Chronic prostatitis: causes, symptoms, and treatment methods
- Definition and causes of chronic prostatitis
- Etiology of chronic prostatitis
- The clinical picture of chronic prostatitis
- Expert opinion on treatment methods for chronic prostatitis
- Methods of diagnosing chronic prostatitis
- Methods for treating chronic prostatitis
- Measures for the prevention of chronic prostatitis
- Amazing facts about chronic prostatitis
- FAQ
Definition and causes of chronic prostatitis
Chronic prostatitis is an inflammatory disease of the prostate gland, characterized by a prolonged course and possible exacerbations. The main causes of chronic prostatitis may include bacterial infections, inadequate treatment of acute prostatitis, as well as damage or abnormalities of the prostate gland.
The pathogenesis of chronic prostatitis is quite complex and involves various factors, such as immune disorders, impaired microcirculation in the tissues of the prostate gland, endocrine system abnormalities, and more. It is important to consider both biological and psychological aspects when studying this pathological condition in order to develop effective approaches to treatment and prevention.
Etiology of chronic prostatitis
Chronic prostatitis is an inflammatory disease of the prostate gland characterized by a long-term and recurrent course. The causes of chronic prostatitis can be numerous and range from infectious agents such as bacteria or viruses to other factors such as autoimmune reactions, structural abnormalities of the prostate, or disturbances in the organ’s blood circulation. The underlying mechanisms leading to the development of chronic prostatitis require further research for a deeper understanding of this condition and the development of effective treatment methods.
- Infectious agents: bacteria, viruses, or fungi can cause inflammation in the prostate gland.
- Autoimmune reactions: uncontrolled immune responses can contribute to the development of chronic prostatitis.
- Anomalies in the structure of the prostate gland: changes in the anatomy of the organ can lead to chronic inflammation.
- Circulatory disorders: poor circulation can hinder the delivery of immune cells to the site of infection.
- Tissue damage: injuries or damage to the prostate gland can promote the development of chronic prostatitis.
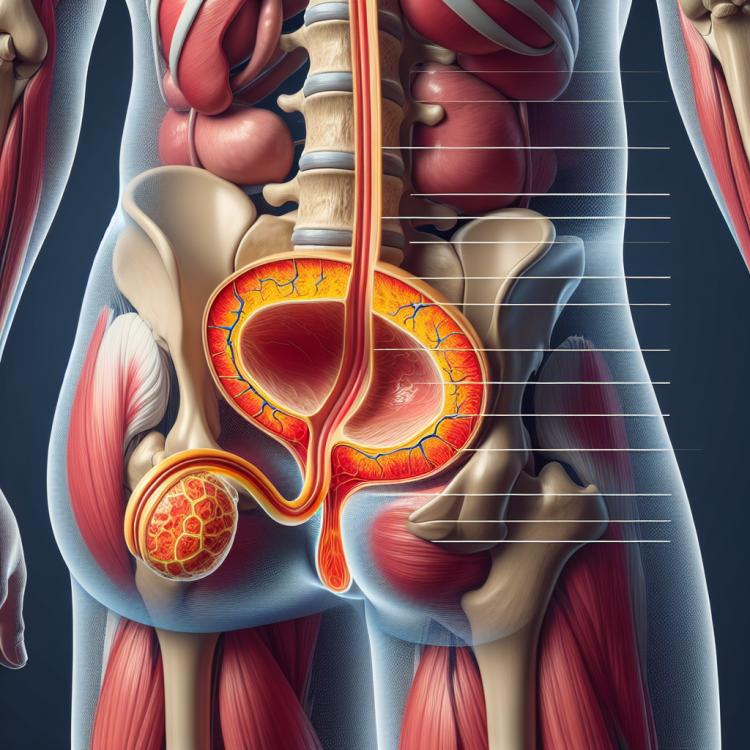
The clinical picture of chronic prostatitis
The clinical picture of chronic prostatitis can be diverse and include symptoms such as pain in the perianal area, urination, and sexual arousal. Patients may also experience frequent and painful urogenital disorders, including dysuric symptoms such as anxiety during urination and urinary stream instability. Moreover, chronic prostatitis can lead to erectile dysfunction and sexual function issues, affecting the overall quality of life of the patient.
- Pain in the perianal area: a feeling of discomfort and pain in the area of the rectum and sacral region.
- Dysuric symptoms: possible discomfort and pain during urination, as well as changes in the stream of urine.
- Sexual arousal: increased libido and possible changes in sexual function.
- Erectile disorders: potential problems with erection, which may negatively impact the quality of the patient’s sex life.
- Urogenital disorders: frequent and painful issues in the area of urination and genital organs, caused by inflammatory processes in the prostate.
Expert opinion on treatment methods for chronic prostatitis
It is known that methods for treating chronic prostatitis provoke discussions among experts in the field of urology. Some specialists emphasize the importance of antibiotics to eliminate the infection that may be the cause of the disease. Other experts focus on physiotherapeutic methods and prostate massage to improve blood flow and reduce inflammation.
However, all experts acknowledge the importance of an individual approach to each patient and combined treatment, which may include both medications and physical therapy. Regular consultations with a doctor and adjustments to treatment measures depending on changes in the patient’s condition are important aspects of effective management of chronic prostatitis.

Methods of diagnosing chronic prostatitis
The diagnosis of chronic prostatitis includes a number of methods aimed at determining the presence of an inflammatory process in the prostate gland. This process may involve a urine test for bacterial infections, a semen analysis, and a digital rectal exam to assess the condition of the prostate gland. Additionally, the doctor may prescribe an ultrasound of the pelvic organs to visualize changes in the prostate gland and identify possible tumors or other pathologies.
- Urine analysis: a laboratory urine analysis helps to detect the presence of bacteria and other infections in the urinary tract.
- Semen analysis: a semen examination can reveal inflammatory processes and disorders in the seminal fluid.
- Digital rectal examination: allows the doctor to assess the size, shape, and texture of the prostate gland through the rectum via a finger.
- Ultrasound examination: is performed to visualize the structure of the prostate gland and identify changes in the organ’s tissues.
- Prostate massage: a special massage helps to obtain prostate secretions for analysis and assess the degree of inflammation.
Methods for treating chronic prostatitis
- Antibiotics: In bacterial chronic prostatitis, antibiotics are often used to eradicate the cause of inflammation.
- Anti-inflammatory medications: Used to relieve inflammation and reduce pain associated with prostatitis.
- Physical therapy: Includes various methods such as ultrasound therapy and heat treatments aimed at improving blood circulation and alleviating prostatitis symptoms.
- Prostate massage: Massage can help improve microcirculation, reduce spasms, and enhance the drainage of secretions.
- Surgical treatment: In rare cases, surgery may be required, such as drainage of an abscess or resection of the prostate, to improve the patient’s condition.
Measures for the prevention of chronic prostatitis
- Healthy lifestyle: Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy diet contribute to the overall strengthening of the body.
- Avoiding stress: Stress can have a negative impact on the pelvic organs, including the prostate gland.
- Genital hygiene: Following hygiene rules helps prevent the development of infections that can lead to prostatitis.
- Regular medical check-ups: In-person visits to the doctor help identify potential problems at early stages and maintain prostate health.
- Personal hygiene: Timely and correct attention to intimate hygiene helps reduce the risk of infections in the urogenital area.