Tooth cyst: diagnosis, causes, and treatment methods
- Let’s examine what a tooth cyst is.
- Factors leading to the formation of a tooth cyst
- How to recognize the symptoms of a tooth cyst
- Approaches of specialists to the treatment of dental cysts
- How to determine a dental cyst: diagnostic methods
- Approaches to treating a tooth cyst
- Ways to prevent a dental cyst
- Funny facts about a tooth cyst
- FAQ
Let’s examine what a tooth cyst is.
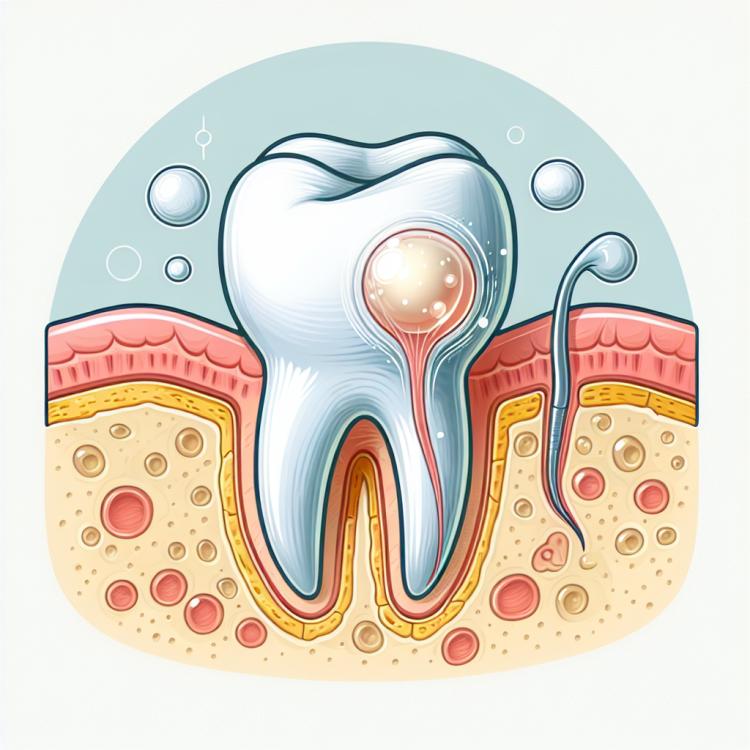
A tooth cyst is a pathological formation that occurs as a result of fluid filling a cavity formed in the bone tissue. It can be caused by various reasons, including inflammation of the tooth root tip or obstruction of the tissue contents’ outflow. As the cyst develops, it can lead to the destruction of surrounding tissues and cause pain in the patient, which requires timely diagnosis and competent treatment from a dental specialist.
Factors leading to the formation of a tooth cyst
A tooth cyst is the result of chronic inflammation of the tooth that remains untreated. The process begins with the formation of an infection in the tooth, which can occur due to cavities, dental trauma, or other reasons. In response to the infection, the body forms a cyst as a protective reaction to limit the infection and prevent its spread in the body.
Another factor leading to the formation of a tooth cyst can be incorrect or incomplete removal of tooth roots during endodontic treatment. Remaining roots can become a source of inflammation, contributing to the formation of a cyst. Additionally, congenital developmental anomalies of the teeth can promote the occurrence of a cyst.
- Chronic dental inflammation: Untimely or poor treatment of infection in the tooth can lead to the formation of a cyst.
- Incorrect root treatment: Incomplete or incorrect removal of tooth roots during endodontic treatment can contribute to cyst development.
- Tooth trauma: Tooth damage, including physical trauma or surgical interventions, can cause the formation of a cyst.
- Congenital dental development anomalies: Some congenital defects in tooth development can lead to cyst formation.
- Prolonged exposure to irritating factors: Constant irritation or trauma to the tooth can contribute to the formation of a cyst in the periapical region.
How to recognize the symptoms of a tooth cyst
Recognizing the symptoms of a tooth cyst can be difficult, as it often manifests without clear signs. However, one of the most common symptoms is the appearance of a small but sensitive growth in the area of the affected tooth. A cyst can cause slight swelling that may be felt when touching or applying pressure to the tooth.
Other symptoms of a tooth cyst may include pain that occurs or intensifies when biting down on food on the affected side, the presence of purulent discharge, as well as swelling in the area of the affected tooth. However, in some cases, a cyst may present itself without obvious symptoms, making it important to have regular dental check-ups to identify such conditions.
- Formation of a sensitive lump: the appearance of a small, sensitive formation in the area of the affected tooth.
- Pain when biting: pain that intensifies when biting food on the affected side.
- Appearance of purulent discharge: drawing attention to the presence of infection and possible development of a cyst.
- Swelling in the area of the affected tooth: swelling and puffiness that may indicate the development of a tooth cyst.
- Sensations upon touching: sensitivity or tenderness when touching or applying pressure on the tooth.
Approaches of specialists to the treatment of dental cysts
When treating a dental cyst, experts often adhere to a conservative approach, which includes performing endodontic treatment or tooth extraction. Endodontic treatment aims to remove the infection from inside the tooth and seal the root canals to prevent disease recurrence. In cases where the cyst is too large or causes serious complications, specialists may recommend tooth extraction and cleaning of the formed cyst.
However, the approach to treating a dental cyst may be adjusted depending on the individual characteristics of the patient, such as overall health status, presence of other oral diseases, possible complications, and patient preferences. It is important that treatment is carried out under the supervision of qualified specialists who can choose the optimal method in each specific case to achieve the best result.

How to determine a dental cyst: diagnostic methods
To determine a tooth cyst, the doctor reviews the patient’s medical history and examines the affected area. The diagnosis may also include X-rays, which help to determine the size and shape of the cyst, as well as its location relative to the surrounding tissues. Computed tomography (CT) may also be used to obtain more detailed information about the cyst and the structure of the surrounding tissues.
Additional diagnostic methods for a tooth cyst include ultrasound examination (ultrasonography) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). They provide more accurate detailing of the structure and characteristics of the tooth cyst, which helps the doctor choose the most effective treatment method.
- Medical history: The doctor collects and examines the patient’s medical history to identify any previous infections or dental issues.
- Examination: Examining the affected area allows determining the presence of inflammation, swelling, or other signs of a tooth cyst.
- X-ray: X-rays help determine the size, shape, and location of the cyst in relation to the surrounding tissues.
- Computed Tomography (CT): This method provides more detailed information about the structure of the cyst and the surrounding tissues.
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasonography): Ultrasound allows visualization of finer details of the cyst’s structure and its characteristics.
Approaches to treating a tooth cyst
Surgical intervention may be required in cases where the size of the cyst is too large or it exerts significant pressure on surrounding tissues. Surgical treatment may involve the removal of the cyst, treatment of the tooth and surrounding tissues, as well as restoration of damaged dental structures. It is important to consult with a qualified dentist or surgeon to determine the most appropriate approach for treating a tooth cyst.
- Conservative treatment of a dental cyst may include taking antibiotics to reduce infection and prevent its spread.
- Endodontic treatment may be performed to remove the source of infection in the tooth.
- Surgical intervention may be required in the case of a large cyst or compromise of surrounding tissues.
- Cyst removal may involve removing the cyst itself, treating the tooth, and restoring damaged structures.
- The decision on the method of treating a dental cyst is made based on its size, location, and the overall condition of the patient.
Ways to prevent a dental cyst
Particular attention should be paid to dental injuries, as damage to a tooth can be the starting point for cyst formation. Preventing tooth injuries by using protection during sports activities or preventing conditions that contribute to injuries can reduce the risk of tooth cysts. It is important to adhere to an individual medical plan developed by the dentist to prevent tooth cysts.
- Regular visits to the dentist: Visiting the dentist for preventive check-ups and monitoring helps to identify dental problems at early stages and to begin treatment in a timely manner, preventing the development of cysts.
- Maintaining oral hygiene: Regular tooth brushing, using dental floss, and applying additional oral care products help reduce the risk of infection in the teeth and gums.
- Avoiding dental injuries: Preventing dental injuries by using protection during sports or active recreation helps reduce the chance of developing a tooth cyst after damage.
- Timely treatment of dental problems: Regular treatment of dental caries, dental plaque, periodontitis, and other oral diseases helps prevent the development of infection and the formation of cysts.
- Following doctor’s recommendations: It is important to adhere to the individual medical plan developed by the dentist and to follow all recommendations for dental and oral care, which will help minimize the risk of tooth cysts.
Funny facts about a tooth cyst
Another surprising fact about a tooth cyst is that it can be asymptomatic and show no obvious signs for a long time. This can lead to the cyst being discovered only during a dental examination or through radiographic investigation. Such features of a tooth cyst emphasize the importance of regular dental visits for early detection and treatment of this condition.