Dacryocystitis: causes, symptoms, and treatment methods
Understanding Dacryocystitis
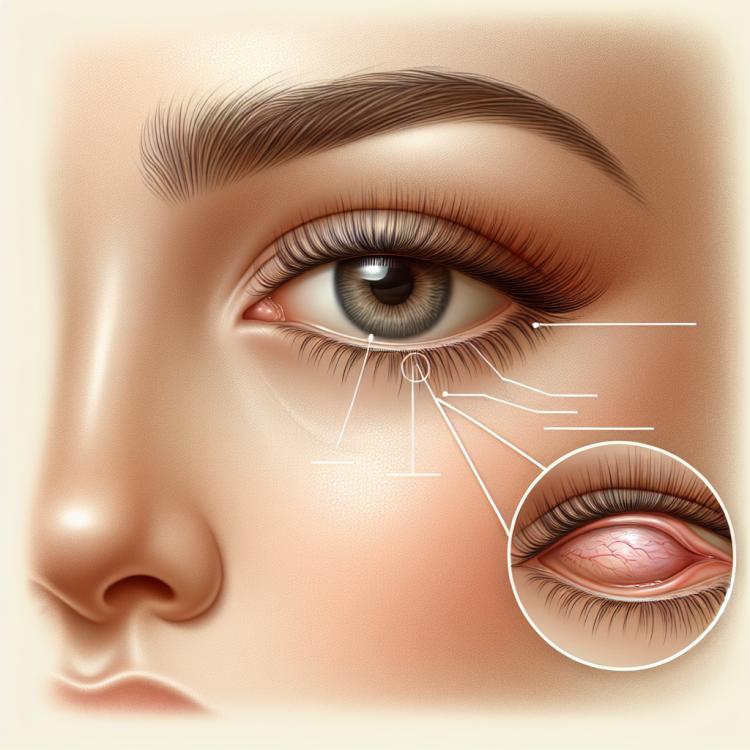
Dacryocystitis is an inflammatory disease of the lacrimal system, most often caused by blockage of the nasolacrimal duct. The main symptoms of dacryocystitis are swelling and redness in the corner of the eye, tearing, purulent discharge from the lacrimal puncta, as well as suppuration in the area of the inner corner of the eye. Treatment may include conservative methods such as inhalations or the use of antibiotics, but in some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to restore the patency of the lacrimal duct.
Etiology of Dacryocystitis
The onset of dacryocystitis is usually due to a disruption in tear drainage, which leads to the stagnation of secretions in the tear ducts and subsequent bacterial proliferation. The main causes of dacryocystitis include the presence of obstruction in the tear ducts, anatomical anomalies of the tear pathways, the growth of infection in the lacrimal sac or excretory pathways, as well as mechanical trauma, foreign bodies, or other irritants that contribute to the development of inflammation in this area.
- Obstruction of the tear ducts: The presence of obstacles in the tear ducts can lead to stagnation of secretions and infection.
- Anomalies in the structure of the tear ducts: Defects in the anatomy of the tear pathways can contribute to the development of dacryocystitis.
- Infectious growth in the tear sac: Proliferation of bacteria in the tear sac can cause inflammation and infection.
- Mechanical trauma: Injuries, including a blow or foreign body, can be a source of inflammatory processes.
- Infection by various pathogens: Various microorganisms, such as bacteria or viruses, can be provoking factors for dacryocystitis.
The clinical picture of Dacryocystitis
The clinical picture of dacryocystitis often includes signs of inflammation in the area of the lacrimal sac, such as swelling, redness, and pain in the outer corner of the eye. Patients may also experience discharge from the lacrimal sac, characterized by serous or purulent secretion. Increased pressure in the nasal area and the planes of the paranasal sinuses may lead to a feeling of discomfort, and sometimes to infection in the facial sinuses.
- Swelling and redness in the area of the outer corner of the eye: characteristic symptoms of inflammation.
- Pain or discomfort when touching the tear ducts: possible intensification of symptoms as the disease progresses.
- Discharge from the lacrimal sac: may show the release of serous or purulent fluid from the eye.
- Pressure and discomfort in the area of the nose: possible symptoms related to obstruction of the tear ducts.
- Recurrences of infections in the paranasal sinuses: possible complications with prolonged cases of dacryocystitis.
Expert opinion on the treatment of Dacryocystitis
The experts’ opinion on the treatment of dacryocystitis emphasizes the importance of an individualized approach for each patient. Identifying the specific causes of dacryocystitis and assessing the degree of the inflammatory process are crucial for determining the optimal treatment method. Experts recommend using both conservative methods (such as the administration of antibiotics in the form of local drops or systemic treatment) and surgical intervention in cases where conservative approaches prove insufficiently effective.

Approaches to the diagnosis of Dacryocystitis
Approaches to the diagnosis of dacryocystitis include visual examination by a doctor, checking for swelling, redness, and discharge in the area of the lacrimal sac. Additional diagnostic methods may include the use of special instruments to study the tear ducts, such as the lacrimal duct test, or dacryocystography to assess the patency of the tear pathways.
Conducting computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging can be useful for evaluating anatomical anomalies and identifying potential problem areas for surgical intervention. Additional diagnostic methods, such as bacteriological analyses of discharge from the lacrimal sac, can assist the doctor in selecting the optimal treatment for each specific case of dacryocystitis.
- Visual examination: The doctor examines the area of the lacrimal sac for swelling, redness, and discharge.
- Schirmer test: Used to assess the patency of the tear ducts and identify problem areas.
- Dacryocystography: A special study that helps to evaluate the condition of the tear ducts in detail.
- Computed tomography (CT): A method for identifying anatomical anomalies and assessing structures in the area of the tear ducts.
- Bacteriological analyses: Examination of discharge from the lacrimal sac to identify possible infection and determine optimal treatment.
Methods of treating Dacryocystitis
Depending on the severity and specifics of each particular case, the doctor may decide on the necessity of applying certain methods for treating dacryocystitis. It is important to conduct a comprehensive examination and determine an individualized approach for each patient, taking into account their health status and the characteristics of the disease.
- Conservative treatment: Includes the use of warm compresses and massage of the tear ducts to stimulate tear drainage, as well as systemic or local application of antibiotics to combat infection.
- Surgical intervention: Dacryocystorhinostomy – a surgery aimed at restoring the patency of tear ducts by removing obstructions.
- Removal of foreign bodies: If foreign bodies are the cause of dacryocystitis, a procedure to remove these bodies is performed followed by treatment of the infection.
- Local application of medications: Local administration of antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs for treating the inflammatory process in the area of the tear ducts.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures: Physiotherapeutic methods, such as ultrasound therapy or electrophoresis, are sometimes used to improve tear drainage and accelerate the recovery process.
Prevention of Dacryocystitis
- Hygiene maintenance: Regular cleaning action to remove microbes that can cause inflammation in the tear ducts.
- Flushing of tear ducts: This process helps prevent obstruction of the tear ducts and stagnation of secretions, which can contribute to the development of dacryocystitis.
- Timely consultation with a doctor: At the first signs of inflammation in the area of the tear sac, it is important to consult a doctor for timely diagnosis and treatment of dacryocystitis.
- Avoiding injuries and irritants: Preventing injuries to the eyes and surrounding areas, as well as minimizing exposure to irritating factors, helps prevent the development of inflammatory processes.
- Following doctor’s recommendations: After treatment of dacryocystitis, it is important to follow all of the doctor’s recommendations for preventive measures to avoid recurrences and complications of the disease.