Ovarian cyst: symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment methods.
Understanding Ovarian Cysts: Key Aspects
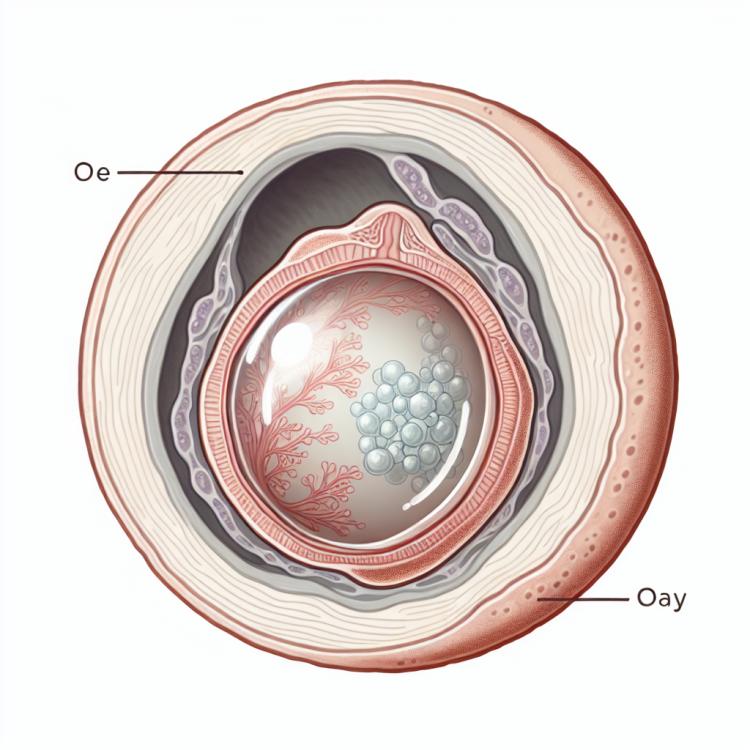
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms on the ovary. It is a common condition among women and may present with various symptoms or remain asymptomatic. Understanding ovarian cysts involves studying their types, causes of occurrence, diagnosis through laboratory and instrumental methods, as well as developing optimal management and treatment strategies depending on the characteristics of the cyst and clinical circumstances.
Etiology of ovarian cysts
Ovarian cysts are caused by various factors. One of the main reasons is the irregularity of menstrual cycles, which can lead to the formation of fluid in the ovarian follicles. Hormonal imbalance, including excessive estrogen production, can also contribute to the formation of cysts. In addition, genetic factors as well as the presence of certain diseases, such as polycystic ovary syndrome, may be associated with the appearance of cysts on the ovaries.
- Irregular menstrual cycles: Inadequate ovulation control can lead to fluid accumulation in the ovarian follicles.
- Hormonal imbalance: Excessive estrogen production or insufficient progesterone can contribute to the formation of cysts on the ovaries.
- Genetic factors: Hereditary predisposition may increase the likelihood of developing cysts on the ovaries.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome: An endocrine disorder characterized by hormonal imbalance may be associated with the formation of ovarian cysts.
- Mechanical injuries: Trauma, surgeries, or other mechanical impacts on the ovaries may contribute to the occurrence of cysts.
Signs of an ovarian cyst
Symptoms of an ovarian cyst can vary depending on its size, type, and possible complications. Often in the early stages, ovarian cysts may be symptomless or exhibit mild manifestations such as lower abdominal pain or slight changes in the menstrual cycle. However, with the increase in size of the cyst or possible rupture, more serious symptoms may arise, such as sharp lower abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, increased pressure, fever, and other signs requiring immediate intervention from a specialist.
- Lower abdominal pain: Patients often complain of dull or sharp pain in the area of the ovary, especially during physical activity or sexual activity.
- Menstrual cycle disturbances: Irregularities in the menstrual cycle or abnormal menstruation can be a sign of an ovarian cyst.
- Abdominal swelling: Patients with ovarian cysts may experience bloating or a feeling of a mass in this area.
- Difficulties with urination: Large cysts can adversely affect bladder function and cause frequent urges to urinate.
- Pregnancy-like symptoms: Some women may experience breast enlargement, nausea, or morning sickness similar to signs of pregnancy due to an ovarian cyst mimicking hormone effects.
Specialists’ view on ovarian cyst therapy
Experts’ opinions on the treatment of ovarian cysts may include a variety of approaches depending on the characteristics of the patient and the cyst. Some specialists lean towards conservative treatment, including monitoring the cyst over time with follow-up examinations and ultrasound screenings. For some cases of small functional cysts, this method may be effective, limiting it to minimal intervention.
However, in more serious cases or when complications arise, experts may recommend surgical removal of the cyst. The approach may depend on the size of the cyst, symptoms, the likelihood of complications, and the patient’s desire to preserve reproductive health. Surgical intervention may include laparoscopy to remove the cyst or even removal of the ovary in some cases. The question of the treatment method is best discussed with a qualified specialist to choose the optimal strategy for medical intervention.

Methods for diagnosing an ovarian cyst
Diagnosis of an ovarian cyst includes a variety of methods, starting with the examination and assessment of the patient using methods such as ultrasound (US) and computed tomography (CT), which allow visualization of the structure of the ovaries and identification of the presence of cysts. To clarify the diagnosis, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), X-ray, and laboratory tests, including hormone level determination, may be used. A biopsy may also be required for further investigation of the cyst and to rule out the possibility of malignant changes. The accuracy of ovarian cyst diagnosis is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment method, taking into account the individual characteristics of each patient.
- Ultrasound (US): one of the most common diagnostic methods that allows for the visualization of the structure of the ovaries and the detection of cysts.
- Computed Tomography (CT): provides a more detailed image of internal organs and can be used for the diagnosis of ovarian cysts.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): allows for a three-dimensional image of the ovaries and more detailed information about the structure and size of the cysts.
- X-ray: used in cases where additional study of the pelvic bones or surrounding tissues is necessary for the diagnosis of cysts.
- Laboratory tests: may include measurement of hormone levels, such as estrogens and progesterone, to assess ovarian function and confirm the diagnosis of an ovarian cyst.
Methods of treating ovarian cysts
- Observation and waiting: In the case of small, asymptomatic ovarian cysts, the doctor may suggest a watchful waiting strategy, where the patient is regularly monitored for changes.
- Medication therapy: For some types of cysts, such as endometriomas, medications may be prescribed to reduce cyst size or relieve symptoms like pain and menstrual dysfunction.
- Laparoscopic removal: Surgical removal of cysts can be performed laparoscopically, which minimizes tissue trauma, speeds up recovery after surgery, and reduces the risk of complications.
- Laparotomy: In cases of large cysts or complicated cases, a more invasive procedure such as a laparotomy may be required, where an incision is made in the abdomen to remove the cyst.
- Hormonal therapy: For certain types of cysts related to hormonal imbalance, treatment with hormonal medications may be recommended to normalize ovarian function and reduce the likelihood of new cyst formation.
Measures to prevent ovarian cysts
- Regular check-ups with a gynecologist: Visiting a doctor for preventive examinations and check-ups helps identify ovarian problems at early stages.
- Healthy eating: A balanced diet enriched with fruits, vegetables, whole grains, protein sources, as well as moderate consumption of fats and sugars, contributes to overall health and may reduce the likelihood of ovarian cysts.
- Physical activity: Regular exercise and physical activity help normalize hormonal balance and overall body health, which aids in the prevention of ovarian diseases, including cysts.
- Stress management: A stable emotional state and the ability to cope with stress are also considered important factors in preventing ovarian cysts.
- Timely treatment of underlying diseases: Treating various gynecological conditions, such as ovarian inflammation or endometriosis, helps prevent possible complications, including the formation of cysts on the ovaries.