Pharyngitis: symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment methods
- Definition of pharyngitis
- Pathological factors contributing to the development of pharyngitis
- Clinical manifestations of pharyngitis
- Reviews from specialists on the treatment of pharyngitis
- Methods for diagnosing pharyngitis
- Methods of treating pharyngitis
- Prevention measures for pharyngitis
- Curious aspects of pharyngitis
- FAQ
Definition of pharyngitis
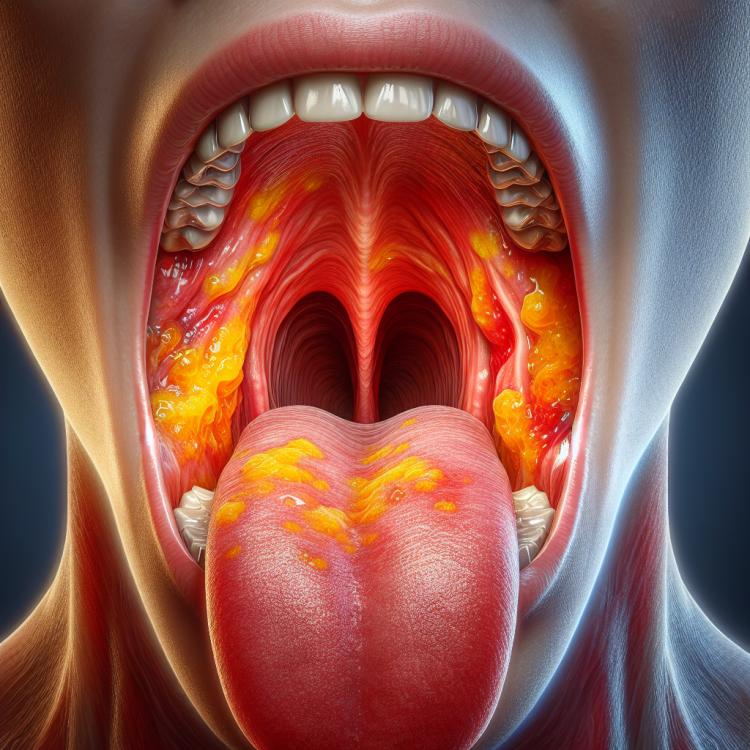
Pharyngitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the back wall of the throat, or pharynx. The main cause of its development is usually an infection caused by bacteria or viruses. Patients with pharyngitis may experience various symptoms such as pain and irritation in the throat, difficulty swallowing, as well as an increase in body temperature.
Pathological factors contributing to the development of pharyngitis
Pharyngitis, as an inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane of the throat, has numerous possible pathological causes. One of the most common is infectious exposure caused by viruses, bacteria, or fungi. Other factors that may contribute to the development of pharyngitis include prolonged exposure to harmful chemicals, allergens, hypothermia or overheating of the body, as well as smoking and other harmful habits that weaken the protective functions of the mucous membrane of the throat.
- Infections: Viruses, bacteria, and fungi can cause inflammation of the throat.
- Harmful effects: Prolonged contact with chemicals or allergens can irritate the mucous membrane of the throat.
- Overcooling or overheating: Extreme temperatures can weaken the protective functions of the mucous membrane of the throat.
- Smoking: Harmful substances in tobacco smoke can irritate and damage the throat.
- Dry air: Lack of moisture in the air can lead to dehydration of the mucous membrane and increase the risk of developing pharyngitis.
Clinical manifestations of pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is characterized by a variety of clinical manifestations, including pain and irritation in the throat, difficulty swallowing, a sensation of tickling and dryness, as well as fever, general weakness, and enlarged lymph nodes. The consequences of pharyngitis may be accompanied by a cough, changes in voice, as well as bad breath. The main characteristics of this condition are inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx and the accompanying discomfort that the patient experiences during the illness.
- Sore throat and irritation: patients often experience discomfort and pain in the throat area during pharyngitis.
- Difficulty swallowing: the infectious process accompanying pharyngitis can cause difficulties when swallowing food and liquids.
- Sense of tingling and dryness: patients may experience a sensation of tingling or dryness in the throat, which is a typical symptom of pharyngitis.
- Increased body temperature: acute inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa can lead to an increase in body temperature in the patient.
- Enlarged lymph nodes: during pharyngitis, enlargement of the lymph nodes in the neck is often observed, which is a response of the immune system to the infection.
Reviews from specialists on the treatment of pharyngitis
The opinions of experts on the treatment of pharyngitis often emphasize the importance of a comprehensive approach based on causal relationships and the individual characteristics of the patient. Specialists recommend taking into account the type of pathogen causing the disease when choosing a treatment method, whether it is viral, bacterial, or fungal pharyngitis. Each case requires an individualized approach, considering not only the symptoms but also the overall condition of the patient, the presence of complications, and the factors contributing to the development of the disease. The competent selection of treatment regimens and the use of effective medications are key points that experts focus on in the process of combating pharyngitis.

Methods for diagnosing pharyngitis
Diagnosis of pharyngitis includes a doctor’s examination, medical history of the disease, and clinical manifestations such as sore throat, cough, and voice changes. To clarify the diagnosis, laboratory tests may be used, including a complete blood count, throat swab analysis for infections, and instrumental methods such as pharyngoscopy, which allows for a visual assessment of the condition of the mucous membrane of the throat.
In case of suspected pharyngitis, it is important to conduct a comprehensive examination to determine the cause of the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment. Inadequate diagnosis and incorrect treatment of pharyngitis can lead to complications and a chronic course of the disease.
- Doctor’s examination: The doctor examines the throat, assesses the presence of redness, swelling, and plaque, and palpates the lymph nodes in the neck area.
- Medical history: The doctor clarifies the nature of the patient’s complaints, the duration of symptoms, the presence of previous illnesses, and risk factors.
- Laboratory tests: Include a complete blood count, which can indicate the presence of inflammation, smear tests for infections, and other studies.
- Instrumental methods: Pharyngoscopy allows the doctor to visually assess the condition of the pharynx, oropharynx, and nasopharynx using a special instrument.
- Additional methods: In some cases, additional examinations may be prescribed, such as a bacteriological study of a smear for sensitivity to antibiotics.
Methods of treating pharyngitis
For effective treatment of pharyngitis, anti-inflammatory medications and topical analgesics are also used. In some cases, antifungal medications may be necessary, especially when a fungal pharyngitis is diagnosed. It is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations and complete the entire course of treatment to prevent recurrences and complications of the disease.
- Symptomatic treatment: use of pain relievers, antipyretic agents, and cough suppressants.
- Antibiotic therapy: prescription of antibiotics for bacterial pharyngitis.
- Anti-inflammatory medications: use of agents that reduce inflammation and swelling of the throat.
- Local anesthetics: use of sprays, lozenges, or gargles to relieve throat discomfort.
- Antifungal therapy: treatment of fungal pharyngitis using antifungal medications.
Prevention measures for pharyngitis
Regularly airing rooms and humidifying the air can help prevent irritation of the throat mucosa. Avoiding contact with people suffering from acute respiratory infections is also an important factor in the prevention of pharyngitis. If taking medications that may irritate the throat, it is important to consult a doctor and follow the recommended guidelines for use.
- Personal hygiene compliance: Regular hand washing and teeth brushing help prevent the transmission of infections, including possible causes of pharyngitis.
- Quit smoking: Smoking damages the mucous membrane of the throat and weakens its protective functions, leading to an increased risk of developing pharyngitis.
- Moderate alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can contribute to inflammation of the throat mucosa and exacerbate pharyngitis symptoms.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: A balanced diet, physical activity, and overall immune strengthening help prevent pharyngitis.
- Regular ventilation of rooms: Good ventilation and humidification of the air help reduce irritation of the throat mucosa and prevent factors that can cause pharyngitis.
Curious aspects of pharyngitis
Another intriguing aspect of pharyngitis is that some people may experience excessive dryness or scratchiness in the throat, leading to discomfort and requiring special attention during treatment. Understanding the differences and characteristics of pharyngitis can assist both patients and medical professionals in the effective diagnosis and treatment of this condition.