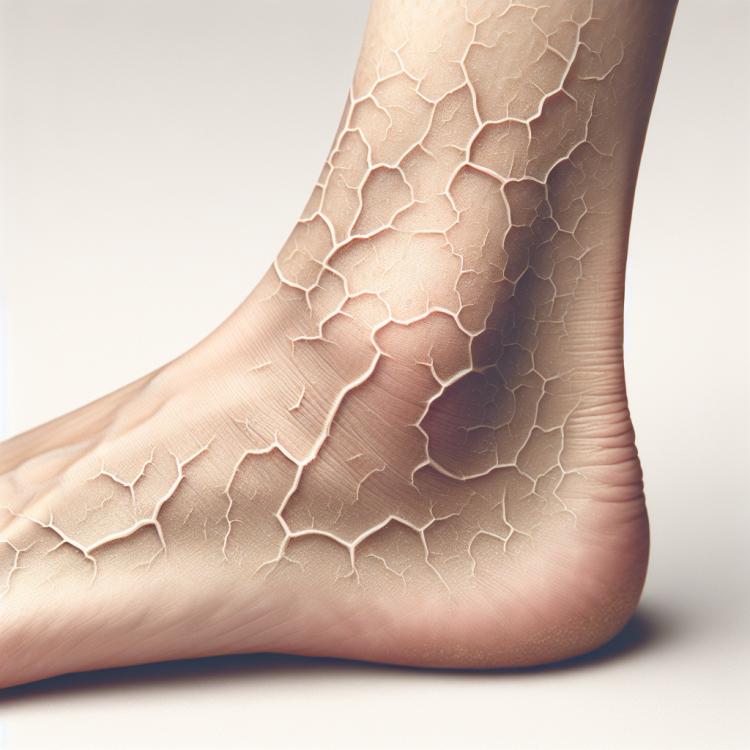
Cracks in the skin of the ankles: causes, treatment, and prevention
About the Symptom
Cracks in the skin of the ankles are a common problem that can occur in people who are predisposed to skin diseases, as well as those who experience dry skin due to changing weather conditions, lack of care, or other factors. Symptoms of cracks often include a burning sensation, itching, and discomfort in the ankle area. The skin becomes rough and less elastic, which increases the risk of cracks and inflammation. Without proper care, the condition can worsen, leading to pain and risky complications.
Additionally, cracks in the skin of the ankles may be a sign of more serious diseases, such as eczema, psoriasis, or fungal infections. It is important to pay attention to accompanying symptoms, such as redness, swelling, cracks that do not heal, and discharge, as they may indicate the need for medical intervention. Regular hygiene, the use of moisturizers, and overall strengthening of the body can significantly reduce the risk of cracks and improve skin condition; however, when pronounced symptoms appear, it is strongly recommended to consult a specialist.
Diseases
Crracks on the skin of the ankles can be a symptom of numerous skin diseases and disorders that require proper attention and timely treatment. One of the most common causes of cracks is eczema, characterized by inflammation and dryness of the skin. It can cause itching and discomfort, exacerbating the condition of the skin and leading to the formation of cracks.
Another common cause of cracks on the ankles is dermatitis, which may arise as a result of allergic reactions or exposure to irritating substances. It is also worth paying attention to fungal infections, such as candidiasis, which can lead to the formation of cracks and peeling of the skin. Finally, diabetes can cause poor circulation and damage to nerve endings, which can also contribute to the appearance of cracks on the skin of the ankles.
- Eczema
- Dermatitis
- Fungal infections (candidiasis)
- Psoriasis
- Diabetic infection
- Contact allergic dermatitis
- Skin losing syndrome (dysplastic erythroderma)
Diagnosis
Cracks on the skin of the ankles can be a sign of various diseases and conditions that require careful diagnosis. Doctors use a comprehensive approach to determine the cause of the cracks, including an initial examination of the patient, analysis of the medical history, and conducting necessary laboratory and instrumental studies. It is important not only to identify the presence of cracks but also to determine their depth, location, and the presence of inflammatory or infectious processes.
During the diagnosis, a specialist may order a series of tests, such as blood and urine tests, which can help identify systemic diseases interacting with skin problems. Dermatoscopy and ultrasound may also be useful for a detailed analysis of the condition of the skin and underlying tissues. Developing an individual diagnostic plan will enable the doctor to accurately determine the cause of the cracks and prescribe effective treatment.
- Complete blood count
- Blood sugar level test
- Allergy tests
- Dermatoscopy
- Ultrasound examination of soft tissues
- Skin biopsy
- Bacteriological analysis
Which doctor to contact
If you are facing the problem of cracks on the skin of the ankles, it is important not to delay a visit to the doctor. These cracks can be a sign of various diseases or conditions that require careful diagnosis and treatment. The first step is to consult a dermatologist, who specializes in skin diseases and can determine the exact cause of the cracks. He will conduct the necessary assessment of the skin condition and may prescribe additional tests if needed.
In some cases, cracks on the ankles may be a result of systemic diseases or disorders of internal organs, and in such cases, a consultation with related specialists may be required. For example, an endocrinologist can help identify possible hormonal disorders, while a venereologist can rule out infectious diseases. In case of an acute inflammatory process, the assistance of a surgeon may also be necessary. Thus, depending on your health condition, the doctor can refer you to the appropriate specialist for the most effective treatment.
- Dermatologist
- Endocrinologist
- Venereologist
- Surgeon
- Allergist
- Rheumatologist
Types of Cracks on the Skin of the Ankles
Cracks on the skin of the ankles can vary in type, depth, and causes. One of the most common classifications is the division into superficial and deep cracks. Superficial cracks usually occur due to insufficient hydration of the skin, exposure to cold weather, or wearing uncomfortable shoes. They may manifest as tiny裂 and redness, causing mild discomfort.
Deep cracks, on the other hand, may be the result of serious illnesses or metabolic disorders. They often cause intense pain and can lead to infection if proper care is not provided. The appearance of deep cracks requires mandatory attention and medical assistance, as this may be a symptom of more severe health issues.
- Superficial cracks
- Deep cracks
- Cracks caused by dermatological diseases
- Cracks triggered by allergic reactions
- Cracks resulting from improper foot care
Causes of Cracks on Ankle Skin
Cracks on the skin of the ankles can occur for various reasons, and understanding these factors is key to their prevention and treatment. One of the most common causes is dry skin, which often arises from a lack of moisture, improper care, changes in climatic conditions, or exposure to harsh cosmetic products. When the skin loses its natural elasticity, it becomes more susceptible to cracks and damage.
There are also a number of medical conditions that can contribute to the formation of cracks on the skin of the ankles. For example, eczema and psoriasis can cause inflammation of the skin, leading to cracks and flaking. Skin infections, such as fungal diseases, can also be a cause of discomfort and cracks. Finally, factors such as poor nutrition, stress, and hormonal changes can also impact skin health, contributing to its degradation.
- Dry skin
- Eczema
- Psoriasis
- Fungal infections
- Poor nutrition
- Climate changes
- Use of harsh cosmetic products
- Hormonal changes
Common Related Pathologies
Cracks on the skin of the ankles can be a symptom of various diseases and conditions that affect the health of the skin and soft tissues. One of the most common pathologies is eczema, which leads to inflammation and dryness of the skin, potentially causing cracks, especially in the ankle area. Dermatitis caused by allergic reactions or contact exposure can also contribute to the formation of microcracks on the skin, triggering itching and discomfort.
Additionally, cracks on the ankles often occur against the backdrop of diabetes, which can lead to impaired circulation and deterioration of skin condition. Another common pathology is a fungal infection, which can affect the skin of the ankles, making it dry and prone to cracking. All these conditions require close monitoring and, if necessary, intervention from a specialist to prevent further complications.
- Eczema
- Dermatitis
- Diabetes
- Fungal infections (mycoses)
- Psoriasis
- Atopic dermatitis
- Keratosis
Expert Opinion
Cracks on the skin of the ankles are not just an aesthetic problem, but a symptom that can indicate various diseases or disorders in the body. From a dermatological perspective, such cracks can occur not only due to mechanical impact but also as a result of food and vitamin deficiencies. As a sign of dry skin, cracks may indicate a deficiency of vitamins A, E, and B group, as well as low levels of a number of minerals in the body, such as zinc and magnesium.
From a medical standpoint, it is important to understand that cracks on the ankles may be associated with more serious pathologies, such as diabetic neuropathy, psoriasis, or eczema. It is crucial to consult a doctor in a timely manner for a comprehensive diagnosis and determination of the root cause of the problem. Consult a specialist: timely intervention can prevent the development of chronic diseases and significantly improve the quality of life for the patient.

Treatment of Cracks on the Skin of the Ankles
Treating cracks on the skin of the ankles is an important aspect of skin health care and preventing complications. First of all, it is necessary to determine the cause of the cracks, as this affects the treatment plan. If the cracks have arisen due to dry skin, the main focus should be on moisturizing and nourishing the skin. The use of special creams and ointments containing moisturizing components such as glycerin and urea will help restore the skin’s hydro-lipid balance and accelerate the healing process.
If the cause of the cracks is fungal or bacterial infections, treatment should include antiseptic and antifungal medications. It is important not only to control external manifestations but also to strengthen the immune system to reduce the risk of recurrent cracks. Protective measures should be taken when in contact with irritating substances, such as cleaning agents and detergents.
- Use of moisturizing creams
- Application of antiseptic preparations
- Antifungal therapy if necessary
- Diet correction and vitamin intake
- Protection of the skin from external influences
Complications
Cuts on the skin of the ankles can lead to various complications if proper attention is not paid to their treatment. One of the most common complications is inflammation, which can develop in the area of skin damage. This inflammation may manifest as redness, swelling, and pain, significantly reducing the patient’s quality of life and limiting their mobility.
Furthermore, cracks can become gateways for infections. The penetration of pathogenic microbes into open wounds can lead to the development of more serious diseases, such as dermatitis or cellulitis. In advanced cases, this may require antibiotic therapy or even surgical intervention if purulent abscesses form. To prevent these complications, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly and follow skincare recommendations.
- Inflammatory processes
- Skin infections
- Purulent abscesses
- Chronic skin diseases
- Scar formation