Symptoms, causes, and treatment of nail fungus
- Understanding Nail Fungus: Key Aspects
- Etiology of nail fungal infection
- Clinical picture of nail fungal infection
- Expert opinion on treating nail fungus
- Methods for diagnosing nail fungal infection
- Methods for treating nail fungal infections
- Measures to prevent nail fungal infections
- Intriguing aspects of nail fungal infections
- FAQ
Understanding Nail Fungus: Key Aspects
Nail fungus, or onychomycosis, is an infectious disease that affects the nail plate and surrounding tissues, caused by fungi. It manifests as changes in the color, shape, and texture of the nails, and may also be accompanied by itching and pain. Fungal infections of the nails are most commonly found on the toenails, but can also affect the nails on the hands. An important aspect of treating nail fungus is early consultation with a doctor to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment aimed at eliminating the fungal infection and restoring nail health.
Etiology of nail fungal infection
Nail fungal infection, or onychomycosis, is usually caused by dermatophytes, yeast-like fungi, or mold. These pathogens enter under the nail plate through microtrauma or by contact with infected objects. Risk factors include tight footwear, increased humidity, and circulatory disorders, creating ideal conditions for the development of infection.
- Dermatophytes: fungi of this type most often cause fungal nail infections by entering microtraumas on the skin.
- Yeast-like fungi: the second most common type of pathogens that can cause onychomycosis, often thrive in high humidity conditions.
- Mold: as the third type of pathogens, can cause nail infections, especially through contact with contaminated objects.
- Tight shoes: create a warm and humid environment that is favorable for the development of fungal nail infections.
- Microtraumas: small injuries to the nail plate can serve as entry points for pathogens, promoting their manifestation.
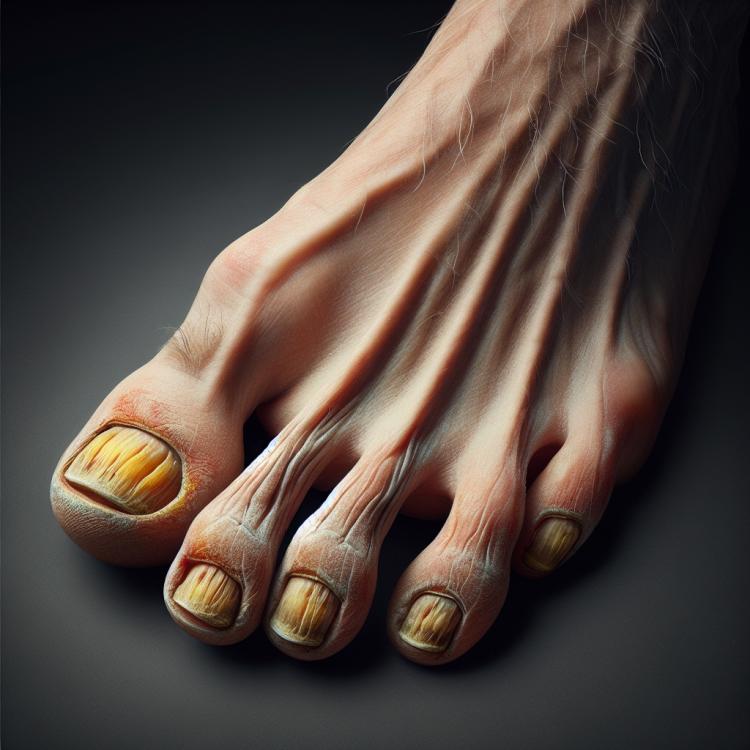
Clinical picture of nail fungal infection
Fungal nail infection manifests as changes in the nail plate, including yellowing, thickening, brittleness, and flaking. Sinusitis and destruction of the nail plate may be observed underneath the nail. Symptoms may be accompanied by itching, pain, and an unpleasant odor.
It is important to note that the infection can spread to neighboring nails, causing their damage. Prolonged progression of the disease can lead to serious changes in the nail plate and even functional impairments. Timely detection of nail fungus symptoms requires competent treatment to prevent complications and restore nail health.
- Yellowish color of nails: infection can cause a change in nail color to a yellowish shade.
- Thickness and deformation of the nail plate: affected nails may become thicker, bent, and lose their natural shape.
- Brittleness and splitting of nails: the nail plate becomes brittle and may start to split.
- Appearance of abscesses under the nail: disturbances in the nail bed can lead to the formation of pus collections.
- Itching, tenderness, and unpleasant odor: infection may be accompanied by itching, discomfort, and an unpleasant smell.
Expert opinion on treating nail fungus
Experts’ opinions on the treatment of nail fungal infections emphasize the importance of a comprehensive approach. Effective treatment may include antifungal medications for systemic therapy, as well as localized treatment using special nail preparations. Experts recommend taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient, the degree of nail damage, and potential complications when choosing treatment methods.
Modern methods of treating nail fungus include procedures such as laser removal of the infection or chemical treatment to eliminate fungi. Experts also highlight the importance of adhering to hygiene recommendations and preventing recurrences after successful treatment. Careful monitoring by specialists and following recommendations will help patients effectively overcome this infection.

Methods for diagnosing nail fungal infection
To diagnose a fungal nail infection, the doctor may examine the nails, paying attention to the nature of the changes in the nail plate. Additional methods such as microscopy of nail material and culture tests can help identify the pathogen and confirm the presence of infection. Other diagnostic methods include dermatoscopy and laboratory tests to detect mycoses.
It is important to note that accurate diagnosis of fungal nail infections is essential for determining the best treatment approach. Doctors at specialized dermatological centers have the necessary skills and equipment to perform precise diagnoses and prescribe appropriate therapy.
- Nail examination: the doctor conducts a visual examination of the nails, paying attention to the nature of changes in the nail plate.
- Microscopy of nail material: analysis under a microscope helps to identify fungal structures and confirm the presence of infection.
- Cultural studies: growing fungi on nutrient media allows for the identification of the pathogen and determination of its sensitivity to medications.
- Dermatoscopy: a method of examining the nails using a dermatoscope for detailed study of changes in the nail plate.
- Laboratory tests: blood tests and analyses of nail material may be conducted to identify the presence of fungi or other pathogens.
Methods for treating nail fungal infections
The principle of the approach to treating nail fungal infections is to eliminate the pathogen and restore the health of the nail plate. A combined approach, which includes the use of antifungals, regular nail care, and strict sanitation, provides the best results in combating this ailment.
- Topical medications: Include cuticle lacquers and creams for application on affected nails.
- Systemic antifungals: Used in cases of advanced infection or when multiple nails are affected.
- Surgical removal of affected tissue: Used in cases of prolonged infection when other methods are ineffective.
- Laser therapy: Is gaining popularity due to its effectiveness in destroying fungi without side effects.
- Combined approach: Involves the use of several treatment methods simultaneously for the best results.
Measures to prevent nail fungal infections
Other important preventive measures include using individual nail scissors and regularly trimming nails to prevent the accumulation of microorganisms under the nails. Remember that maintaining overall immunity and a healthy lifestyle also contributes to strengthening the body’s defense mechanisms against nail fungal infections.
- Nail hygiene: Wash your feet daily, especially between the toes, and dry them thoroughly after washing to prevent the development of fungal infections.
- Wearing appropriate footwear: Prefer shoes made of breathable materials to prevent excessive sweating and the creation of a moist environment favorable for fungal growth.
- Avoiding injuries: Avoid nail damage by trimming them carefully and avoiding contact with contaminated surfaces to prevent the entry of infection agents.
- Individual nail scissors: Use separate tools for nail care to prevent the spread of agents between nails and reduce the risk of infection.
- Maintaining overall health: Lead a healthy lifestyle, support your immune system, and eat a balanced diet to strengthen the body’s defenses against fungal infections.
Intriguing aspects of nail fungal infections
Another interesting aspect is the ability of nail fungal infection to spread to adjacent nails or even to other areas of the skin. This makes treatment as well as prevention of this disease important, in order to prevent its further spread and possible complications. All these aspects underscore the importance of diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nail fungal infection to maintain the health of the nail plate and prevent potential complications.