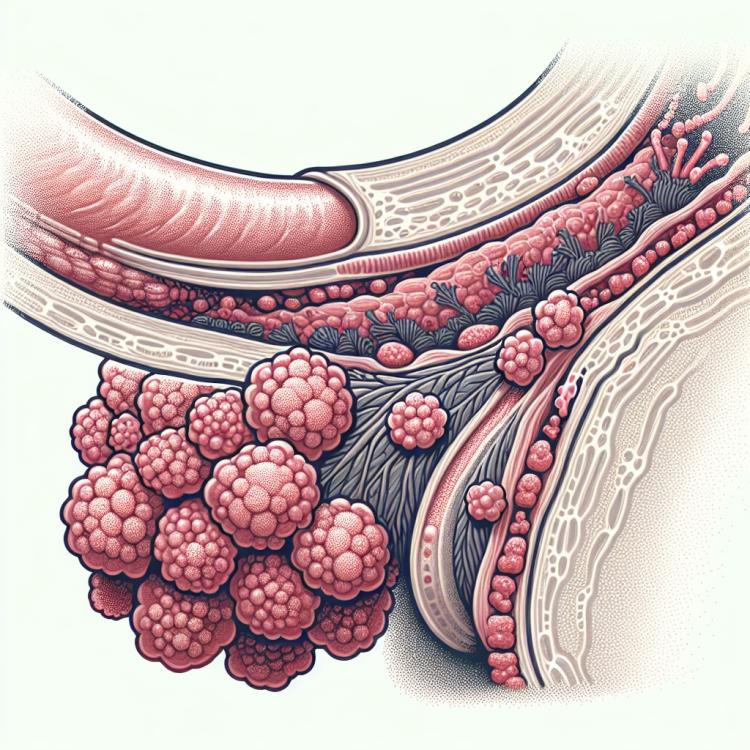
Condylomas: diagnosis, complications, and prevention
- Understanding condyloma: symptoms, causes, and treatment
- Etiology of condylomas: factors and mechanisms of occurrence
- Clinical picture of condylomas: signs and manifestations
- Expert opinion on methods for treating warts
- Methods for diagnosing condylomas
- Methods of treating papillomas
- Prevention measures for condyloma
- Amazing features of condyloma
- FAQ
Understanding condyloma: symptoms, causes, and treatment
Condylomas are wart-like formations on the skin and mucous membranes caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They are one of the most common sexually transmitted infections and can be transmitted through sexual contact. Symptoms of condylomas include the presence of warts in the genital area, rectum, or mouth, which may be accompanied by itching or discomfort. Treatment may include medication therapy, cryodestruction, surgical removal, or laser therapy, depending on the size and location of the formations. It is important to see a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and subsequent prescription of appropriate treatment.
Etiology of condylomas: factors and mechanisms of occurrence
Warts are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), which is transmitted through sexual contact. The infection is spread through contact with infected skin or mucous membranes. There are more than 100 types of HPV, and some of them can lead to the formation of warts in various areas of the body, including the genitals, mouth, and throat.
Risk factors include unprotected sex, frequent changes of sexual partners, observing warts in a sexual partner, and prolonged exposure to a moist environment. All these factors contribute to the occurrence and transmission of HPV infection, which can lead to the formation of warts.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV): Warts are caused by an infection with the HPV virus, which is transmitted through sexual contact.
- Sexual contact: HPV infection is transmitted through contact with infected skin or mucous membranes during sexual intercourse.
- Risky behavioral factors: Unprotected sex, frequent change of sexual partners, and the presence of warts in a sexual partner can increase the likelihood of contracting HPV.
- Moist environment: Prolonged exposure to a moist environment can contribute to the development of HPV infection and the formation of warts.
- Development of infection: HPV infects epithelial cells, causing their uncontrolled division and leading to the formation of warts.
Clinical picture of condylomas: signs and manifestations
Warts caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) typically appear as soft, firm nodules on the skin or mucous membranes. Depending on the location of the lesion, warts can be flat, conical, or spindle-shaped. They can vary in size and color, usually closely adhering to the surface of the skin or mucosa.
Signs of warts may include itching, burning, or discomfort in the affected area, bleeding sores, or rash. In women, warts may be observed on the external genitalia or inside the vagina. In men, they are more commonly found on the penis. If such symptoms are detected, it is important to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and treatment.
- Soft warts: condylomas usually appear as soft, dense warts on the skin or mucous membranes.
- Various shapes and sizes: condylomas can be flat, conical, or spindle-shaped, of varying sizes and colors.
- Discomfort and burning: are accompanied by itching, burning, as well as bleeding ulcers or rash in the affected area.
- Localization in women and men: in women, more often on the external genital organs or in the vagina, in men – on the penis and around the anal opening.
- The importance of consulting a doctor: upon noticing such signs, one should consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Expert opinion on methods for treating warts
Expert opinion on the methods of treating condylomas emphasizes the importance of an individualized approach for each patient. Doctors recommend assessing the nature and location of the condylomas, as well as considering the individual’s characteristics when choosing the optimal treatment strategy. Intervention may include drug therapy, chemical treatment, cryodestruction, laser removal, or surgical intervention, and the choice of method depends on individual factors and patient preferences.
The main goals of treatment are the elimination of existing condylomas, prevention of recurrences, and reducing the risk of transmission of the infection to a partner. Expert opinion highlights the importance of regular monitoring of the patient’s condition after treatment to detect possible recurrences or complications in a timely manner. Doctors recommend following all specialist instructions and leading a healthy lifestyle to prevent the recurrence of condylomas.

Methods for diagnosing condylomas
For the diagnosis of condylomas, it is important to conduct a visual examination of the affected areas, and colposcopy, cytological examination (Cytological examination using the Pap test), or polymerase chain reaction (PCR) may be required to detect the human papillomavirus (HPV). A biopsy of the affected tissue may be used to clarify the diagnosis and rule out other diseases.
Diagnosis of condylomas based on objective research methods allows for an accurate diagnosis to be established and the most effective treatment method to be chosen. Early detection and diagnosis help prevent possible complications and promote the patient’s path to recovery.
- Visual inspection: The doctor performs a visual inspection of the affected areas to assess the external signs of warts.
- Colposcopy: This is a method that uses a special magnifying device for a more detailed examination of the affected tissues.
- Cytological examination (Pap smear method): Analyzing cells from the affected area can help identify changes characteristic of HPV infection.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR): This method is used to detect the human papillomavirus (HPV) in the affected tissues.
- Biopsy: Examination of a sample of the affected tissue may be performed for an accurate diagnosis and to rule out other diseases.
Methods of treating papillomas
An individualized approach to the treatment of condylomas is necessary, taking into account the specifics of each case. The determination of the optimal treatment method should be conducted by a dermatologist or another specialist who specializes in treating conditions caused by the HPV virus.
- Surgical removal: one of the primary methods for treating warts, in which the growths are surgically removed, usually with a scalpel or through scraping.
- Cryotherapy: a method of removing warts by freezing the lesions with liquid nitrogen, which leads to their destruction and subsequent disappearance.
- Chemical treatment: the application of medications, such as ointments or solutions, to destroy warts through chemical action on the affected areas.
- Electrocoagulation: a treatment method in which warts are removed using electric current, leading to their coagulation and destruction.
- Laser therapy: the use of laser irradiation for removing warts, ensuring precise and effective elimination of the growths.
Prevention measures for condyloma
Other prevention methods include vaccination against HPV, which is particularly important for individuals who are not infected with the virus. Caution against casual sexual relationships and the use of protective measures (condoms) are also key factors in the prevention of condylomas and other HPV-related diseases.
- Use of condoms: using condoms during sexual intercourse reduces the risk of transmission of the human papillomavirus (HPV).
- Regular medical check-ups: it is important to consult a dermatologist-venereologist to identify and timely treat warts, which helps in controlling the disease.
- HPV vaccination: vaccines against HPV help prevent infection with the virus and the occurrence of warts and are recommended as a preventive measure for individuals who have not contracted the virus.
- Warning against casual sexual relationships: limiting the number of partners and using protective measures helps reduce the risk of HPV transmission and development of warts.
- Education about symptoms and protective methods: informing about the symptoms of warts, modes of HPV transmission, and protective methods such as stable partnerships and the use of condoms contributes to overall awareness and disease prevention.
Amazing features of condyloma
Warts can also appear on different areas of the body, including the genitals, oral cavity, throat, and other regions. This wide localization of lesions adds complexity to treatment and requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and disease management. Systematic research on the features of warts is crucial for ensuring effective treatment and preventing potential complications.