Hydrosalpinx: diagnosis, consequences, and treatment methods
- Understanding Hydrosalpinx: Key Aspects, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
- Factors contributing to the development of Hydrosalpinx
- The main manifestations of Hydrosalpinx
- Experts’ views on treatment methods for Hydrosalpinx
- Modern methods for diagnosing Hydrosalpinx
- Methods of Hydrosalpinx Therapy
- Measures to prevent Hydrosalpinx
- Amazing aspects of Hydrosalpinx
- FAQ
Understanding Hydrosalpinx: Key Aspects, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
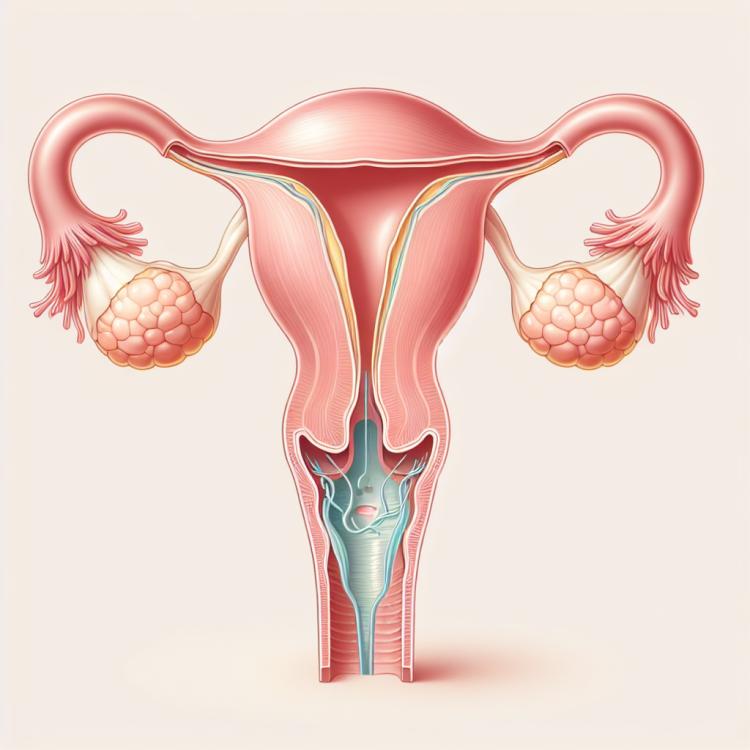
Hydrosalpinx is a pathological condition of the female reproductive organs, characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the fallopian tubes. This can lead to the expansion and deformation of the tubes, causing reproductive function disorders. The main symptoms include lower abdominal pain, irregular menstruation, and painful intercourse. Diagnosis of hydrosalpinx usually involves ultrasound examination, hysterosalpingography, computed tomography, or magnetic resonance imaging.
Factors contributing to the development of Hydrosalpinx
Hydrosalpinx, an anomaly characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the fallopian tubes, can have a variety of causes, including inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, surgical interventions, hormonal disorders, and developmental abnormalities of the fallopian tubes. In the presence of inflammatory processes such as chlamydia or gonorrhea, the formation of adhesions and the basis for the development of hydrosalpinx is possible. Additionally, surgical interventions in the pelvic area or structural defects of the fallopian tubes may predispose to the occurrence of this condition.
- Inflammatory diseases: Chlamydia, gonorrhea, and other infections can lead to inflammation of the tubes.
- Surgical interventions: Surgery in the pelvic area can cause scarring and narrowing of the fallopian tubes.
- Hormonal disorders: Hormonal imbalance can affect the function of the tubes, contributing to hydrosalpinx.
- Vascular disorders: Poor blood supply to the tubes can lead to their deformation and dysfunction.
- Developmental anomalies: Structural defects of the fallopian tubes from birth may be a risk factor for the development of hydrosalpinx.
The main manifestations of Hydrosalpinx
Hydrosalpinx can manifest with various symptoms, including lower abdominal pain, especially during menstruation or sexual intercourse, as well as irregular or painful menstrual bleeding. Some women may experience discomfort or unpleasant sensations in the pelvic area, which can also be a sign of this pathological condition.
In addition, infertility may arise due to impaired patency of the fallopian tubes, which is one of the main complications of hydrosalpinx. It is important to note that the symptoms of this disease can be hidden or mimic other conditions, so comprehensive examination is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
- Lower abdominal pain: pain often occurs, especially during menstruation or sexual intercourse, and may be accompanied by discomfort.
- Irregular menstruation: women with hydrosalpinx may experience an irregular cycle and painful periods.
- Pain in the pelvic area: some patients may experience discomfort and unpleasant sensations in the pelvic region.
- Infertility: obstruction of the fallopian tubes can lead to infertility, which is one of the main complications of hydrosalpinx.
- Hidden or atypical symptoms: manifestations of hydrosalpinx may be unobvious or mimic other diseases, necessitating a comprehensive diagnostic approach.
Experts’ views on treatment methods for Hydrosalpinx
Experts in the field of gynecology point out the variety of approaches to the treatment of Hydrosalpinx, which include conservative and surgical methods. Conservative therapy may involve the use of anti-inflammatory medications and antibiotics to combat infection, as well as physiotherapy procedures to improve blood flow and regulate inflammatory processes. However, in some cases, especially with serious pathologies present, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove fluid-retaining formations in the tube or even partial removal of the fallopian tube itself.
Specialists also emphasize the importance of an individualized approach to the treatment of Hydrosalpinx, taking into account factors such as the patient’s age, overall health, presence of additional diseases, and desire to preserve or restore reproductive health. In making such decisions, specialists are guided not only by the clinical manifestations of the disease but also by its causes, in order to ensure the best treatment outcomes and reduce the likelihood of recurrence and complications.

Modern methods for diagnosing Hydrosalpinx
For accurate diagnosis of Hydrosalpinx, a variety of examination methods are currently used, including ultrasound, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging. Ultrasound is one of the most accessible and informative methods, allowing visualization of the presence of fluid in the fallopian tubes and determining the degree of dilation.
Additionally, to confirm the diagnosis and assess the condition of surrounding tissues, hysterosalpingography may be performed, which allows for a detailed study of the patency of the fallopian tubes. The combination of various diagnostic methods enables specialists to get a complete picture of the woman’s reproductive system and determine the optimal treatment plan for Hydrosalpinx.
- Ultrasound examination: one of the main methods for visualizing the presence of fluid in the fallopian tubes and assessing their condition.
- Computed tomography: provides a more detailed image of tissues and may be used for additional diagnosis of Hydrosalpinx.
- Magnetic resonance imaging: possible for assessing the dilation of the fallopian tubes and the condition of surrounding tissues.
- Hysterosalpingography: a specialized radiological method for evaluating the patency of the fallopian tubes and diagnosing pathologies.
- Laparoscopy: an invasive method that allows for direct visualization and assessment of the condition of the fallopian tubes and pelvic tissues.
Methods of Hydrosalpinx Therapy
In cases where conservative methods do not bring the desired results and in the presence of significant dilation of the fallopian tubes, surgical intervention may be required, including the removal of affected areas or the restoration of the anatomical integrity of the fallopian tubes. However, the treatment strategy for Hydrosalpinx should carefully consider all factors of the disease and the patient’s condition to achieve optimal outcomes.
- Medication therapy: Carried out with the aim of eliminating inflammatory processes and restoring the patency of the fallopian tubes.
- Surgical intervention: In cases where other methods are ineffective, surgery is performed to remove affected areas or restore the integrity of the fallopian tubes.
- Physical therapy: Used to relieve pain syndrome and improve blood flow in the pelvic area.
- Alternative medicine: Some patients turn to alternative medicine methods, such as herbs and Ayurveda, as additional support in the treatment of Hydrosalpinx.
- Psychological support: Considering the psychological state of women diagnosed with Hydrosalpinx, an important aspect of treatment is emotional support and counseling.
Measures to prevent Hydrosalpinx
Regular consultations with a gynecologist and adherence to recommendations for the prevention of inflammatory processes in the reproductive system will help reduce the risk of developing Hydrosalpinx. By consulting a specialist at the first signs of pain or menstrual cycle disturbances, one can timely identify possible issues and prevent their further development.
- Regular check-ups: Visiting a gynecologist for preventive examinations helps identify potential disease problems at early stages.
- Treatment of inflammatory diseases: Timely medical intervention upon detection of pelvic infections and their complete cure helps prevent the development of Hydrosalpinx.
- Healthy lifestyle: Proper nutrition, an active lifestyle, quitting harmful habits such as smoking, and moderate alcohol consumption contribute to maintaining overall health and strengthening the immune system.
- Following doctor’s recommendations: It is important to adhere to the doctor’s instructions regarding the treatment and prevention of gynecological diseases to avoid potential complications.
- Paying attention to symptoms: It is important to pay attention to the emergence of pain, irregular changes in the menstrual cycle, and other symptoms in order to respond promptly and seek medical help.