Atrophic rhinitis: features, diagnosis, and treatment methods
- Understanding atrophic rhinitis: symptoms, causes, and diagnosis
- Factors contributing to the development of atrophic rhinitis
- Possible manifestations of atrophic rhinitis
- The views of specialists on the treatment of atrophic rhinitis
- Diagnostic system for atrophic rhinitis
- Methods of treating atrophic rhinitis
- Preventive measures for atrophic rhinitis
- Amazing aspects of atrophic rhinitis
- FAQ
Understanding atrophic rhinitis: symptoms, causes, and diagnosis
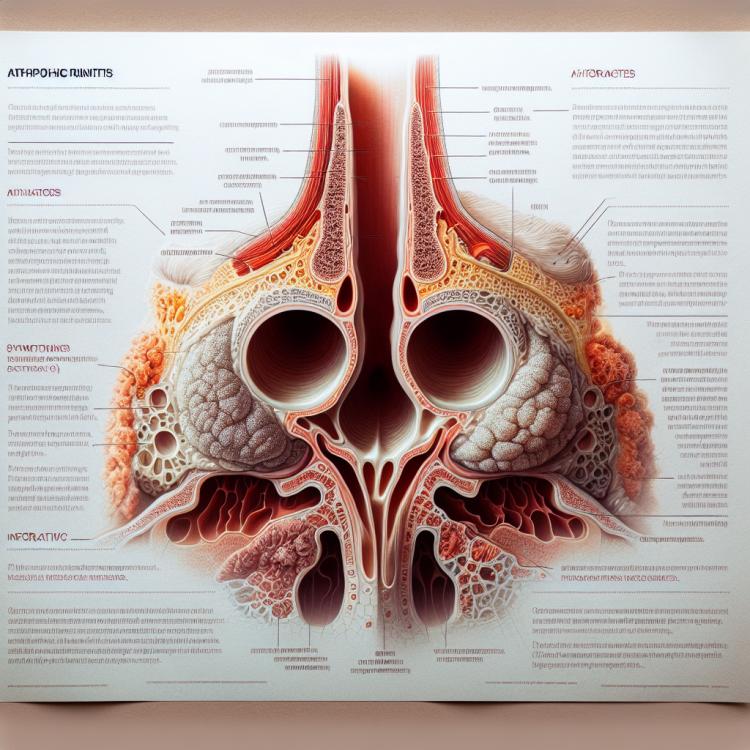
Atrophic rhinitis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the nasal mucosa, characterized by the gradual degeneration and atrophy of the epithelium. The main symptoms of this condition are disturbances in smell, dryness in the nose, frequent crusting, and an unpleasant odor from the nose. The causes of atrophic rhinitis can be both infectious processes and external factors, such as prolonged use of vasoconstrictor nasal drops and exposure to irritating substances on the mucosa.
The diagnosis of atrophic rhinitis is based on gathering history, clinical examination, rhinoscopy, and radiological methods such as X-ray examination of the sinuses and computed tomography. An important stage is the differential diagnosis with other forms of rhinitis. Incorrect treatment of atrophic rhinitis can lead to its progression and complications, so it is important to timely identify and treat this condition.
Factors contributing to the development of atrophic rhinitis
Atrophic rhinitis can be caused by various factors, such as chronic infections, allergies, prolonged use of vasoconstrictor nasal drops, and irritants in the environment. Viruses, bacteria, and fungi can also contribute to the development of this condition by causing inflammation of the nasal mucosa, which over time can lead to its atrophy.
Genetic factors and heredity are of great importance in atrophic rhinitis. People with a family history of this disease are at a higher risk of developing it. In addition, exposure to external agents, such as tobacco smoke, polluted air, and prolonged exposure to allergens, can contribute to damage to the nasal mucosa and result in the appearance of atrophy.
- Chronic infections: Persistent inflammation of the nasal mucosa can lead to its atrophy.
- Prolonged use of vasoconstrictor drops: Frequent use of these remedies can cause irritation and damage to the mucosa.
- Genetic factors and heredity: A predisposition to atrophic rhinitis can be inherited from parents.
- Exposure to allergens: Constant contact with allergens in the environment can stimulate the development of rhinitis and its transition to an atrophic form.
- Bad habits: Smoking, polluted air, and other harmful factors can exacerbate the atrophic process in the nasal mucosa.
Possible manifestations of atrophic rhinitis
Atrophic rhinitis is characterized by a variety of symptoms, including nasal congestion, nasal discharge, unpleasant odor, deterioration of smell, a feeling of dryness and burning in the nose, as well as bleeding from the blood vessels of the mucous membrane. Patients with atrophic rhinitis may also experience pain in the nasal area, headaches, frequent nasopharyngeal complications, and possible deterioration of overall health.
To diagnose atrophic rhinitis, it is necessary to consider the clinical picture, radiological data, risks of air saturation, etiological and pathogenetic factors. The main diagnostic methods include rhinoscopy, fluoroscopy, bacteriological and histological studies. Diagnosis allows for determining the severity of symptoms and taking measures to choose the most effective treatment for the patient.
- Nasal congestion: patients with atrophic rhinitis often face difficulty breathing through the nose due to the shrinkage and atrophy of the mucous membrane.
- Nasal discharge: characteristic signs of atrophic rhinitis include scanty discharges, often having a foul smell due to anaerobic bacteria.
- Deterioration of smell: atrophy of the nasal mucous membrane may lead to a deterioration of smell or its complete loss in the patient.
- Feeling of dryness and burning in the nose: patients with atrophic rhinitis may experience a feeling of dryness and irritation in the nasal cavity caused by the atrophy of the mucous membrane.
- Hemorrhages from the mucosal blood vessels: some patients with atrophic rhinitis show a tendency to hemorrhages from the blood vessels of the nasal mucosa due to its thinning and increased fragility.
The views of specialists on the treatment of atrophic rhinitis
The expert opinion on the treatment of atrophic rhinitis focuses on a comprehensive approach that includes both conservative and surgical methods. The main goal of treatment is to alleviate symptoms, improve the patient’s quality of life, and prevent the progression of the disease. Conservative treatment includes the use of local medications, such as oils and nasal drops, which moisturize and relieve symptoms of dryness and irritation of the mucous membrane.
Surgical methods for treating atrophic rhinitis, such as endoscopic surgery, may be necessary in cases of severe disease progression or lack of effectiveness of conservative treatment. The decision on the choice of treatment method in each specific case should be made by an otolaryngologist based on the characteristics of the disease, individual features of the patient, and the expected effect of the treatment undertaken.

Diagnostic system for atrophic rhinitis
The diagnosis of atrophic rhinitis is a complex process that includes examination and medical history of the patient, rhinoscopy, radiography, analysis of nasal mucus, bacteriological and histological studies. Rhinoscopy allows for a visual assessment of the condition of the nasal mucosa and to determine the presence of atrophy. Radiography of the nose may be performed to identify structural changes in the nasal cavities.
Additional diagnostic methods, such as computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and endoscopy, can be used for a more detailed examination of the structures of the nasopharynx and detection of possible complications of atrophic rhinitis. Diagnostic procedures help to determine the stage of the disease, identify pathogenic factors, which then allows for the selection of an optimal treatment plan for the specific patient.
- Examination and history: Conducting a detailed examination of the patient and gathering information about symptoms and issues in the nasal area.
- Rhinoscopy: Visual examination of the nasal cavity using special instruments to assess the condition of the mucous membrane and identify atrophy.
- X-ray: Radiological examination of the nasal sinuses to determine structural changes and the presence of atrophic processes.
- Nasal mucus analysis: Laboratory examination of nasal mucus to identify the presence of inflammatory processes and possible pathogens.
- Bacteriological and histological studies: Analysis of biological material to identify microorganisms and assess tissue condition.
Methods of treating atrophic rhinitis
For patients with a bacterial component of atrophic rhinitis, the use of antibiotics may be recommended. In addition, important treatment methods include regular rinsing of the nasal passages, the application of topical glucocorticoids to reduce inflammation and improve the condition of the mucous membrane, as well as following recommendations for nasal care and overall immunity strengthening.
- Inhalations with saline: help to moisturize and cleanse the nasal mucosa.
- Nasal moisturizers: contribute to reducing dryness and irritation of the mucous membrane.
- Soft ointments and sprays for the mucous membrane: can help alleviate symptoms of atrophic rhinitis.
- Antibiotics: can be used when a bacterial infection is identified to combat pathogenic microflora.
- Regular rinsing of the nasal passages: contributes to the cleansing of the mucous membrane and improving respiratory function.
Preventive measures for atrophic rhinitis
Regular moisturizing of the nasal passages, using gentle cleaning agents for the nose, as well as restoring the mucosa after illnesses, can help reduce the risk of developing atrophic rhinitis. Adhering to hygiene norms, strengthening the immune system, leading a healthy lifestyle, and timely treatment of upper respiratory tract diseases also play an important role in the prevention of this condition.
- Avoid prolonged exposure to irritants: Tobacco smoke, polluted air, and allergens can negatively affect the condition of the nasal mucosa.
- Maintain humidity levels in indoor spaces: Regular ventilation, humidifying the air, and using moisturizing agents help prevent the drying out of the mucous membranes.
- Monitor the hygiene of the nasal passages: Regular moisturizing and cleansing of the nasal cavities, as well as using gentle care products for the nose, reduce the risk of diseases of the mucosa.
- Strengthen the immune system: A healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, physical exercise, and timely treatment of illnesses help keep the immune system functioning well.
- Follow preventive measures for upper respiratory tract diseases: Seek medical attention promptly at the first signs of illness, adhere to treatment and regimen recommendations to avoid complications and the development of atrophic rhinitis.
Amazing aspects of atrophic rhinitis
Another interesting aspect of atrophic rhinitis is its effect on olfaction. Patients with this condition may experience olfactory disturbances or even anosmia, which can significantly affect their quality of life. Research in this area is ongoing in order to gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms underlying the connection between atrophic rhinitis and olfactory disorders.