Hypertrophic rhinitis: symptoms, causes, and treatment
- Definition and characteristics of hypertrophic rhinitis
- Etiology of hypertrophic rhinitis
- The clinical picture of hypertrophic rhinitis
- Expert opinion on the treatment of hypertrophic rhinitis
- Methods for diagnosing hypertrophic rhinitis
- Methods of treating hypertrophic rhinitis
- Prevention of hypertrophic rhinitis
- Interesting aspects of hypertrophic rhinitis
- FAQ
Definition and characteristics of hypertrophic rhinitis
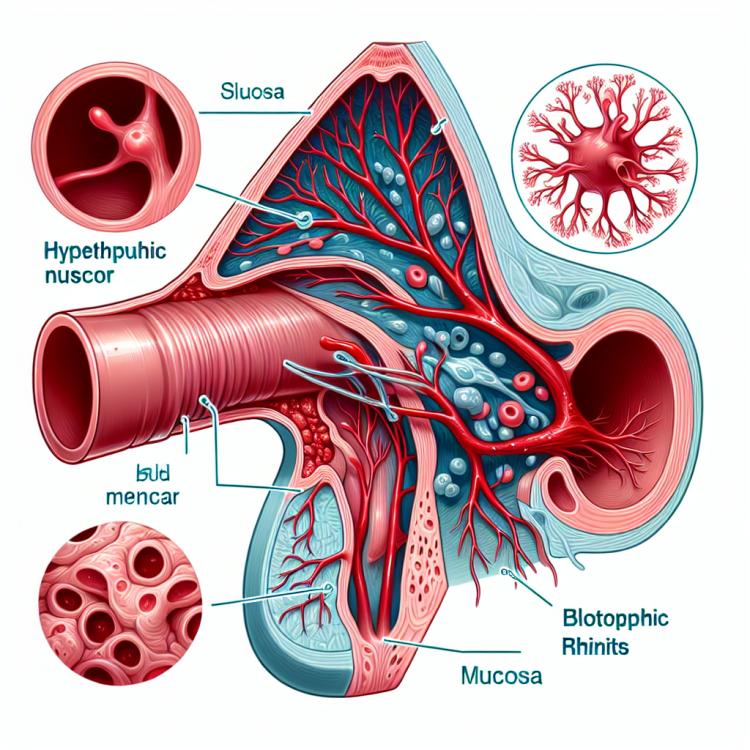
Hypertrophic rhinitis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the nasal mucosa, characterized by an increase in the volume and changes in the structure of the nasal turbinates. This condition is usually accompanied by nasal breathing impairment, difficulty in mucus clearance, and abundant mucous or mucopurulent discharge from the nose.
Hypertrophic rhinitis is caused by various factors such as chronic upper respiratory tract infections, allergic reactions, mechanical irritants, or immune system disorders. This condition is often associated with respiratory insufficiency, decreased sense of smell, and headaches. An important aspect of treating hypertrophic rhinitis is an individualized approach, which includes conservative methods and, sometimes, surgical intervention.
Etiology of hypertrophic rhinitis
Hypertrophic rhinitis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the nasal mucosa characterized by excessive tissue growth. The main causes of hypertrophy include recurrent inflammatory processes, allergic rhinitis, anomalies in the development of the nasal cavity, and hereditary factors. The intense growth of tissues, including vessels and glands, leads to noticeable changes in the structure of the mucosa and results in a number of characteristic symptoms, such as nasal congestion, persistent mucus discharge, and difficulty breathing through the nose.
Understanding the causes of hypertrophic rhinitis is an important aspect for effective treatment of this condition. Timely diagnosis and identification of the underlying factor contributing to the mucosal hypertrophy allows for targeted treatment aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease and alleviating symptoms in the patient.
- Recurring inflammatory processes: Frequent infections of the upper respiratory tract can contribute to the development of hypertrophy of the nasal mucosa.
- Allergic rhinitis: A constant allergic reaction to certain allergens can lead to excessive tissue growth in the nose.
- Anomalies of nasal cavity development: Structural deviations or issues with the shape of the nasal sinuses can contribute to mucosal hypertrophy.
- Hereditary factors: Genetic predispositions may play a role in the development of hypertrophic rhinitis in some individuals.
- Tobacco and other harmful substances: Prolonged exposure to tobacco smoke or other irritating substances on the nasal mucosa can lead to its hypertrophy.
The clinical picture of hypertrophic rhinitis
Hypertrophic rhinitis is characterized by symptoms related to specific changes in the nasal cavity. Patients often complain of persistent nasal congestion, difficulty breathing through the nose, excessive mucous discharge, and a constant feeling of inadequate ventilation. Increased secretory function of the mucous membrane and tissue hypertrophy lead to abundant nasal discharge, swelling, and discomfort. Patients may also experience frequent night awakenings due to difficulty breathing and sleep disturbances.
Additionally, hypertrophic rhinitis may be accompanied by headaches, dizziness, and a reduced sense of smell, as well as, due to disrupted normal nasal function, the occurrence of swellings, sinusitis, and other complications. Patients with such symptoms usually consult an otolaryngologist for the diagnosis and treatment of hypertrophic rhinitis.
- Constant nasal congestion: patients feel a persistent obstruction of breathing through the nose due to tissue hypertrophy.
- Excessive mucous discharge: characterized by abundant mucus secretion from the nose as a reaction to inflammatory processes.
- Sleep disturbances: nighttime awakenings due to breathing difficulties and discomfort may accompany hypertrophic rhinitis.
- Dizziness and headaches: occur due to disruptions in normal ventilation through the nose and brain oxygenation.
- Reduced sense of smell: due to damage to the nasal afferent nerves and dysfunction of the olfactory system.
Expert opinion on the treatment of hypertrophic rhinitis
Medical experts believe that the treatment of hypertrophic rhinitis should be comprehensive and individualized based on the specifics of each particular case. The main methods of treating this condition include conservative therapy, surgical interventions, and symptomatic treatment to alleviate the patient’s condition. Experts emphasize the need for proper diagnosis to determine the most effective treatment methods and prevent possible complications.
Specialists also note the importance of preventive measures, such as avoiding exposure to irritants, maintaining optimal humidity in the room, and regular ventilation. Regular consultations with a doctor and correctly following specialists’ recommendations are key aspects of successful treatment of hypertrophic rhinitis, according to experts in the field of otolaryngology.

Methods for diagnosing hypertrophic rhinitis
The diagnosis of hypertrophic rhinitis includes a visual examination of the nasal cavity using rhinoscopy or rhinofibroscopy, which allows for the determination of the degree of mucosal hypertrophy and the identification of other pathological changes. Computed tomography of the nose may also be applied for a more detailed visualization of the nasal cavity structures, which helps to clarify the diagnosis and prepare a treatment plan.
Laboratory studies, such as blood tests, allergy tests, and bacteriological smears, can help exclude other causes of chronic nasal discharge and identify factors contributing to the development of mucosal hypertrophy. The diagnosis of hypertrophic rhinitis is closely related to determining the cause of the disease, which allows for the appointment of effective treatment and the prevention of possible complications.
- **Visual examination:** Conducting rhinoscopy and rhinoscopy to assess the condition of the mucous membrane.
- **Computed tomography:** Using CT scanning for more detailed visualization of the nasal cavity and surrounding tissues.
- **Laboratory studies:** Including blood tests, allergy tests, and bacteriological swabs for additional diagnosis and identification of possible concomitant pathologies.
- **Allergy tests:** Allow for the identification of allergens that may provoke hypertrophic rhinitis or exacerbate its manifestations.
- **Instrumental studies:** Including radiological studies, spirometry, and other methods to assess the functional state of the respiratory tract.
Methods of treating hypertrophic rhinitis
In addition, the use of physiotherapeutic procedures, such as nasal rinsing with saline solutions or ultraviolet irradiation of the mucous membrane, may also be recommended as part of the comprehensive treatment of hypertrophic rhinitis. It is important to individualize the treatment approach for each patient, taking into account the characteristics of their condition and the course of the disease, in order to achieve the best results and reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Medication treatment: Includes the use of nasal decongestant drops, steroid medications, and antihistamines to reduce swelling and inflammation.
- Surgical methods: In cases where conservative treatment is ineffective, surgical intervention such as turbinate reduction or turbinectomy may be required.
- Physiotherapy: Use of physiotherapeutic procedures, including nasal irrigation with saline solutions and ultraviolet irradiation of the mucous membrane.
- Immunotherapy: In rare cases, immunotherapy may be applied to reduce allergic manifestations that contribute to the development of hypertrophic rhinitis.
- Individualized approach: It is important to consider the characteristics of each patient to develop an optimal treatment plan that will ensure the best outcomes and reduce the risk of disease recurrence.
Prevention of hypertrophic rhinitis
Special attention should be paid to preventing recurrent upper respiratory infections and strengthening the body’s immunity. Following the doctor’s recommendations for chronic upper respiratory diseases, regular check-ups with a specialist, and timely treatment of nasopharyngeal diseases will help reduce the likelihood of developing hypertrophic rhinitis and maintain the health of the nasal passages.
- Maintaining humidity in the room: it is recommended to use humidifiers to prevent the drying out of the nasal mucosa.
- Avoiding contact with allergens: identifying and avoiding allergens that can trigger rhinitis, including pollen, fibers, and household dust.
- Regular ventilation of the room: regular ventilation helps to prevent the accumulation of dust and other allergens in the air.
- Caring for the mucous membrane: using saline solutions for nasal irrigation and special moisturizing nasal drops helps maintain the health of the mucous membrane.
- Selecting nasal hygiene products: using gentle cleaning products for the nose, such as saline or isotonic solutions, helps maintain the normal functioning of the nasal passages.
Interesting aspects of hypertrophic rhinitis
Another interesting aspect of hypertrophic rhinitis is its impact on the quality of life of patients. Chronic symptoms such as difficulty breathing, constant mucus discharge, and impaired sense of smell can significantly affect the overall well-being and physical activity of patients. Therefore, the development of effective treatment and prevention methods for hypertrophic rhinitis is crucial for improving the quality of life of patients.