Exophthalmos: symptoms, causes, and treatment methods
- Understanding Exophthalmos: Key Aspects and Characteristics
- Etiology of Exophthalmos
- Main clinical manifestations of Exophthalmos
- Expert recommendations for the treatment of Exophthalmos
- Methods for diagnosing Exophthalmos
- Methods of treating Exophthalmos
- Prevention of Exophthalmos
- Amazing facts about Exophthalmos
- FAQ
Understanding Exophthalmos: Key Aspects and Characteristics
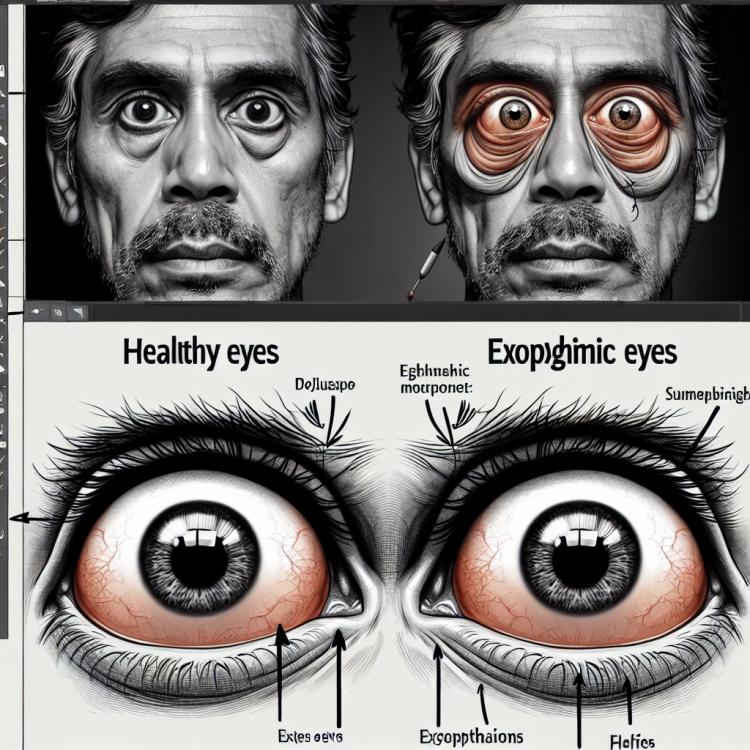
Exophthalmos is a condition in which the eye protrudes from the eye socket. It can be caused by various diseases, such as goiter, orbital tumors, or inflammatory processes. Patients with exophthalmos may experience various symptoms, including visible eye protrusion, dryness and discomfort in the eye area, and vision disturbances. It is important to consult a doctor for diagnosis and to determine appropriate treatment, as managing exophthalmos may require a personalized approach depending on its underlying cause.
Etiology of Exophthalmos
Exophthalmos, or protrusion of the eyes, can have a variety of causes. One of the most common causes of exophthalmos is hyperthyroidism, which is characteristic of diseases such as goiter, autoimmune thyroiditis, and Graves’ disease. Enlargement of the thyroid gland and increased levels of thyroid hormones lead to swelling of the tissues around the eye socket, causing exophthalmos.
Other causes of exophthalmos may include orbital tumors, inflammatory processes, trauma, or genetic disorders. It is important to conduct a thorough examination of the patient to determine the specific cause of the eye protrusion and to decide on appropriate treatment strategies.
- Hyperthyroidism: Hyperproduction of thyroid hormones due to thyroid gland diseases can lead to swelling around the eye socket and exophthalmos.
- Orbital tumors: Malignant or benign tumors located in the orbital area can cause the eyeball to protrude.
- Inflammatory processes: Conditions such as orbital cellulitis or orbital myositis can cause exophthalmos due to inflammation in the eye socket area.
- Injuries: Damage in the orbital or eye area can lead to changes in the position of the eye and result in its protrusion.
- Genetic disorders: Some genetic conditions, such as Marfan syndrome or Cushing’s syndrome, may be associated with the development of exophthalmos.
Main clinical manifestations of Exophthalmos
Exophthalmos is often accompanied by a number of characteristic clinical manifestations, such as bulging of the eyeballs, a feeling of pressure or pain in the eyes, limited eye mobility, improper closure of the eyelids, dryness of the eyes, and possible changes in vision. Patients with exophthalmos may exhibit an increase in the volume of the eye sockets, leading to changes in the appearance of the eyes and face.
It is important to note that the symptoms of exophthalmos can vary depending on its cause and severity. Patients with such manifestations should consult a doctor for diagnosis and the determination of an optimal treatment plan aimed both at alleviating symptoms and treating the underlying condition.
- Protrusion of the eyeballs: the eyes bulge out of the orbit, leading to a change in appearance.
- Feeling of pressure or pain in the eyes: unpleasant sensations in the eye area may accompany exophthalmos.
- Limited mobility of the eyes: reduced ability of the eyes to perform the full range of movements.
- Improper closing of the eyelids: possible issues with normal eyelid function, which can lead to problems with eye moisture.
- Dryness of the eyes and possible changes in vision: symptoms related to changes in the moisture of the ocular surfaces and possible issues with visual function.
Expert recommendations for the treatment of Exophthalmos
Experts’ opinions on the treatment of exophthalmos usually emphasize the importance of an individualized approach for each patient. The main treatment methods may include conservative measures, such as the prescription of medications to reduce inflammation and swelling, as well as surgical interventions if necessary. Experts generally recommend seeking medical help at the first signs of exophthalmos to timely identify the cause and start effective treatment.
For the successful treatment of exophthalmos, it is important to coordinate efforts between ophthalmologists, endocrinologists, and other specialists. Experts recommend conducting a comprehensive examination and determining a strategy for individualized treatment in each specific case, taking into account the patient’s characteristics, the degree of disease progression, and the causes of exophthalmos.

Methods for diagnosing Exophthalmos
Diagnosis of exophthalmos includes various methods, starting from a doctor’s examination and measurement of the protrusion of the eyeballs to more complex studies such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the orbit. A doctor’s examination can reveal visual changes and asymmetries, while precise measurements can be conducted using special tools to determine the degree of exophthalmos. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe additional examinations to study the condition of the eyes and surrounding tissues in more detail.
To clarify the diagnosis and plan treatment, more complex studies may be required, such as tumor biopsy or scanning to identify inflammatory processes. Exophthalmos requires an individualized approach to diagnosis, taking into account the patient’s characteristics and the presumed cause of the eyeball protrusion.
- Doctor’s examination: The doctor performs a visual inspection of the eyes and measures the degree of protrusion of the eyeballs.
- Use of special instruments: Special devices, such as an exophthalmometer, may be used for precise measurements and assessment of exophthalmos.
- Computed tomography (CT): Allows for detailed images of the orbit and structures around the eye to identify possible causes of exophthalmos.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): A study that provides detailed images of soft tissues in the eye socket for the diagnosis of exophthalmos.
- Tumor biopsy: In case of suspicion of a tumor, a tissue sample may be required for further analysis and clarification of the diagnosis.
Methods of treating Exophthalmos
An optimal approach to the treatment of exophthalmos requires a differentiated strategy that considers both the physiological and psychological aspects of the patient’s condition. When providing assistance to patients with exophthalmos, it is essential to take into account not only the medical aspects but also the psychological state and expectations from treatment to ensure the most effective and safe impact on this condition.
- Treatment of the underlying condition: Upon identification of the primary cause of exophthalmos, such as hyperthyroidism, it is crucial to focus on treating the underlying condition, which may lead to an improvement in the symptoms of exophthalmos.
- Medication therapy: Various medications may be used to reduce swelling around the eyes and improve control over inflammation, depending on the individual needs of the patient.
- Surgical intervention: In some cases, especially when there is pressure on the optic nerve or other complications, surgical treatment of exophthalmos may be necessary.
- Physiotherapy: Physiotherapy procedures can help improve blood circulation, reduce swelling, and generally enhance the condition of the tissues surrounding the eye socket.
- Psychological support: For patients with exophthalmos, especially with prolonged chronic disease progression, psychological support and counseling are important to help cope with emotional stress and adapt to changes in appearance.
Prevention of Exophthalmos
Regular consultations with a doctor, especially when risk factors are present, and undergoing necessary examinations can help detect early signs of diseases that may lead to exophthalmos and take timely measures for their treatment or correction. Special attention should be paid to maintaining overall health and seeking medical help promptly when unusual symptoms appear, which in turn contributes to maintaining eye health and preventing the development of exophthalmos.
- Regular check-ups with an endocrinologist: to monitor the condition of the thyroid gland and identify possible dysfunctions that may lead to exophthalmos.
- Healthy lifestyle: maintaining a balanced diet, exercising, and avoiding harmful habits to reduce the risk of diseases that contribute to eye bulging.
- Regular consultations with a doctor: especially in the presence of risk factors or initial signs of diseases that lead to exophthalmos.
- Maintaining overall health: strengthening the body through proper nutrition, physical activity, and health care helps reduce the likelihood of developing exophthalmos.
- Timely consultation with a doctor: if unusual eye symptoms appear, immediate medical help should be sought to prevent complications and the development of exophthalmos.
Amazing facts about Exophthalmos
Interestingly, in many cases, exophthalmos can lead to changes in a person’s physical appearance, which can affect self-perception and psychological well-being. This underscores the importance of a comprehensive approach to the examination and treatment of exophthalmos, considering not only medical aspects but also psychological and aesthetic factors.