Bursitis of the foot: symptoms, causes, and treatment
Understanding Foot Bursitis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
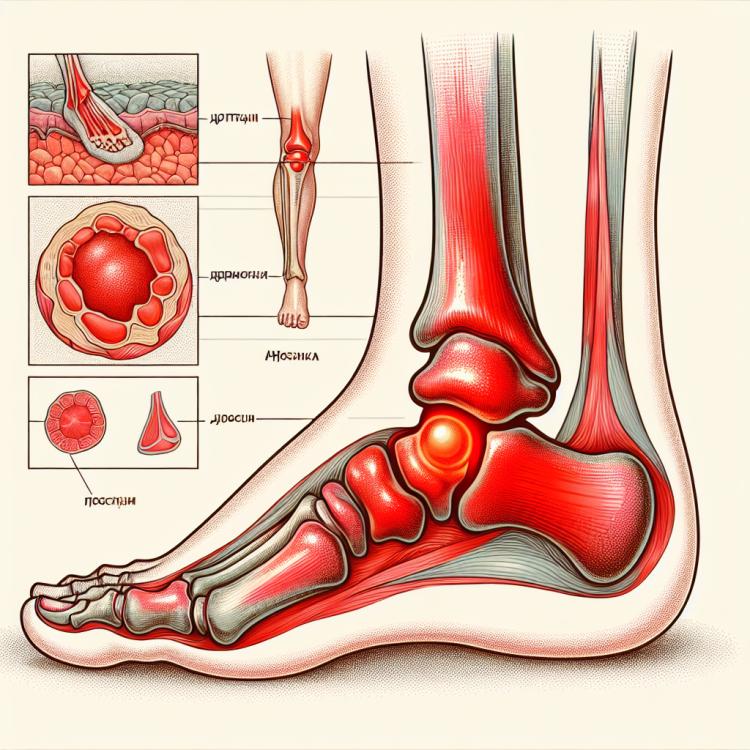
Bursitis of the foot is an inflammatory disease characterized by inflammation of the sacs (bursae) in the foot area. The main symptoms of foot bursitis include swelling, pain, redness of the skin, and limited movement in the area of the affected bursa. The causes of foot bursitis may include trauma, hypothermia, or infection, which can lead to fluid accumulation in the bursae and cause an inflammatory process. Treatment of foot bursitis usually involves the use of anti-inflammatory medications, physiotherapy, specific exercises, and in some cases, procedures to remove fluid from the bursa.
Causes of foot bursitis
The causes of foot bursitis can be varied and include mechanical injury or joint overexertion, leading to inflammation of the bursal sac. This can occur with repetitive microtraumas, improper footwear, specific sports loads, or prolonged standing. Viral or bacterial infections can also be a cause of bursitis development.
In addition, rheumatic diseases such as gout or rheumatoid arthritis may be associated with the development of foot bursitis. Often, bursitis may arise as a complication after an injury or surgery on the foot. It is important to see a doctor at the first signs of joint inflammation to determine the specific causes and discuss a treatment plan.
- Mechanical injury: Injuries to the foot caused by a blow, fall, or other traumatic events can contribute to the development of bursitis.
- Joint overuse: Increased strain on the joint caused by prolonged standing or walking can provoke inflammation of the bursa.
- Viral or bacterial infections: Infections can affect the joint and lead to the development of foot bursitis.
- Rheumatic diseases: Certain rheumatic conditions, such as gout or rheumatoid arthritis, can increase the risk of developing bursitis.
- Complications after injury or surgery: Surgical intervention or foot injury can be a factor contributing to the development of inflammation in the bursa.
The main symptoms of foot bursitis
Bursitis of the foot is characterized by various symptoms, including inflammation of the joint capsule located close to the big toe or heel. Patients may experience pain, swelling, and redness in the joint area. Increased skin temperature at the site of inflammation is often noted, as well as limited movement in the joint. Other possible symptoms include thickening of the tissues around the joint and the appearance of discharge from the joint.
For an accurate diagnosis and determination of the affected area, it is important to conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient, including a physical examination, X-rays, and sometimes testing for infections. Prompt consultation with a doctor is necessary when symptoms of foot bursitis appear to start treatment in a timely manner and prevent complications.
- Pain: Patients often experience pain in the area of the foot, which may intensify with movement or pressure on the joint.
- Swelling: Swelling around the joint is a typical sign of foot bursitis and is associated with fluid accumulation in the joint capsule.
- Redness and increased temperature: The inflamed area may become reddened and warm to the touch due to increased blood flow.
- Restriction of movement: Due to pain and swelling, patients may experience difficulty moving the foot, especially when walking or standing.
- Tissue hardening: Hardened areas may form in the inflamed zone, associated with an increase in the volume of fluid around the joint.
Expert opinions on the treatment of foot bursitis
When treating foot bursitis, experts usually recommend a comprehensive approach that includes the use of medications, physiotherapy, as well as physical rehabilitation methods. An individual treatment plan is developed taking into account the patient’s characteristics, the severity of the disease, and the presence of complications.
An important aspect in the treatment of foot bursitis, according to experts, is the prevention of the inflammatory process and the restoration of joint functional activity. Specialists also emphasize the need to follow the doctor’s recommendations, carry out regular procedures, and monitor the dynamics of the disease for successful and effective treatment of foot bursitis.

Diagnosis of foot bursitis
To diagnose foot bursitis, it is important to conduct a thorough physical examination, including assessing symptoms, palpating the joint, and the area of inflammation. The doctor may also perform additional diagnostic methods, such as X-rays, to rule out other joint pathologies, or analysis of synovial fluid to check for infection. Sometimes, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or other imaging methods may be required for a more accurate diagnosis.
After establishing a diagnosis of foot bursitis, the doctor will determine the optimal treatment plan, which may include prescribing anti-inflammatory medications, pain relievers, physical therapy, or even surgical intervention in case of complications. It is crucial to follow all the doctor’s recommendations and to have follow-up examinations to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and prevent possible recurrences.
- Physical examination: The doctor conducts an assessment and palpation of the affected area, evaluating the presence of a tumor, redness, pain sensations, and movement restrictions.
- X-ray: An X-ray examination may be performed to rule out other joint pathologies and assess the condition of the bones.
- Analysis of arthrosynovial fluid: Examination of joint fluid to identify signs of inflammation, blood, or infection.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): MRI can help the doctor obtain a more accurate view of the structure and condition of the joint’s soft tissues.
- Additional imaging methods: Additional imaging methods, such as ultrasound or computed tomography, may be used for further diagnosis.
Treatment of foot bursitis
In cases of resistance to conservative treatment or the presence of complications, surgical intervention may be required to remove the inflamed bursa or to adjust the structures around the joint. The decision on the method of treatment and therapy for foot bursitis is always discussed with the patient, taking into account individual characteristics and factors of the disease.
- Use of anti-inflammatory medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain in the affected joint.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy procedures, such as ultrasound therapy, massage, and stretching exercises, can help improve circulation and strengthen the muscles surrounding the joint.
- Limiting physical activity: It is important to limit the load on the affected joint to prevent further irritation and speed up the healing process.
- Steroid injections: In some cases, the doctor may prescribe steroid injections into the area of inflammation for quick relief of inflammation and pain.
- Surgical intervention: In cases of resistance to conservative treatment or the presence of complications, surgical removal of the inflamed bursa may be necessary. Individual patient characteristics and disease factors should be considered before making a decision about surgery.
Prevention of foot bursitis
To prevent the development of the infectious form of foot bursitis, particular attention must be paid to foot hygiene, avoiding contact with potentially contaminated surfaces, and promptly consulting a doctor when there are signs of infection or inflammation. Regular physical exercise and strengthening the muscles and joints of the foot can also contribute to the prevention of bursitis and reduce the risk of developing this condition.
- Choosing the right footwear: choose shoes with good arch support and avoid tight or uncomfortable footwear.
- Avoid overloading: maintain a balanced physical activity regime, avoiding excessive strain on the feet, which can lead to fatigue and injuries.
- Pay attention to foot hygiene: regularly wash and dry your feet, avoid wearing damp shoes for long periods to prevent infections.
- Be aware of signs of fatigue: if your feet often feel tired or painful, give them rest and relaxation.
- Strengthen the joints and muscles of the feet: regular exercises to strengthen the muscles and joints will help prevent injuries and improve joint mobility.
Fascinating aspects of foot bursitis
In addition, foot bursitis has its own features in diagnosis and treatment, highlighting the importance of the specialist’s approach to each patient, taking into account individual characteristics and factors in the development of the condition. Understanding the various aspects of foot bursitis combines both scientific and practical components, making it an intriguing subject of study and discussion in medical practice.