Hyperaldosteronism: mechanism of development, diagnosis, and treatment
- Understanding Hyperaldosteronism
- Etiology of Hyperaldosteronism
- Clinical manifestations of Hyperaldosteronism
- Expert opinion on the treatment of Hyperaldosteronism
- Methods of diagnosing Hyperaldosteronism
- Methods of treating Hyperaldosteronism
- Prevention of Hyperaldosteronism
- Interesting aspects of Hyperaldosteronism
- FAQ
Understanding Hyperaldosteronism
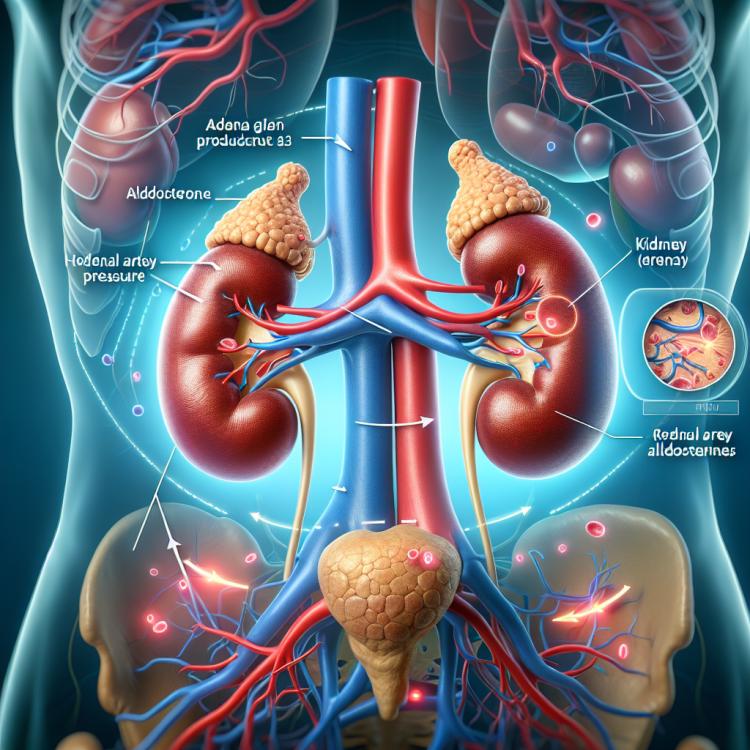
Hyperaldosteronism is a condition characterized by excessive secretion of aldosterone by the adrenal glands. The main causes of hyperaldosteronism may include adrenal adenomas, hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex, or in some cases, congenital genetic mutations. This can lead to the development of hypertension, dehydration, and other serious complications. Diagnosis is based on the analysis of aldosterone levels in plasma, a general clinical examination, and conducting educational tests for resistance to aldosterone. Treatment typically involves the use of drugs that block the action of aldosterone or surgical removal of a tumor to restore normal adrenal function.
Etiology of Hyperaldosteronism
Hyperaldosteronism is a pathological condition characterized by excessive secretion of aldosterone from the adrenal cortex. The manifestation of this condition can be caused by various reasons, including primary hyperaldosteronism and secondary hyperaldosteronism. Primary hyperaldosteronism is most often associated with adenoma, hyperplasia, or carcinoma of the adrenal cortex, while secondary hyperaldosteronism may be based on increased stimulation of aldosterone secretion due to conditions such as disorders of the renin-angiotensin system or hypokalemia.
- Adrenal cortex adenoma: One of the common triggering factors of primary hyperaldosteronism is the presence of an adrenal cortex adenoma.
- Adrenal cortex hyperplasia: An increase in the volume of adrenal cortex tissue may also contribute to excessive production of aldosterone and the development of hyperaldosteronism.
- Renin hyperproduction: Elevated levels of renin in the body can promote increased production of aldosterone, leading to hyperaldosteronism.
- Potassium deficiency in the body: Hypokalemia can be one of the causes of hyperaldosteronism, as aldosterone facilitates sodium reabsorption and potassium excretion in the urine.
- Excessive salt intake: Excessive salt in the diet can lead to an overproduction of aldosterone in the body, causing hyperaldosteronism.
Clinical manifestations of Hyperaldosteronism
Hyperaldosteronism can manifest with various clinical symptoms, including hypertension, headaches, weakness, muscle cramps, arrhythmias, hypokalemia, renal failure, and edema. The main symptoms associated with excessive activation of mineralocorticoid receptors are fluid retention in the body, elevated blood pressure, and potassium loss, which can lead to metabolic disorders. Patients with hyperaldosteronism may also experience neurological symptoms such as headaches, instability, drowsiness, and psychomotor agitation.
- Hypertension: high blood pressure is one of the main clinical signs of hyperaldosteronism.
- Headaches: patients often complain of frequent and intense headaches characteristic of hyperaldosteronism.
- Muscle cramps: due to potassium loss, muscle cramps and weakness may occur, which are typical symptoms of this condition.
- Heart rhythm disturbances: hyperaldosteronism can cause arrhythmias and other heart rhythm disturbances.
- Hypokalemia: low potassium levels in the blood can lead to various symptoms such as muscle weakness, arrhythmias, and fatigue.
Expert opinion on the treatment of Hyperaldosteronism
Experts in the field of endocrinology express the opinion on the necessity of an individualized approach to the treatment of Hyperaldosteronism, taking into account the characteristics of each clinical case. The main treatment methods include pharmacological correction using medications aimed at reducing the level of aldosterone or its action on the body, such as mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists.
Actual data and clinical studies also emphasize the significance of surgical treatment in cases of primary hyperaldosteronism, especially if an adrenal cortex adenoma is present. Expert opinion highlights the importance of regular monitoring of patients with Hyperaldosteronism and adjusting treatment based on the dynamics of clinical condition to achieve the best outcomes and prevent complications.

Methods of diagnosing Hyperaldosteronism
Diagnosis of Hyperaldosteronism typically includes laboratory and instrumental methods. One of the key tests for detecting Hyperaldosteronism is measuring the level of aldosterone in the blood, as well as renin, to determine the activity level of the renin-aldosterone system. Additional methods may include performing magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) to detect adrenal tumors or specialized tests for the differential diagnosis of primary and secondary Hyperaldosteronism.
- Measurement of aldosterone and renin levels in the blood: performing laboratory tests to assess the degree of activity of the renin-aldosterone system.
- Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA): an imaging method used to detect adrenal tumors or other changes in the structure of organs.
- Differential diagnostic tests: specialized procedures to distinguish between primary and secondary hyperaldosteronism.
- Salt restriction and licorice intake test: a method for identifying hyperaldosteronism based on changes in aldosterone levels after certain interventions.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and adrenal glands: the use of ultrasound diagnostics to visualize structural changes in organs and tumors.
Methods of treating Hyperaldosteronism
On the other hand, secondary Hyperaldosteronism, caused by other diseases or conditions, may require treatment of the underlying condition, such as treating hypertension or correcting electrolyte imbalances. In general, the treatment of Hyperaldosteronism should be individualized based on the underlying cause and the patient’s condition.
- Surgical intervention: In the case of primary Hyperaldosteronism caused by an adenoma or adrenal cortex hyperplasia, surgery to remove the tumor or affected tissue may be recommended.
- Drugs that block the release of aldosterone: In primary Hyperaldosteronism caused by adrenal hyperplasia, drugs that regulate aldosterone secretion may be used.
- Drugs acting on mineralocorticoid receptors: Such drugs, like spironolactone, may be used to affect mineralocorticoid receptors in primary Hyperaldosteronism.
- Treatment of the underlying condition: In cases of secondary Hyperaldosteronism related to other conditions, it is important to treat the underlying condition, such as hypertension or electrolyte imbalance.
- Individualized approach: Treatment of Hyperaldosteronism requires an individualized approach that takes into account the characteristics of each patient and the underlying causes of the disease.
Prevention of Hyperaldosteronism
- Healthy lifestyle: maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition, physical exercise, and avoiding harmful habits, can reduce the risk of developing Hyperaldosteronism.
- Blood pressure monitoring: regular monitoring of blood pressure and keeping it at a normal level are important components of preventing Hyperaldosteronism.
- Regular medical check-ups: it is recommended to undergo regular medical examinations to identify early signs of hypertension or other conditions that may contribute to the development of Hyperaldosteronism.
- Limiting sodium intake: reducing salt in the diet helps control blood pressure and may lower the risk of developing Hyperaldosteronism.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: controlling weight and preventing obesity contribute to reducing the risk of many diseases, including Hyperaldosteronism.