Hyperkeratosis of the nails: symptoms, causes, and treatment
- Understanding Nail Hyperkeratosis
- Factors contributing to the development of nail hyperkeratosis
- Main signs of nail hyperkeratosis
- Expert recommendations for the treatment of nail hyperkeratosis
- Methods for diagnosing nail hyperkeratosis
- Methods for treating nail hyperkeratosis
- Preventive measures against nail hyperkeratosis
- Amazing aspects of nail hyperkeratosis
- FAQ
Understanding Nail Hyperkeratosis
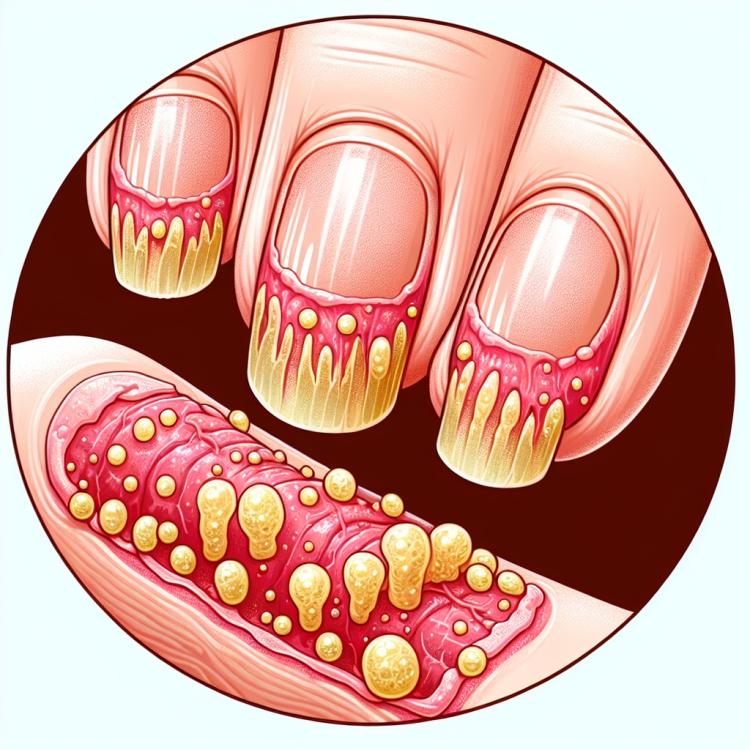
Hyperkeratosis of the nails is a pathological condition characterized by thickening of the nail plate due to excessive keratin production. This often occurs due to mechanical damage, chronic inflammation, or inadequate nail care. Nail hyperkeratosis may manifest as thickening, yellowing, splitting, or changes in nail shape, which can cause discomfort and aesthetic issues for patients.
Factors contributing to the development of nail hyperkeratosis
Nail hyperkeratosis can be caused by various factors, including mechanical injury to the nail plate, prolonged wearing of uncomfortable or tight shoes, as well as flat feet or other foot deformities that can increase pressure on the nail. Spinal or joint disorders, such as arthritis or gout, can also contribute to the development of nail hyperkeratosis. Circulatory disorders, diabetes, and other systemic diseases can negatively affect the condition of the nails and contribute to the occurrence of hyperkeratosis.
Determining the specific cause of nail hyperkeratosis requires a detailed medical examination of the patient. It is important to identify the underlying disease or factor responsible for this nail condition to provide the patient with the most effective and targeted treatment aimed at both eliminating the cause and alleviating the symptoms of nail hyperkeratosis.
- Mechanical trauma: Damage to the nail plate can cause hyperkeratosis.
- Uncomfortable shoes: Wearing tight or uncomfortable shoes can create pressure on the nail, contributing to the development of hyperkeratosis.
- Flat feet and other foot deformities: Foot deformities can lead to increased pressure on the nail plate, promoting hyperkeratosis.
- Spinal and joint pathologies: Joint diseases, such as arthritis and gout, can increase the risk of developing nail hyperkeratosis.
- Systemic diseases: For example, diabetes and circulatory disorders can negatively impact nail health, contributing to hyperkeratosis.
Main signs of nail hyperkeratosis
The main symptoms of nail hyperkeratosis may include thickening of the nail plate and changes in its shape, the appearance of white or yellowish spots on the surface of the nail, the formation of grooves and cracks. Patients often experience discomfort when wearing shoes due to increased nail thickness and structural changes, slowed nail growth, or increased brittleness.
Complications such as nail hypertrophy, onycholysis, ingrown nails, inflammation, or even infections may arise if nail hyperkeratosis is not monitored and treated. Given the importance of early diagnosis and timely intervention, it is essential to consult a doctor at the first signs of changes in nail condition for necessary examinations and optimal therapy selection.
- Thickening of the nail plate: it is possible that the nail plate becomes thicker and less elastic due to hyperkeratosis.
- Change in nail shape: nail hyperkeratosis can cause deformation of the nail plate, leading to changes in its shape and structure.
- Appearance of white or yellowish spots: distinct white or yellowish spots may appear on the surface of the nail as a result of hyperkeratosis.
- Formation of grooves and cracks: nail hyperkeratosis can trigger the appearance of vertical or horizontal grooves, as well as unhealthy cracks on the surface of the nail.
- Discomfort when wearing shoes: increased thickness of the nails, structural changes, and other signs of hyperkeratosis can cause discomfort and painful sensations when wearing shoes.
Expert recommendations for the treatment of nail hyperkeratosis
Experts in the fields of dermatology and pediatrics emphasize the importance of a comprehensive approach to the treatment of nail hyperkeratosis, including the elimination of the underlying trigger factor that led to the development of the condition. The main methods for treating nail hyperkeratosis are local procedures to soften, remove the thickened layer, and regular adherence to preventive measures.
Experts advise physicians to prescribe individual therapy regimens depending on the severity of the disease and associated factors. For example, in mild forms of nail hyperkeratosis, gentle keratolytics and moisturizing agents can be used, whereas in more serious cases, a combination of local treatment with systemic therapy may be required. A well-designed treatment plan, based on expert recommendations, contributes to effective control over the condition of the nails and the prevention of possible complications.

Methods for diagnosing nail hyperkeratosis
Diagnosis of nail hyperkeratosis typically begins with a visual inspection of the nail structure and assessment of thickness. The doctor may use tools such as a dermatoscope or microscope for a more detailed study of changes in the nail plate. Additional diagnostic methods may include laboratory tests to rule out other conditions, such as fungal infections or nail psoriasis, as well as radiography or other imaging studies to identify structural deformities of the feet and nail bed that may contribute to the development of nail hyperkeratosis.
Accurate diagnosis of nail hyperkeratosis is crucial for determining the optimal treatment plan. Consulting a qualified dermatologist or other specialist will help carry out all necessary diagnostic procedures, identify the underlying causes of nail hyperkeratosis, and prescribe targeted treatment.
- Visual inspection: The doctor conducts a careful examination of the nails, assessing their shape, thickness, presence of spots or deformities.
- Dermatoscopy: The use of a dermatoscope allows for magnification of the nail image for a more detailed study and identification of changes in their structure.
- Microscopy: This method allows for a closer examination of the condition of the nails and detection of pathological changes such as hyperkeratosis.
- Laboratory tests: Investigations of skin material from the nails can help identify fungal infections or other pathologies that may accompany hyperkeratosis.
- X-ray: Conducting X-rays of the feet and nail bed can help reveal structural deformities that may be associated with the development of nail hyperkeratosis.
Methods for treating nail hyperkeratosis
In more complex cases, when conservative methods do not lead to improvement or in the presence of serious nail deformities, surgical intervention may be necessary, such as the removal of part of the nail plate or correction of the deformity. In any case, it is important to consult a qualified specialist to determine the optimal treatment course and prevent possible complications.
- Conservative methods: Include the use of soft cushions to relieve pressure from the nail plates, shortening and correcting nails, using moisturizing creams and nail care products.
- Pharmacological treatment: Antibiotics or antifungal medications may be used to treat accompanying infections or inflammations.
- Surgical intervention: In complex cases with severe nail deformities, surgery may be necessary, such as partial removal of the nail plate or correction of the deformity.
- Physiotherapy: The use of physical methods, such as ultrasound therapy, to improve blood circulation and reduce nail thickness.
- Manicure and pedicure: Regular nail care, proper shortening, and professional procedures can help improve the condition of the nails in cases of hyperkeratosis.
Preventive measures against nail hyperkeratosis
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, weight control, and an active lifestyle can also contribute to strengthening the nails and preventing various deformities. Following recommendations for healthy nail care and regular consultations with a dermatologist can help maintain optimal nail condition and prevent the onset of hyperkeratosis.
- Regular nail care: includes proper trimming and shaping of the nail plates, regular use of moisturizing products to prevent dryness and dehydration.
- Avoiding injuries and pressure: nails should avoid injuries and pressure, which includes choosing comfortable and properly fitted shoes, as well as avoiding walking barefoot on rough surfaces.
- Regular medical check-ups: allow for timely detection of changes in the nails and taking necessary measures to prevent the development of hyperkeratosis.
- Healthy lifestyle: a balanced diet, weight control, and an active lifestyle contribute to strengthening the nails and preventing deformities.
- Following specialists’ recommendations: regular consultations with a dermatologist and adherence to nail care recommendations will help maintain their optimal condition and prevent the occurrence of hyperkeratosis.
Amazing aspects of nail hyperkeratosis
Another interesting fact is that preventive measures and regular nail care can be effective in preventing the development of nail hyperkeratosis or in minimizing its consequences. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition and foot care, also plays an important role in maintaining nail health and preventing possible complications associated with hyperkeratosis.