Gangrene: causes, symptoms, and treatment methods
- Understanding Gangrene: Key Aspects and Definition
- Pathogenesis of gangrene: factors contributing to its development.
- Main signs of gangrene.
- Expert opinion on methods of treating gangrene
- Methods of diagnosing gangrene
- Approaches to the treatment of gangrene
- Prevention measures for gangrene
- Inadequate and improper treatment can lead to the worsening of the condition and the spread of infection, which increases the risk of developing gangrene.
- FAQ
Understanding Gangrene: Key Aspects and Definition
Gangrene is a serious complication characterized by tissue necrosis due to impaired blood supply. It usually arises from thrombosis of vessels, trauma, infection, or diabetes. When gangrene develops, immediate intervention from specialists is necessary to prevent the spread of infection and preserve the patient’s health.
Pathogenesis of gangrene: factors contributing to its development.
Gangrene is a serious medical condition caused by tissue necrosis due to impaired blood circulation. The causes of gangrene can be numerous and differentiated. The main factors contributing to the development of gangrene include thrombosis of blood vessels, atherosclerosis, diabetes, obesity, as well as injuries and infections that can lead to extensive tissue necrosis. It is important to consider that adhering to the proper treatment and preventive measures for the underlying causes of gangrene is crucial for preventing potential complications.
- Thrombosis of blood vessels: the formation of blood clots in blood vessels can block normal blood flow and contribute to the development of gangrene.
- Atherosclerosis: the deposition of cholesterol on the walls of blood vessels leads to impaired blood flow, increasing the risk of tissue necrosis.
- Diabetes mellitus: high blood glucose levels damage blood vessels and nerves, making diabetic patients more susceptible to the development of gangrene.
- Obesity: excess weight places additional strain on the heart and blood vessels, which can disrupt tissue blood supply and contribute to the development of gangrene.
- Injuries and infections: tissue damage, such as from traumatic impact or infections, can initiate the process of gangrene development.
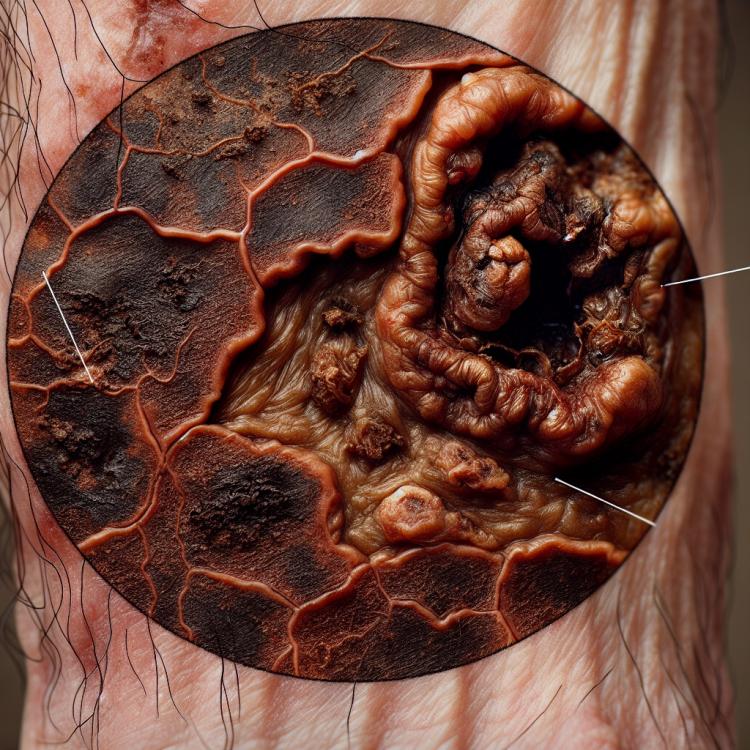
Main signs of gangrene.
Gangrene is characterized by typical clinical manifestations, including changes in color and texture of the skin in the affected area, tissue necrosis, as well as the release of a characteristic odor. Patients may experience localized pain, swelling, hyperthermia in the affected area, as well as general symptoms of body intoxication, such as fever, chills, and weakness. The diagnosis of gangrene is based on the clinical picture, visual examination of the affected tissue, the use of various educational diagnostic methods such as ultrasound and MRI, and requires immediate medical evaluation and intervention to prevent severe complications.
- Change in skin color: the affected area becomes pale, bluish, or black due to tissue necrosis.
- Tissue necrosis: characterized by tissue death and the formation of ulcers or ulcerative defects in the affected area.
- Local pain and swelling: the patient may experience pain and an increase in tissue volume at the site of injury.
- General signs of intoxication: fever, chills, weakness, and disturbances in the overall condition of the body may occur.
- Characteristic smell: the affected area may emit a characteristic smell of decay, caused by the decomposition of necrotic tissues.
Expert opinion on methods of treating gangrene
Experts in the field of medicine categorically emphasize that successful treatment of gangrene requires a comprehensive approach, including surgical intervention, antibiotic therapy, and addressing the underlying causes of the disease. Surgical methods such as amputation of the affected tissue, drainage of abscesses, and revascularization of blood vessels play an important role in the treatment of gangrene, especially in advanced stages of the disease.
Considering the unique features of the clinical case and the overall condition of the patient, doctors make a decision on the most appropriate therapeutic plan. Emphasis is also placed on regular monitoring of the patient, control over the wound healing process, and prevention of recurrences. The medical community continuously improves methods for treating gangrene with the aim of enhancing the effectiveness of therapy and improving outcomes for patients.

Methods of diagnosing gangrene
Diagnosis of gangrene involves a comprehensive approach based on an extensive clinical examination and the conduct of additional instrumental and laboratory studies. Medical professionals may use various methods such as X-ray, ultrasound, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging to more accurately identify areas of necrosis and determine the degree of tissue damage. Biochemical blood tests and other laboratory studies may also be performed for a thorough analysis of the patient’s overall condition and to identify possible disruptions in the body related to gangrene.
- Clinical examination: The doctor performs a visual assessment of the affected area, identifying signs of necrosis and changes in the tissues.
- Instrumental methods: Include X-ray, ultrasound examination, CT, and MRI for a more precise determination of the characteristics of the affected tissues.
- Laboratory blood tests: Allow for the assessment of the overall condition of the body, the level of inflammation, and the presence of infection.
- Tissue biopsy: Used to obtain a sample of the affected tissue for detailed analysis and establishing an accurate diagnosis.
- Infectious tests: May include microbial culture and antibiotic sensitivity tests to determine the type of infection and response to medical treatment.
Approaches to the treatment of gangrene
- Surgical intervention: Removal of necrotic tissue and restoration of blood supply to the affected area is a key stage in the treatment of gangrene.
- Antibiotic therapy: The use of antibiotics is necessary to control infection, reduce inflammation, and prevent the spread of bacteria in the body.
- Supportive therapy: Includes measures to stabilize the patient’s condition, maintain proper fluid and nutrient levels in the body.
- Monitoring and control: Regular observation of the patient’s condition and monitoring the wound healing process play an important role in the effective treatment of gangrene.
- Individual approach: Each case of gangrene is unique, so it is important to develop individual therapeutic schemes, taking into account the patient’s characteristics and the nature of the disease.
Prevention measures for gangrene
- Maintaining good circulation: avoid sitting or lying in one position for long periods, engage in moderate physical activity to stimulate blood flow.
- Monitor skin condition: it is especially important to pay close attention to the skin of individuals at high risk for developing gangrene, promptly addressing cuts, wounds, and other injuries.
- Practice hygiene: regularly clean and treat wounds; using antiseptics can help prevent infections, which are a triggering factor for the development of gangrene.
- Support a strong immune system: proper nutrition, regular physical exercise, and moderate intake of vitamins and minerals contribute to maintaining a healthy immune system.
- Medical supervision: visiting a doctor to monitor skin condition, especially in patients with chronic diseases or circulatory disorders, can help identify potential problems early and prevent the development of gangrene.