Conjunctivitis: signs, diagnosis, and treatment methods
- Definition of conjunctivitis: symptoms, causes, and treatment
- Factors causing conjunctivitis
- Characteristics of conjunctivitis symptoms
- Expert opinion on methods for treating conjunctivitis
- Methods of diagnosing conjunctivitis
- Approaches to the treatment of conjunctivitis
- Preventive measures for conjunctivitis
- Unusual aspects of conjunctivitis
- FAQ
Definition of conjunctivitis: symptoms, causes, and treatment
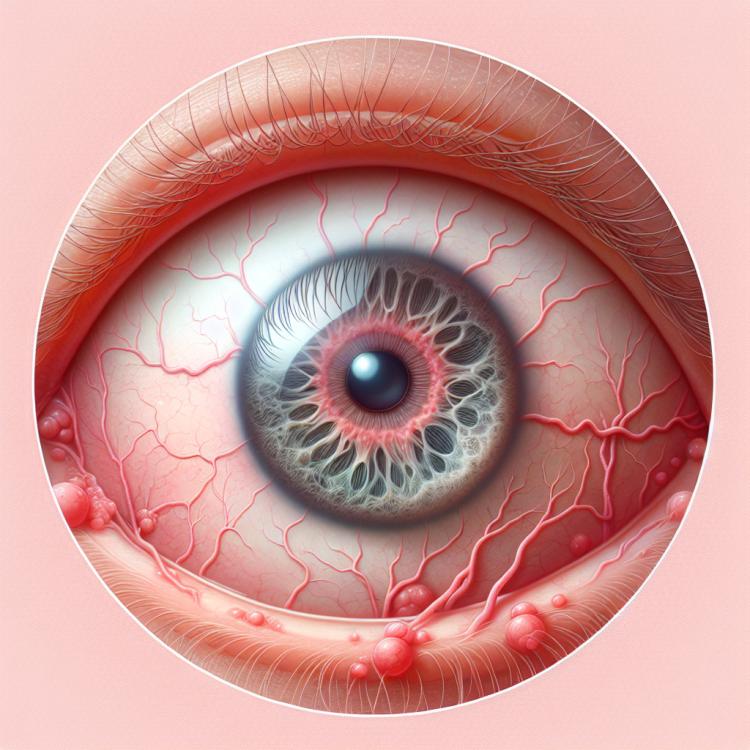
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the transparent membrane covering the front of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelids. Symptoms of this disease may include redness of the eyes, itching, tearing, a sensation of sand in the eye, as well as the formation of crusts on the eyelashes. Causes of conjunctivitis can include infections, allergic reactions, eye injuries, or contact with irritating substances. Treatment depends on the type of conjunctivitis and may include the use of medications, including antibiotics or antihistamines, comfortable eye drops, as well as adherence to hygienic measures.
Factors causing conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis can be caused by various factors, including viruses, bacteria, allergens, and irritants. Viral conjunctivitis usually results in a red and inflamed eye, as well as a discharge of mucus or purulent secretion. Bacterial conjunctivitis is also accompanied by redness of the eyes and purulent discharge. Allergic conjunctivitis often develops due to allergens such as pollen, dust, animals, or certain foods, causing itching, redness, and tearing of the eyes.
- Viruses: Various viruses, such as adenoviruses, herpes, and others, can cause viral conjunctivitis.
- Bacteria: Bacterial infections, such as streptococci or staphylococci, can be a cause of bacterial conjunctivitis.
- Allergens: Pollen, dust, pet dander, as well as other allergens, can cause allergic conjunctivitis.
- Irritants: Exposure to irritants, such as chlorine in swimming pools, smoke, or chemicals, can cause conjunctivitis.
- Injuries and contact lenses: Eye injuries or the use of unapproved or dirty contact lenses can be a cause of conjunctivitis.
Characteristics of conjunctivitis symptoms
Conjunctivitis can manifest various symptoms, including redness of the eyes, itching, heavy tearing, a foreign body sensation in the eye, and discharge of a purulent substance. Patients often experience discomfort, dryness, and a burning sensation in the eyes. Some patients with conjunctivitis may also exhibit swelling of the eyelids, especially in cases of allergic conjunctivitis.
Additional symptoms of conjunctivitis include increased sensitivity to light, blurred vision, as well as possible crusting on the eyelashes in the morning. Symptoms can vary significantly depending on the type of conjunctivitis and its possible causes – from viruses to bacteria or allergic reactions.
- Eye redness: one of the main symptoms of conjunctivitis is redness of the conjunctiva, leading to general visual discomfort.
- Itching and discomfort: patients often experience itching and discomfort in the eye area, leading to a constant need to scratch or rub their eyes.
- Severe tearing: conjunctivitis is often accompanied by increased tearing, which can make vision difficult and cause additional discomfort.
- Foreign body sensation: patients may feel that there is a foreign body in the eye, which is a characteristic symptom of conjunctivitis.
- Purulent discharge: some types of conjunctivitis may be accompanied by the discharge of pus from the eye, which is a sign of inflammation and infection.
Expert opinion on methods for treating conjunctivitis
Experts in the field of ophthalmology typically recommend an individualized approach to the treatment of conjunctivitis depending on its type – viral, bacterial, or allergic. For viral and bacterial forms, local medications in the form of eye drops or ointments are usually prescribed, aimed at destroying the pathogen and reducing inflammation symptoms.
In the case of allergic conjunctivitis, experts often recommend avoiding contact with allergens, using antihistamine eye drops, and taking antihistamine medications to relieve symptoms. Additionally, it is important to pay attention to hygiene measures, such as cleaning and removing eye makeup, to prevent irritation and worsening of the conjunctivitis condition.

Methods of diagnosing conjunctivitis
Diagnosis of conjunctivitis includes a visual examination of the eye by a doctor, who assesses the symptoms, the appearance of the conjunctiva, the degree of swelling, and the presence of discharge. To clarify the type of conjunctivitis, additional testing of smears or allergy testing may be conducted. If bacterial conjunctivitis is suspected, bacteriological examination may be recommended.
Diagnosis may also include checking the intraocular pressure and assessing the function of the tear glands. Sometimes, screening of the fundus can help identify possible complications, especially in chronic conjunctivitis. Consultation with an optometrist or ophthalmologist can be beneficial for an accurate diagnosis and determining an effective treatment plan.
- Visual inspection: the doctor examines the eye, assessing the appearance of the conjunctiva, the presence of redness, swelling, and discharge.
- Bacterial smears: to confirm a bacterial infection, a smear may be taken from the surface of the eye for bacteriological examination.
- Allergen testing: when an allergic type of conjunctivitis is suspected, tests for allergens are conducted to identify the triggering irritant.
- Checking intraocular pressure: measuring intraocular pressure may be performed to assess potential complications or damage to the eyes in cases of conjunctivitis.
- Fundus screening: sometimes a fundus screening is conducted to identify characteristics and complications associated with conjunctivitis.
Approaches to the treatment of conjunctivitis
In allergic conjunctivitis, it is recommended to avoid contact with allergens, use anti-allergic drops or antihistamine medications. It is important to consult an ophthalmologist for an accurate diagnosis and to determine the most effective treatment in each specific case.
- Antibacterial drugs: in bacterial conjunctivitis, antibacterial drops or ointments are often used to combat the infection.
- Antiviral drugs: in the case of viral conjunctivitis, the use of antiviral agents may be necessary, but often the condition resolves spontaneously.
- Antiallergic agents: for the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis, antiallergic drops or tablets are used, and it is also recommended to avoid contact with allergens.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: in conjunctivitis, the use of anti-inflammatory drugs may sometimes be required to reduce inflammation and discomfort.
- Urea: urea can be used to moisturize and soften the eyes, especially in viral conjunctivitis.
Preventive measures for conjunctivitis
To prevent allergic conjunctivitis, it is important to avoid contact with known allergens such as pollen, dust, fluff, mold, and pets. Regular cleaning of the home and using air conditioning can help reduce the number of allergens in the environment. Following the recommendations and prescriptions of a doctor is also an important aspect of conjunctivitis prevention.
- Compliance with eye hygiene: regular washing of the face and eyes always before coming into contact with them helps reduce the risk of infection.
- Use of personal protective equipment: wearing protective glasses or contact lenses can prevent the entry of infections or irritants into the eyes.
- Avoiding eye rubbing: refraining from rubbing or scrubbing the eyes with dirty hands helps prevent infection and irritation of the conjunctiva.
- Cleaning of premises and additional measures: regular cleaning of premises, increasing humidity, and using air conditioning can reduce the number of allergens in the environment.
- Following doctor’s recommendations: adhering to prescribed treatment and the doctor’s instructions, especially in cases of allergic conjunctivitis, helps prevent exacerbations and reduce the risk of disease.
Unusual aspects of conjunctivitis
Another interesting fact is the possibility of developing conjunctivitis in newborns, called neonatal conjunctivitis. This condition can be caused by an infection transmitted from the mother during the birth process and requires special attention and treatment to prevent possible complications and preserve the child’s eye health.