Erosive gastritis: symptoms, causes, and treatment
- Definition of erosive gastritis
- Factors contributing to the development of erosive gastritis
- Clinical manifestations of erosive gastritis
- Experts’ opinions on the treatment of erosive gastritis
- Methods for diagnosing erosive gastritis
- Methods of treating erosive gastritis
- Preventive measures for erosive gastritis
- Funny facts about erosive gastritis
- FAQ
Definition of erosive gastritis
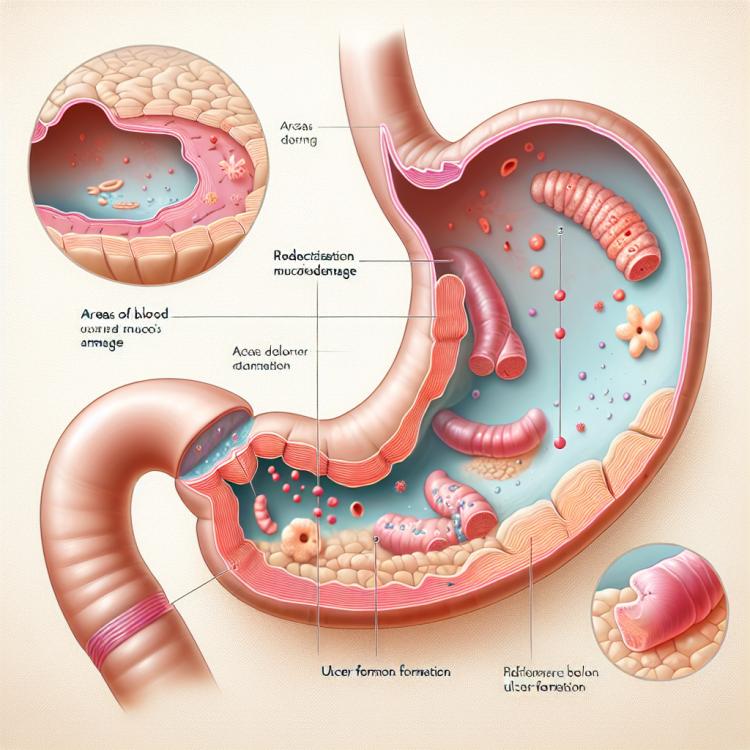
Erosive gastritis is an inflammatory disease of the gastric mucosa, characterized by the formation of erosions and ulcers. These changes in the gastric mucosa can be caused by various factors, including the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, the use of certain medications, alcohol and tobacco, as well as stressful situations. Erosive gastritis can manifest with various symptoms, including pain and discomfort in the epigastric region, nausea, vomiting, gastrointestinal bleeding, and anemia. Medications and dietary treatment, as well as managing risk factors, play an important role in the treatment and prevention of erosive gastritis.
Factors contributing to the development of erosive gastritis
The development of erosive gastritis is caused by various factors, including the use of certain medications, such as neketines and some non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Another important factor is the Helicobacter pylori infection, a bacterium that can cause inflammation of the gastric mucosa and contribute to the development of the erosive process.
In addition, harmful habits such as smoking and alcohol consumption can also contribute to the development of erosive gastritis. Other factors, including stressful situations, poor nutrition, as well as immune system malfunctions, can affect the condition of the gastric mucosa and promote the development of erosions.
- Use of medications: Some medications, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can damage the stomach lining and contribute to the development of erosive gastritis.
- Helicobacter pylori infection: The bacterium Helicobacter pylori is one of the most common causes of erosive gastritis, as it promotes inflammation of the stomach lining.
- Bad habits: Smoking and alcohol consumption can exacerbate inflammatory processes in the stomach and contribute to the development of erosive gastritis.
- Dietary factors: Poor nutrition, including spicy or acidic foods, can irritate the lining and contribute to its damage.
- Stressful situations: Prolonged stress can negatively impact the gastrointestinal tract, increasing the risk of developing erosive gastritis.
Clinical manifestations of erosive gastritis
erosive gastritis can manifest a variety of clinical symptoms, including pain and discomfort in the upper abdomen, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, as well as appetite disorders. Patients may also experience a feeling of fullness in the stomach, heaviness after eating, and even gastrointestinal bleeding in the event of ulcer development.
In addition, erosive gastritis may present more common signs such as weakness, fatigue, pale skin due to blood loss, and even elevated body temperature in the case of infection. It is important to pay attention to such symptoms and seek medical assistance for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
- Pain and discomfort in the upper abdomen: patients may experience sharp or dull pain in the epigastric area.
- Heartburn: a burning sensation or discomfort in the chest caused by the regurgitation of acid from the stomach into the esophagus.
- Nausea and vomiting: patients may experience aversion to food, as well as involuntary expulsion of stomach contents.
- Appetite disorders: changes in appetite, both increase and decrease, may be observed in patients with erosive gastritis.
- Feeling of fullness in the stomach: patients may describe a feeling of fullness or heaviness in the abdomen after eating.
Experts’ opinions on the treatment of erosive gastritis
The experts’ opinions on the treatment of erosive gastritis emphasize a comprehensive approach to managing this condition. The main treatment methods include the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, proton pump inhibitors, and antibiotics in cases where Helicobacter pylori infection is the cause of the disease. Experts also support the rational use of probiotics to restore the balance of the gastrointestinal microbiota.
However, each case of erosive gastritis is unique, and treatment should be tailored to the individual characteristics of the patient and the severity of the disease. Specialists recommend strictly following the doctor’s prescriptions, making adjustments to diet and lifestyle, and maintaining regular monitoring of the disease’s condition to achieve the best results in the treatment of erosive gastritis.

Methods for diagnosing erosive gastritis
For the diagnosis of erosive gastritis, various methods are used, including endoscopy with biopsy of the gastric mucosa, which allows visualization of the gastric lining and collection of cell samples for further analysis. Laboratory tests may include blood tests for the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection and inflammation markers.
Additional diagnostic methods may include gastroesophageal reflux studies to assess gastric function, tests for gastric secretion, as well as urological examinations to evaluate the overall condition of the gastrointestinal tract. The results of these methods help the doctor establish an accurate diagnosis and develop an individual treatment plan for each patient, depending on the severity and nature of the condition.
- Endoscopy with biopsy: this method allows for a detailed examination of the condition of the stomach mucosa and to take samples for further analysis.
- Laboratory tests: blood tests may include checking for Helicobacter pylori infection and inflammation indicators.
- Gastroesophageal refluxography: a method for studying the function of the stomach and assessing the flow of food through the esophagus.
- Test for gastric secretion: allows for evaluating gastric juice secretion and its composition.
- Urological studies: for a comprehensive assessment of the condition of the gastrointestinal tract and to identify possible associated diseases.
Methods of treating erosive gastritis
In addition to pharmacological treatment, important measures may include dietary correction, the cessation of harmful habits, adherence to a diet that promotes the healing of the mucous membrane, and stress level control. An individualized approach to treatment, taking into account the characteristics of each patient and the degree of Helicobacter pylori infection, is key to the successful therapy of erosive gastritis.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: Used to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain symptoms in the gastric mucosa.
- Proton pump inhibitors: These medications lower acidity in the stomach, promoting the healing of erosive damage.
- Antacids: Medications that neutralize stomach acid, helping to reduce heartburn and discomfort.
- Antibacterial therapy: Used to treat Helicobacter pylori infection, which is often a cause of erosive gastritis.
- Dietary compliance: It is recommended to exclude spicy, acidic, smoked foods, alcohol, and coffee from the diet to ease the condition of the mucous membrane.
Preventive measures for erosive gastritis
Regular medical check-ups, timely examination and treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection, if detected, are also important foundations for the prevention of this disease. Maintaining a healthy stress level and adequate physical activity can also contribute to reducing the risk of developing erosive gastritis.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol consumption: Bad habits can increase the risk of developing erosive gastritis.
- Follow a healthy diet: Avoid fatty, spicy, and acidic foods, consume products that promote stomach health.
- Maintain optimal stress levels: Managing stress can help prevent the development of gastritis and other gastrointestinal disorders.
- Regularly check for Helicobacter pylori infection: Timely detection and treatment of this infection help prevent complications, including the development of erosive gastritis.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Include regular physical exercise, get enough sleep, and monitor overall health to prevent erosive gastritis.
Funny facts about erosive gastritis
Another interesting fact is that some studies show that certain types of probiotics may have a beneficial effect on the stomach lining and reduce inflammatory processes, which can be helpful in the prevention and treatment of erosive gastritis. Such discoveries continue to lead to new approaches to the treatment and understanding of this disease.