Chondrocalcinosis: features of diagnosis and treatment methods
- Definition and causes of Chondrocalcinosis
- Etiology of Chondrocalcinosis
- The clinical picture of Chondrocalcinosis
- Opinions of specialists on the treatment of Chondrocalcinosis
- Methods of diagnosing Chondrocalcinosis
- Methods of treating Chondrocalcinosis
- Measures for the prevention of Chondrocalcinosis
- Amazing aspects of Chondrocalcinosis
- FAQ
Definition and causes of Chondrocalcinosis
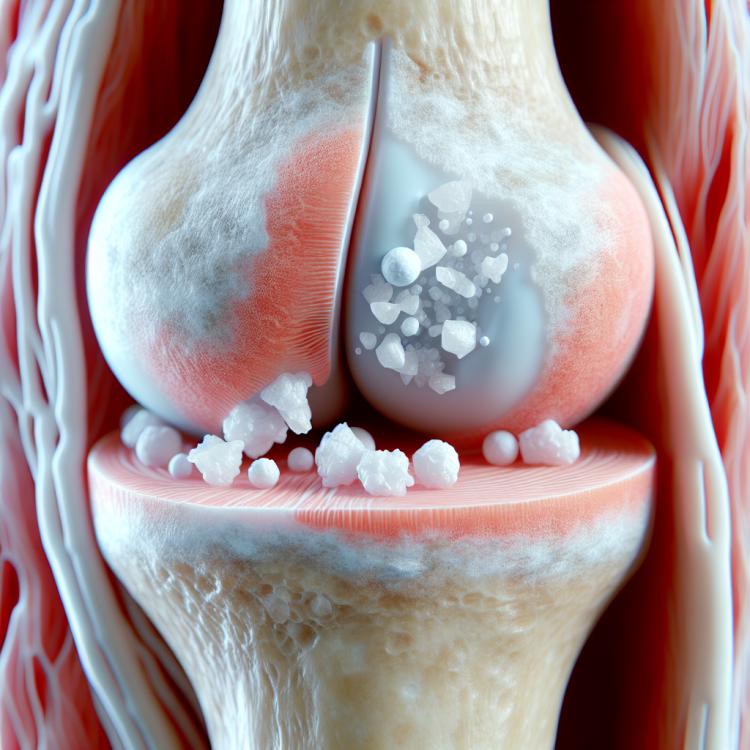
Chondrocalcinosis, also known as pseudogout, is a condition characterized by the deposition of calcium crystals in the joint cartilage, leading to inflammation and destruction of the joints. The causes of this disorder are mainly related to genetic factors, as well as metabolism, resulting in an increased calcium content in the body. As a result, the deposition of calcium crystals in the joints reduces their mobility, causing characteristic painful symptoms that may progress over time.
Etiology of Chondrocalcinosis
Chondrocalcinosis, also known as pseudogout, occurs due to the deposition of calcium pyrophosphate crystals in the cartilage tissue of the joints. This happens as a result of impaired metabolism and calcium metabolism in the body, which predisposes the formation of crystals and subsequent inflammation of the joints.
In addition to metabolic disorders, genetic predisposition also plays a significant role in the development of Chondrocalcinosis. Hereditary factors can influence the rate of crystal formation in the cartilage, which increases the risk of developing this condition. A comprehensive understanding of the etiology of Chondrocalcinosis not only contributes to more effective treatment but also opens up prospects for preventing the onset of this pathological process.
- Calcium crystal deposition: The formation of calcium pyrophosphate crystals in the cartilage tissue of joints is the primary factor leading to the development of Chondrocalcinosis.
- Metabolic disorders: Malfunctions in metabolism and calcium metabolism lead to the accumulation of crystals and inflammation of the joints.
- Genetic predisposition: Hereditary factors may increase the tendency to form crystals in cartilage, raising the risk of developing Chondrocalcinosis.
- Excessive calcium intake: Increased calcium intake through food or medications can contribute to the formation of crystals in the joints.
- Age and sex: Chondrocalcinosis is more commonly found in elderly people and men, which is associated with age-related and hormonal changes in the body.
The clinical picture of Chondrocalcinosis
Chondrocalcinosis usually manifests with symptoms related to joint inflammation, such as swelling, pain, redness, and limited mobility. Patients may also experience joint effusion and increased temperature in the area of the affected joints due to the inflammatory response.
Additional symptoms of Chondrocalcinosis include the formation of calcium deposits under the skin, which can lead to the development of characteristic nodules called gouty nodules. Patients may also experience episodes of acute pain in the joints, exacerbated by physical activity or changes in weather, which decreases quality of life and requires timely treatment.
- Joint symptoms: symptoms of Chondrocalcinosis typically include swelling, pain, redness, and limited mobility of the affected joints.
- Joint effusion: there is an accumulation of fluid in the joints, which is one of the characteristic signs of the disease.
- Calcium deposits: the formation of calcium deposits under the skin may lead to the appearance of knobby formations in the joint areas.
- Acute pain: patients may experience episodes of acute joint pain, especially during physical activity or with changes in weather.
- Increase in temperature: the area of the affected joints may become warmer due to the inflammatory response, which is accompanied by discomfort and pain.
Opinions of specialists on the treatment of Chondrocalcinosis
Experts in the fields of rheumatology and orthopedics highlight several key principles in the treatment of Chondrocalcinosis. One of the main aspects is pain management, which includes the use of anti-inflammatory drugs and pain relievers. Another important aspect is rehabilitation and physiotherapy to improve joint mobility, reduce inflammation, and prevent further cartilage destruction.
Experts also emphasize the significance of an individualized approach for each patient with Chondrocalcinosis, taking into account the specifics of the disease, the degree of joint involvement, the presence of complications, and comorbid conditions. The selection of optimal therapy, based on evidence-based methods and the latest scientific research, plays a crucial role in the successful treatment and improvement of the quality of life for patients with Chondrocalcinosis.

Methods of diagnosing Chondrocalcinosis
Diagnosis of Chondrocalcinosis includes a clinical examination of the patient with an assessment of symptoms and complaints characteristic of this disease. An important element of the diagnosis is the conduct of radiological studies, such as X-ray or MRI of the joints, to identify the presence of calcium deposits in the cartilage and joint tissues. Additionally, laboratory analysis of synovial fluid may be performed to determine the presence of calcium crystals, which confirms the diagnosis of Chondrocalcinosis.
For a complete diagnosis and selection of the optimal treatment strategy, more specialized studies, such as synovial biopsy or analysis of joint tissue for the presence of crystals, may also be required. A comprehensive approach to the diagnosis of Chondrocalcinosis, including clinical, radiological, and laboratory studies, allows for accurate identification of this pathology and the development of an individualized treatment plan.
- Clinical examination: the doctor analyzes the symptoms, examines the affected joints, and identifies characteristic signs of the disease.
- X-ray: conducting an X-ray examination to detect calcium deposits in the cartilage and joint tissues.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): a specialized study that allows for a more detailed examination of the structure and condition of the joints.
- Laboratory analysis of joint fluid: studying the synovial fluid of the joints for the presence of calcium crystals, which confirms the diagnosis of Chondrocalcinosis.
- Synovial biopsy: an invasive method that allows for obtaining a sample of joint tissue for further investigation of the presence of crystals and morphological changes.
Methods of treating Chondrocalcinosis
Additionally, physiotherapeutic procedures such as stretching and muscle-strengthening exercises may be prescribed to enhance joint mobility and improve the overall condition of the patient. In some cases, surgical intervention may be required to remove calcium deposits or repair damaged tissues, especially in the presence of complications such as severe joint deformities or intense pain that is not alleviated by conservative treatment methods.
- Drug therapy: The use of anti-inflammatory and pain relief medications to reduce inflammation and pain in the joints.
- Physical therapy: Stretching and muscle strengthening exercises to enhance joint mobility and improve the overall condition of the patient.
- Diet and lifestyle: Recommendations for dietary and lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of crystal formation and improve metabolism.
- Surgical treatment: In cases of complications or ineffectiveness of conservative methods, surgical intervention may be needed to remove calcium deposits or restore damaged tissues.
- S symptomatic treatment: The use of medications to alleviate pain, improve joint function, and enhance the overall well-being of patients at various stages of Chondrocalcinosis treatment.
Measures for the prevention of Chondrocalcinosis
Regular medical examinations and following the doctor’s recommendations can also help in the early detection of possible symptoms or risks associated with Chondrocalcinosis and the timely initiation of treatment. It is important to follow the specialists’ recommendations and lead a healthy lifestyle to prevent Chondrocalcinosis and maintain joint health.
-
– Monitor your weight and strive to maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on the joints and lower the risk of developing Chondrocalcinosis.
– Maintain an active lifestyle with regular physical exercise, as physical activity helps strengthen muscles and joints, which can help prevent the onset of pathologies.
– Eat a balanced diet, including foods rich in calcium and vitamins, which helps maintain joint health and strengthen cartilage.
– Avoid excessive consumption of alcohol and foods rich in purines, as this can contribute to the formation of calcium crystals in the joints.
– Undergo regular medical check-ups to identify possible metabolic disorders and to start treatment early if the first signs of Chondrocalcinosis appear.
Amazing aspects of Chondrocalcinosis
Another interesting aspect of Chondrocalcinosis is that hereditary factors may play a significant role in the development of this condition. Some genetic factors may increase the tendency to form calcium deposits in the joints, underscoring the importance of studying heredity when analyzing the risks of developing Chondrocalcinosis in individual patients.