Furuncle (boil): diagnosis, treatment, and prevention
- Understanding Furuncle: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
- Etiology of Furuncle: main factors of occurrence
- The clinical picture of a boil: how to recognize the disease
- Expert opinion on treating a furuncle
- Diagnosis Methods for Furuncle
- Methods of treating a furuncle
- Prevention measures for furuncle
- Unusual Aspects of Furuncle
- FAQ
Understanding Furuncle: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
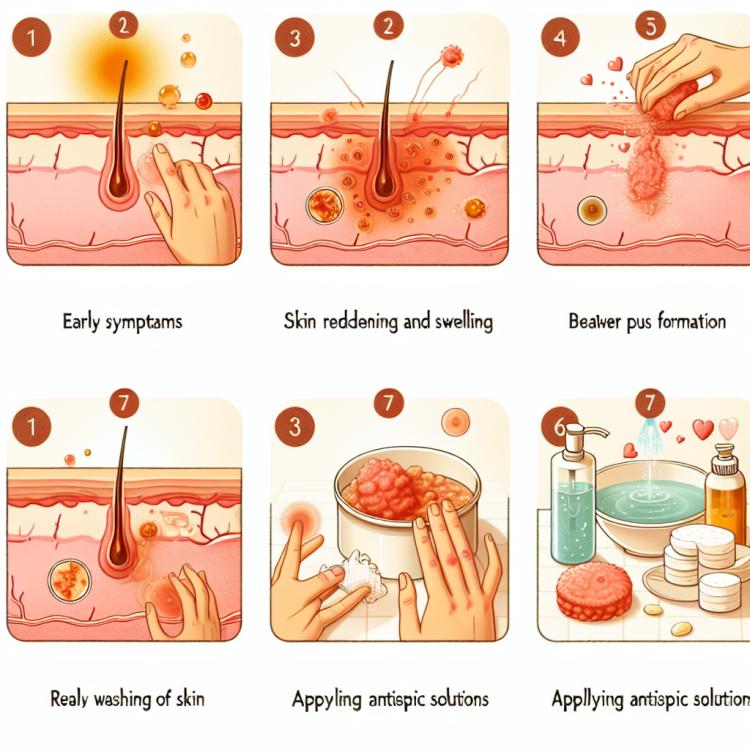
A furuncle, or boil, is a purulent inflammation of the hair follicle and surrounding tissues caused by a bacterial infection, most commonly Staphylococcus aureus. It is characterized by the formation of a painful, red swelling, on top of which a purulent plug appears. Symptoms include tenderness, redness, swelling, and a covering of the purulent abscess. Treatment of a furuncle includes antiseptic procedures, the use of topical antimicrobial agents, and, if necessary, surgical intervention to drain the pathological focus of inflammation.
Etiology of Furuncle: main factors of occurrence
A boil, or furuncle, is a purulent inflammation of the hair follicle and surrounding tissues. The pathogenesis of the disease is caused by the action of staphylococci that inhabit the skin. The main cultivating staphylococcus is Staphylococcus aureus, which can produce exotoxins that cause inflammatory swelling and pathological processes in tissues.
Among the factors that contribute to the occurrence of a boil are insufficient hygiene, increased sweating, skin injuries, the presence of chronic diseases, or immunodeficiency states. In addition, individual characteristics of the skin and disorders in the functioning of sebaceous glands may also contribute to the formation of boils.
- Insufficient hygiene: Daily skin hygiene is an important aspect of preventing boils.
- Increased sweating: Excessive sweating can contribute to the blockage of hair follicles.
- Skin injuries: Mechanical damage to the skin can lead to an inflammatory response and the development of a boil.
- Chronic diseases: The presence of systemic diseases such as diabetes can worsen the immune protection of the skin.
- Immunodeficiency states: Weakening of the immune system makes the body more vulnerable to infections, including boils.
The clinical picture of a boil: how to recognize the disease
The furuncle manifests as a painful red swelling on the skin, which gradually increases in size and becomes tense. The appearance of a blister filled with purulent material is one of the characteristic signs of a furuncle. The skin around this area may be swollen, hot, and painful to the touch.
Other symptoms of a furuncle include general weakness, fever, and localized increase in skin temperature. If similar signs are observed, it is important to consult a doctor for evaluation and confirmation of the diagnosis in order to initiate timely and effective treatment.
- painful skin tumor: A furuncle often starts as a painful red swelling that increases in size.
- Appearance of a blister with purulent mass: A characteristic symptom of a furuncle is the formation of a blister filled with pus.
- Swollen, hot, and painful skin: The skin around the furuncle may be swollen and sensitive to touch.
- General weakness and fever: The appearance of general weakness and increased body temperature often accompanies a furuncle.
- Increased skin temperature: The affected area may be hot to the touch due to inflammation and infection.
Expert opinion on treating a furuncle
Experts in the field of dermatology usually recommend conservative treatment for furuncles, which includes antiseptic treatment of the affected area, the use of antibacterial agents, and the management of purulent foci. In the case of abscess formation or widespread inflammation, surgical intervention may be required to drain the purulent collections.
Expert opinion emphasizes the importance of timely consultation with a physician to assess the severity of the process, prescribe appropriate treatment, and prevent complications. Effective and comprehensive treatment based on specialists’ recommendations contributes to rapid recovery and prevents recurrence of the disease.

Diagnosis Methods for Furuncle
In diagnosing a furuncle, the doctor typically relies on clinical signs, such as characteristic symptoms of inflammation, purulent content, tenderness, and the overall condition of the patient. Additional diagnostic methods include laboratory tests, such as microbiological analyses of smears and cultures, to identify the causative agent of the infection and its sensitivity to antibiotics, which can help in choosing the most effective treatment.
Sometimes the physician may recommend additional diagnostic procedures, such as ultrasound, to assess the depth of tissue involvement or to detect the presence of a purulent abscess. A consultation with a surgeon may also be necessary if complications are suspected or if surgical intervention is needed. It is important to perform a comprehensive diagnosis to determine the severity and nature of the process and to prescribe appropriate treatment.
- Clinical examination: The doctor examines the skin, assessing the characteristic signs of inflammation and purulent process.
- Laboratory tests: Include microbiological examination of smears to identify the infectious agent and its sensitivity to antibiotics.
- Cultural studies: Allow determining the type of microorganism that caused the infection and assist in selecting the most effective treatment.
- Ultrasound examination: May be performed to determine the depth of tissue damage and to identify the presence of abscess.
- Consultation with specialists: If necessary, the doctor may refer the patient for a surgical consultation to assess complications and the possibility of surgical intervention.
Methods of treating a furuncle
In cases where the boil becomes large or is accompanied by complications, drainage of the purulent contents and the use of systemic antibiotic therapy may be required. In some situations, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove the purulent abscess. Consulting a doctor and strictly following their recommendations are important parts of successful boil treatment.
- Local treatment: includes treating the area of the furuncle with antiseptics to prevent infection and inflammation.
- Use of heat therapy: hot compresses help to accelerate the maturation of the furuncle and facilitate the drainage of pus.
- incision of purulent content: in the case of large furuncles or complications, it may be necessary to remove the pus to speed up recovery.
- Anti-inflammatory medications: may be used to reduce inflammation and pain associated with the furuncle.
- Antibiotic therapy: in some cases, systemic use of antibiotics may be required to combat infection and prevent complications.
Prevention measures for furuncle
Another important part of furuncle prevention is maintaining immunity through a healthy diet, moderate physical activity, and regular intake of vitamins and minerals. In the presence of risk factors, such as diabetes or immune system disorders, it is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations and conduct preventive monitoring for the timely detection and control of diseases that contribute to the occurrence of furuncles.
- Personal hygiene compliance: Regularly washing the skin, especially in areas prone to increased sweating, helps prevent the infection of hair follicles.
- Avoiding skin injuries: Preventing cuts, scratches, and other skin injuries lowers the risk of developing boils.
- Maintaining immunity: A healthy diet, regular physical exercise, and moderate intake of vitamins and minerals contribute to strengthening the immune system.
- For diabetes: It is important to carefully monitor blood glucose levels and follow the doctor’s recommendations to control the disease and prevent boils.
- Using individual hygiene items: Using separate towels, clothing, and personal care items helps prevent the transfer of microorganisms and the spread of infection among others.
Unusual Aspects of Furuncle
In addition, boils can develop in various parts of the body, which is related to the activity of sebaceous glands and conditions for bacterial reproduction on the skin. The study of individual factors that may influence the occurrence of boils is ongoing, which will allow for the improvement of prevention and treatment methods for this condition.