Blepharitis: symptoms, causes, and treatment methods
- Understanding the disease: what is blepharitis
- Factors in the development of blepharitis
- Possible signs of blepharitis
- Expert opinion on treatment methods for blepharitis
- Methods of diagnosing blepharitis
- The main methods for treating blepharitis
- Methods of blepharitis prevention
- Amazing aspects of blepharitis
- FAQ
Understanding the disease: what is blepharitis
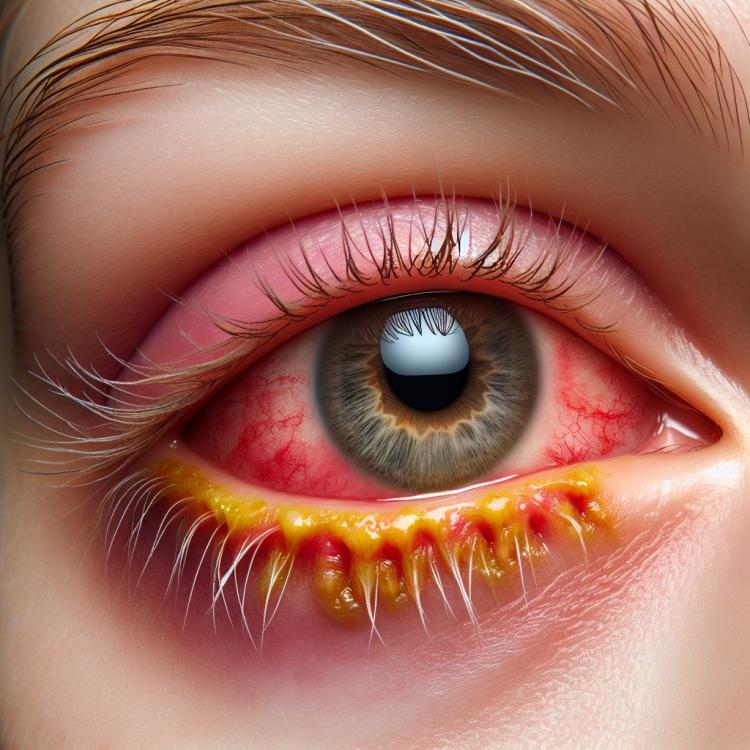
Blepharitis is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects the eyelid margins, most often caused by a bacterial infection or seborrheic dermatitis. It is characterized by symptoms such as itching, redness, swelling, and flaking of the eyelid skin, sometimes with the possible formation of crusts on the eyelashes. Depending on the type of blepharitis (anterior, posterior, or mixed) and the severity of the condition, treatment may include eyelid cleaning, the use of topical antibiotics, hormonal medications, or the application of warm compresses.
Factors in the development of blepharitis
Blepharitis, an inflammatory disease of the eyelid margins, can be caused by various factors. Among the causes of blepharitis may be demodicosis, an allergic reaction to makeup or other medications, bacterial infection, seborrheic dermatitis, and even prolonged wear of contact lenses. It is important to consider both external factors and the overall health status of the patient when analyzing the causes of blepharitis development. Observation, identification, and elimination of factors causing inflammation of the eyelid margins are important elements of the treatment plan for this condition.
- Demodicosis: A parasitic disease caused by the Demodex mite can contribute to the development of blepharitis.
- Allergic reactions: Reactions to cosmetics, makeup, or other substances can lead to inflammation of the eyelid margins.
- Bacterial infection: The presence of bacteria such as staphylococcus or streptococcus can provoke the development of blepharitis.
- Seborrheic dermatitis: A chronic inflammation of the skin, characterized by changes in the function of the sebaceous glands, can be a risk factor for blepharitis.
- Prolonged wearing of contact lenses: Improper use or care of contact lenses can contribute to the development of inflammation of the eyelid margins.
Possible signs of blepharitis
Blepharitis manifests with various symptoms, including redness of the eyelid margins, itching, burning, a sandy feeling in the eyes, eyelid swelling, a sensation of eyelashes sticking together after sleep, discharge, and the formation of crusts on the eyelashes. Sometimes, patients may experience discomfort and eye fatigue, as well as a sudden decline in vision quality. For an accurate diagnosis, it is important to consider the characteristics of the symptoms and consult a specialist upon noticing the mentioned manifestations, as they may resemble other eye conditions.
- Redness of the eyelid edges: usually affects the upper or lower eyelid edge, accompanied by swelling and a feeling of discomfort.
- Itching and burning: patients often complain of an itchy and burning sensation in the eyelid area.
- Feeling of sand in the eyes: sensations of foreign bodies on the surface of the eye may occur.
- Swelling in the accessory eyelids: swelling appears in the eyelid area, which can cause discomfort and worsen appearance.
- Discharge and crusts: purulent or greasy discharge from the meibomian glands combined with the formation of crusts on the eyelashes.
Expert opinion on treatment methods for blepharitis
Experts in the medical field are discussing methods for treating blepharitis with an emphasis on an individualized approach for each patient. The main methods include local treatment using antibiotics, anti-inflammatory agents, antiviral medications, as well as meticulous adherence to eyelid and eyelash hygiene. Experts believe that effective treatment of blepharitis may also include physiotherapeutic procedures, eyelid massage, the use of heating pads or compresses to alleviate symptoms. Early consultation with specialists and strict adherence to expert recommendations will play a crucial role in the successful management of this condition.

Methods of diagnosing blepharitis
Diagnosis of blepharitis is based on the examination of the eyelid margins, assessment of the state of the meibomian glands, as well as the identification of accompanying signs. To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor may perform biomicroscopy to assess the overall condition of the eyelids and eyelashes, as well as use special tests to determine the type of inflammatory process. If necessary, an analysis of the contents of the meibomian glands may be required. Timely and accurate diagnosis of blepharitis allows for effective treatment to be prescribed and prevents possible complications.
- Examination of the eyelid margins: the doctor evaluates the condition of the skin, eyelashes, and checks for redness and swelling.
- Meibomian glands: an assessment of the meibomian glands is conducted, and their contents are periodically examined.
- Biomicroscopy: used for a detailed study of the structure of the eyelids and eyelashes under magnification.
- Inflammation tests: special tests can help determine the type of inflammatory process at the eyelid margins.
- Examination of the contents of the meibomian glands: during periods of exacerbation of the disease, analysis of the gland’s secretion may be required.
The main methods for treating blepharitis
- Hygienic procedures: Regular washing of the eyelids and eyelashes helps reduce the accumulation of oil and debris, promoting healing and improving the condition of the eyelid skin.
- Application of warm compresses: Warm compresses help improve the drainage of meibomian glands, soften crusts, and enhance the condition of the eyelids.
- Prescription of antibiotics: In the case of bacterial blepharitis, antibiotic ointments or drops are used to fight the infection.
- Use of antihistamines: In cases of allergic blepharitis, antihistamines may help reduce swelling and itching around the eyes.
- Treatment of the underlying disease: Addressing the causes of blepharitis, such as demodicosis or seborrheic dermatitis, is an important component of treatment and prevention of disease recurrence.
Methods of blepharitis prevention
Another important aspect of blepharitis prevention is the care of contact lenses, if they are used. It is essential to strictly adhere to the rules and deadlines for lens replacement, and to regularly disinfect them. It is also important to follow the doctor’s recommendations regarding the wearing schedule of lenses and to seek medical assistance if any symptoms of irritation or inflammation of the eyes appear.
- Regular washing of eyelids and eyelashes: Maintaining eye hygiene helps to remove dust, sebum, and other impurities, preventing the development of blepharitis.
- Avoiding eye rubbing: Unwanted rubbing of the eyes can cause injury and worsen the condition of the eyelid margins, so it is important to avoid this.
- Care for contact lenses: Proper use and care of contact lenses, adherence to disinfection rules and replacement schedules reduces the risk of developing blepharitis.
- Following doctor’s recommendations: Prevention of blepharitis includes following the doctor’s recommendations for eye care, wearing schedule for lenses, and regular preventive examinations.
- Consulting a specialist at the first signs: At the appearance of symptoms of eye inflammation, itching, redness, or other unusual manifestations, it is important to consult an ophthalmologist for timely identification and treatment of blepharitis.
Amazing aspects of blepharitis
Interestingly, blepharitis may be part of a broader complex syndrome, such as dry eye syndrome, which includes various symptoms and may require additional attention and care from specialists. Understanding such intriguing factors related to blepharitis may contribute to the development of effective treatment strategies and the prevention of potential complications.