Lacunar angina: clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and effective treatment
- Understanding lacunar angina: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
- Factors for the development of lacunar angina
- Clinical manifestations of lacunar angina
- Effective approaches to treating lacunar angina: specialists’ insights
- Methods for diagnosing lacunar angina
- Methods of treating lacunar angina
- Measures for the prevention of lacunar angina
- Interesting aspects of lacunar angina
- FAQ
Understanding lacunar angina: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
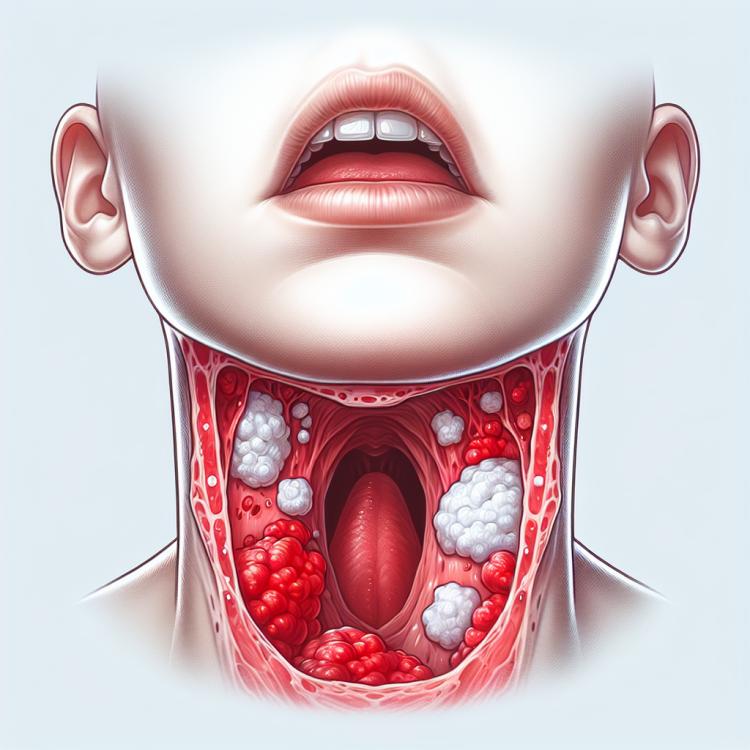
Lacunar angina is one of the forms of acute tonsillitis, characterized by the presence of cavities covered with a grayish coating in the lacunae of the tonsils. Clinical manifestations include pronounced sore throat, elevated body temperature, as well as swelling and hyperemia of the tonsils. Diagnosis is based on medical history, physical examination, and, if necessary, bacteriological examination of throat swabs.
Treatment for lacunar angina usually involves antibacterial therapy to suppress the causative agents of infection, symptomatic relief medications, and recommendations for diet and rest. To prevent complications, it is important to start treatment promptly and follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Factors for the development of lacunar angina
The development of lacunar angina is primarily caused by a bacterial infection, usually triggered by group A streptococci. Certain factors, such as a weakened immune system, contact with infected individuals, or insufficient oral hygiene, can contribute to the onset of this disease. The risk of infection also increases in conditions of body hypothermia or in the presence of chronic illnesses such as diabetes mellitus.
To effectively prevent lacunar angina, it is important to maintain overall health, including strengthening the immune system, following personal hygiene rules, and avoiding contact with sick individuals. If risk factors are present, it is necessary to consult a doctor for recommendations on prevention and timely detection of disease symptoms.
- bacterial infection: Lacunar angina is most often caused by group A streptococci, which can enter the body through contact with infected individuals.
- weakened immune system: A decrease in the body’s protective functions can contribute to the development of bacterial infection and the onset of lacunar angina.
- contact with sick individuals: Close contact with infected people can increase the risk of developing lacunar angina.
- insufficient oral hygiene: Poor oral care can promote the proliferation of bacteria, increasing the likelihood of developing a throat infection.
- hypothermia: Exposure to cold air can weaken the body’s protective functions and provoke the development of lacunar angina.
Clinical manifestations of lacunar angina
Clinical manifestations of lacunar angina include pronounced symptoms of upper respiratory tract involvement, such as severe sore throat, difficulty swallowing, a feeling of soreness, and pain when swallowing. Upon examination of the oropharynx, there is swelling and hyperemia of the tonsils, as well as a grayish coating covering the lacunae of the tonsils.
Additional signs of lacunar angina may include an elevated body temperature, general weakness, headache, and sometimes lymphadenopathy. If lacunar angina is suspected, it is important to consult a doctor for diagnosis, appropriate therapy, and to prevent possible complications.
- Sore throat: Patients often complain of sharp pain and discomfort in the throat, which may worsen when swallowing.
- Difficulty swallowing: The onset of dysphagia, especially when attempting to swallow solid or spicy food, is a characteristic symptom of lacunar angina.
- Hyperemia of the tonsils: Enlargement and redness of the tonsils indicate an inflammatory process in the oropharynx, which may be accompanied by a grayish coating.
- Increased body temperature: An acute infectious process is accompanied by hyperthermia, which can lead to fever and general malaise.
- General weakness: Patients often note a deterioration in overall well-being, drowsiness, and physical and emotional fatigue as accompanying symptoms of lacunar angina.
Effective approaches to treating lacunar angina: specialists’ insights
Experts in the field of medicine recommend a comprehensive approach to the treatment of lacunar angina, which includes the use of antibiotics to combat bacterial infections. However, when prescribing antibiotics, it is important to consider their antibiotic susceptibility testing to avoid resistance of the pathogen to the drug. Alongside antibiotic therapy, anti-inflammatory medications and pain relief agents are used to alleviate symptoms and improve the patient’s well-being.
Experts also emphasize the importance of adhering to rest and nutritional guidelines during the treatment of lacunar angina to expedite recovery. Additionally, it is recommended to take measures to strengthen the immune system, including the consumption of vitamins and minerals, taking probiotics, as well as following personal hygiene rules to prevent re-infection and reduce the risk of possible complications.

Methods for diagnosing lacunar angina
The diagnosis of lacunar angina is based on the patient’s medical history, clinical examination, and laboratory testing methods. The doctor conducts an examination of the oropharynx to identify enlarged and hyperemic tonsils with a grayish coating in the lacunae. Additionally, an essential step in the diagnostics is collecting samples, including a complete blood count and bacteriological examination of throat swabs to determine the causative agent of the infection.
For an accurate diagnosis and to determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics, a bacteriological examination of throat swabs may be required. Sometimes, additional laboratory tests, such as blood tests for antibodies to the infection, may be prescribed. A comprehensive approach to diagnosing lacunar angina allows for the correct treatment to be determined and prevents possible complications.
- Clinical examination: The doctor performs an examination of the oral cavity and throat, identifies enlarged and hyperemic tonsils, the presence of a grayish coating, and other characteristic signs of lacunar angina.
- Complete blood count: Appointed to assess the presence of inflammatory markers, such as the level of leukocytes and C-reactive protein, which helps confirm the infectious process.
- Bacteriological examination of throat swabs: Allows for the identification of the infectious agent and determines its sensitivity to various antibiotics for optimal treatment assignment.
- Antibody blood test: Conducted if necessary to detect antibodies to the infectious agent, which can be useful for additional confirmation of the diagnosis.
- PCR diagnostics: This method allows for the detection of the presence of a specific infectious agent (e.g., Group A Streptococcus) with high sensitivity and specificity.
Methods of treating lacunar angina
Particular attention is given to restoring the body’s strength and strengthening the patient’s immunity. It is recommended to rest, drink plenty of fluids, adhere to a diet, and regularly take vitamin supplements. If necessary, in case of severe pain or other complications, hospitalization may be required for intensive therapy and specialist observation.
- Antibiotic therapy: The use of antibiotics, such as penicillins or macrolides, to effectively eliminate the bacterial infection that caused lacunar angina.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: Used to reduce swelling and inflammation in the throat, which helps cope with the symptoms of the illness.
- Analgesics and antipyretics: Prescribed to alleviate pain, fever, and discomfort associated with lacunar angina.
- Rest and hygiene regimen: It is recommended to rest, consume warm beverages, apply hot compresses to the throat, and follow oral hygiene recommendations during treatment.
- Immune strengthening: Taking vitamins, minerals, probiotics, and maintaining proper nutrition and rest to boost immunity and speed up recovery.
Measures for the prevention of lacunar angina
Regular check-ups with a dentist and an otolaryngologist, as well as timely treatment of infections, contribute to the early detection and treatment of potential gastrointestinal issues. It is important to follow recommendations for preventing respiratory infections and to maintain overall health, which helps reduce the likelihood of developing lacunar angina.
- Maintaining oral hygiene: Regular tooth brushing, using antiseptic mouthwash, and caring for the oral cavity help reduce the number of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Avoiding contact with sick individuals: Take measures to prevent close contact with people suffering from angina, especially during outbreaks of the disease.
- Maintaining a proper diet and rest: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, along with sufficient rest and a daily routine, helps support the immune system and strengthen the body.
- Implementing hygiene measures: Regularly ventilating rooms, maintaining cleanliness at home and at work contribute to reducing the likelihood of infection.
- Vaccination and prevention of respiratory infections: Regular vaccination and adherence to preventive measures against other respiratory diseases help strengthen health and reduce the risk of lacunar angina.
Interesting aspects of lacunar angina
An interesting fact is that lacunar angina is most often caused by group A streptococci, which are transmitted through airborne droplets from infected individuals or carriers of the infection. In addition, special attention is given to the choice of antibiotics for the treatment of this disease to effectively eliminate the pathogen and prevent complications. Thus, studying the unique aspects of lacunar angina helps treating physicians and patients understand the features of this disease and take necessary measures for its management and cure.