Purulent otitis: symptoms, causes, and treatment methods
- Understanding purulent otitis
- Pathogenesis of purulent otitis
- The main signs of purulent otitis media
- Vision of specialists in the treatment of Purulent Otitis
- Methods for diagnosing purulent otitis.
- Basics of treating purulent otitis media
- Prevention measures for purulent otitis media
- Funny aspects of purulent otitis.
- FAQ
Understanding purulent otitis
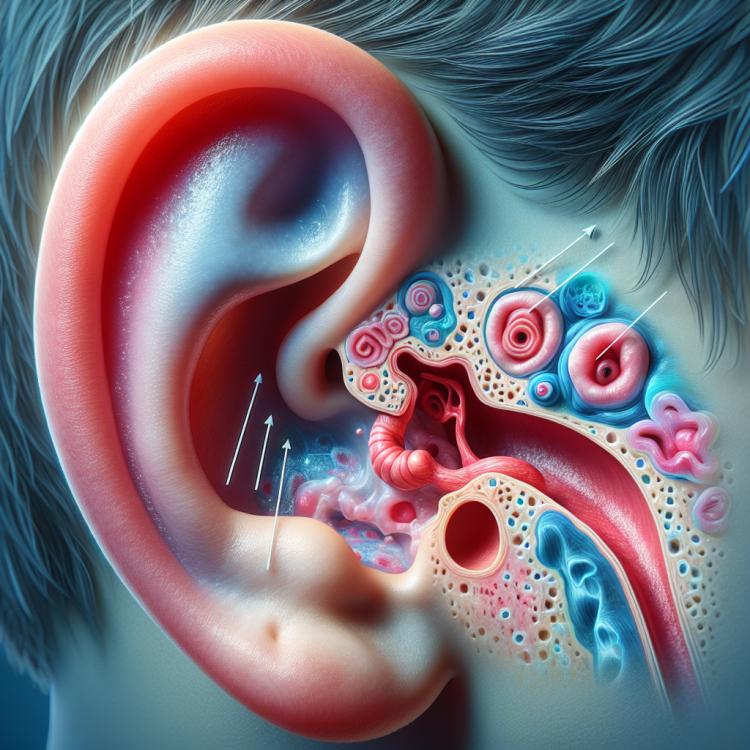
Purulent otitis is an inflammatory disease of the middle ear, usually caused by a bacterial infection. Microorganisms such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis are often responsible for purulent otitis. This process can lead to the accumulation of purulent fluid in the ear, causing pain, discomfort, and reduced hearing.
Understanding purulent otitis is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment of this condition. The absence of adequate therapy can lead to complications such as damage to the tympanic membrane, chronic purulent otitis, or even hearing loss. It is important to seek medical attention at the first signs of the disease to avoid possible complications and ensure effective treatment of purulent otitis.
Pathogenesis of purulent otitis
The pathogenesis of purulent otitis is associated with inflammation of the mucous membrane of the middle ear, most often caused by a bacterial infection. The mechanism of development is related to a disruption of the drainage function of the Eustachian tube, which creates conditions for the multiplication of pathogenic microorganisms in the ear. Increased pressure in the ear cavity, disruption of circulation and diffusion of substances may contribute to the formation of pus and the development of characteristic symptoms of the disease.
- Inflammation of the middle ear mucosa: bacterial infections can cause inflammation by stimulating the body’s immune response.
- Disruption of the drainage function of the auditory tube: difficulty in draining fluid from the ear can contribute to the development of purulent otitis.
- Conditions for the reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms: a moist environment in the ear and the presence of microtraumas create favorable conditions for the multiplication of bacteria.
- Disruption of circulation and diffusion of substances: this can affect oxygen supply and metabolism in the tissues of the ear, promoting inflammation.
- Increased pressure in the ear cavity: can cause pain and discomfort, as well as contribute to the formation of pus in the ear cavity.
The main signs of purulent otitis media
The main symptoms of purulent otitis include ear pain, a feeling of pressure inside the ear, discharge of pus from the ear canal, and hearing loss. Upon examination of the auricle, redness and swelling of the mucous membrane may be observed, sometimes with visible layers of pus. Patients may also experience discomfort, a feeling of fullness in the ear, and sometimes an elevated body temperature in cases of bacterial infection.
- Ear pain: Otitis media often comes with sharp ear pain that can worsen when touching the ear.
- Pressure inside the ear: Patients may feel discomfort and pressure in the ear due to the presence of pus and inflammation, which can cause unpleasant sensations.
- Pus discharge: A characteristic symptom is the discharge of pus from the ear canal, indicating an infectious process in the ear.
- Hearing impairment: Infection and inflammation in the ear can lead to temporary or partial hearing loss, which becomes noticeable to the patient.
- Redness and swelling of the mucous membrane: Upon examining the auricle, redness and swelling of the mucosa may be observed, indicating an inflammatory process.
Vision of specialists in the treatment of Purulent Otitis
Experts in the field of otolaryngology emphasize the importance of an individual approach to the treatment of purulent otitis media depending on the severity of the disease and the patient’s characteristics, such as age, overall health, and the presence of comorbidities. Basic treatment methods include the use of antibiotics to combat the infection, as well as analgesics to relieve pain syndrome.
However, modern studies in the treatment of purulent otitis media also highlight the role of a comprehensive approach, including physiotherapy, ear cavity cleansing procedures, and in some cases, the need for surgical intervention. Experts also emphasize the importance of monitoring the patient during treatment and subsequent observation of ear conditions to prevent possible complications and disease recurrences.

Methods for diagnosing purulent otitis.
Diagnosis of purulent otitis usually involves an examination by an otolaryngologist, who may identify signs of inflammation in the ear canal. Additional diagnostic methods may include audiometry to assess hearing, and otoscopy may be used for a more detailed examination of the condition of the auricle and the tympanic membrane.
Laboratory tests, such as an analysis of ear discharge for sensitivity to antibiotics, can help doctors choose the most effective treatment. X-rays and computed tomography of ear structures may be used to assess the spread of infection and to rule out complications such as destruction of the middle ear bones.
- ENT doctor examination: visual inspection of the auricle and ear canal for signs of inflammation.
- Audiometry: hearing testing using sound stimuli to assess air and bone conduction of sound.
- Otoscopia: performing a more detailed examination of the auricle and eardrum with the use of a special instrument.
- Fluid analysis: laboratory examination of ear discharge to determine sensitivity to antibiotics.
- X-ray and computed tomography: imaging methods used to assess the condition of ear structures and identify possible complications regarding the destruction of the middle ear bones.
Basics of treating purulent otitis media
In cases where conservative treatment does not yield the expected effect, surgical intervention may be required. The removal of drainage and the drainage of the tympanic membrane may be necessary in cases of chronic purulent otitis or in the presence of complications. It is important to choose the treatment method individually, taking into account the features of each clinical case and potential complications.
- Use of antibiotics: Antibiotics are usually used to combat the bacterial infection causing purulent otitis.
- Use of pain relievers: The use of pain relievers helps reduce pain and discomfort in the ear with purulent otitis.
- Proper instillation of medications: It is important to properly instill medications into the ear to ensure their effective action.
- Following the doctor’s recommendations for ear care: Medical advice on ear cleaning and general ear care helps manage purulent otitis.
- Individual approach to treatment: Treatment of purulent otitis should be tailored to the specifics of each clinical case and consider possible complications.
Prevention measures for purulent otitis media
For individuals at increased risk of developing middle ear infections, especially children, it is important to minimize contact with those suffering from respiratory infections, as they can contribute to the development of acute purulent otitis media. Regular medical check-ups and timely treatment of any upper respiratory infections can also help prevent acute purulent otitis media.
- Ear hygiene compliance: regular and gentle cleaning of the ears can help prevent the accumulation of microorganisms and inflammatory processes.
- Avoiding ear trauma: take measures to avoid damage to the auricle, such as improper use of chemical ear cleaning agents or external injuries.
- Minimizing contact with contaminated water: preferably avoid swimming in polluted bodies of water, especially in cold weather, to reduce the risk of ear infections.
- Timely treatment of respiratory infections: promptly seeking medical attention at the first signs of upper respiratory tract infection can help prevent the development of acute purulent otitis media.
- Visiting a doctor for regular check-ups: regular medical examinations can help identify pathologies of the temporal bone in a timely manner and prevent complications related to purulent otitis media.