Coccygeal canal: anatomy, functions, and possible problems
- Understanding the anatomy of the Coccygeal canal
- Etiology of problems with the Coccygeal canal
- Signs and manifestations of problems with the coccygeal canal
- Professional opinion on the treatment of problems with the Coccygeal canal
- Diagnosis of problems with the Coccygeal canal
- Treatment of problems with the coccygeal passage
- Prevention of problems with the Coccygeal canal
- Amazing Aspects of the Coccygeal Canal
- FAQ
Understanding the anatomy of the Coccygeal canal
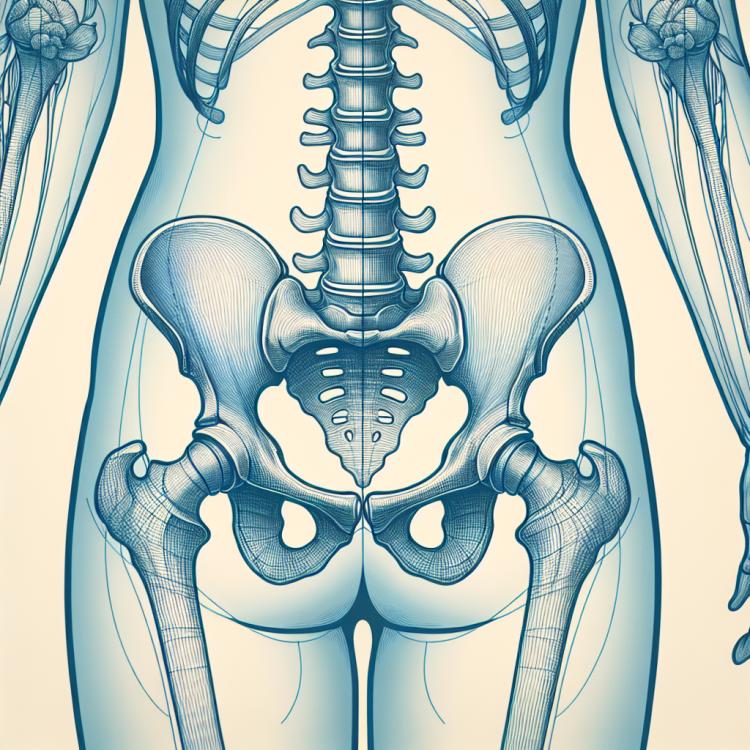
Coccygeal canal, or sacrococcygeal canal, is a narrow space between the coccyx and the rectum. This anatomical structure plays an important role in the anorectal area by providing support for soft tissues and connective structures, as well as serving as a path for the passage of nerves and blood vessels. A deep understanding of the anatomy of the Coccygeal canal is essential for the diagnosis and treatment of various pathologies related to this area, such as cysts, abscesses, or injuries, enabling medical professionals to make informed decisions about treatment methods and the prevention of complications.
Etiology of problems with the Coccygeal canal
The causes of issues with the coccygeal canal can be varied. Some of them include injuries, birth trauma, infections, inflammatory processes, or developmental abnormalities. Congenital deformities, fractures, and even improperly performed medical procedures can become sources of problems that require careful diagnosis and treatment.
- Injuries: Traumatic injuries, such as bruises, fractures, or birth traumas, can contribute to problems with the Coccygeal canal.
- Infections: Infections, such as bacterial, fungal, or viral, can cause inflammation and irritation in the area around the coccyx.
- Inflammatory processes: Various inflammations, such as abscesses or cellulitis, can lead to problems in the Coccygeal canal area.
- Developmental abnormalities: Congenital defects or developmental anomalies in the coccygeal area can contribute to the occurrence of problems with the Coccygeal canal.
- Consequences of surgical interventions: Improperly performed medical procedures in the coccygeal area can be the cause of problems and complications.
Signs and manifestations of problems with the coccygeal canal
Signs of problems with the Coccygeal passage may include pain in the coccyx area, worsening discomfort while sitting, tenderness or intolerance during defecation or movement, as well as discharge from the anal opening. Swelling, redness, and dysfunction in urination may also be characteristic symptoms. These signs require careful monitoring and possibly a differentiated approach in diagnosis and treatment, combining clinical data with instrumental methods to determine a detailed picture of the disease.
- Pain in the coccyx area: often one of the first signs of problems with the coccygeal canal, possibly worsening when sitting.
- Discomfort during defecation: difficulty or painful bowel movements may be related to defects in the coccygeal area.
- Discharge from the anus: unusual discharge, bleeding, or purulent secretion may indicate problems with the coccygeal canal.
- Swelling and redness: inflammatory reactions in the coccyx area can cause swelling and changes in skin color in this area.
- Disruption of urination functions: some problems in the coccygeal area may affect the processes of urination, causing discomfort and unusual symptoms.
Professional opinion on the treatment of problems with the Coccygeal canal
The experts’ opinion on the treatment of problems with the Coccygeal canal reflects the necessity of an individualized approach for each patient, taking into account the specifics of the symptoms, the source of the problem, the patient’s history, possible complications, and the patient’s wishes. Experts recommend a comprehensive approach to treatment, including conservative methods, physiotherapy, medications, and sometimes surgical intervention, as well as rehabilitation procedures to restore functions in the coccygeal area.
It’s also important to highlight the significance of educating the patient about potential causes and treatment measures, as well as preventive measures to avoid recurrences. Under the guidance of qualified specialists, patients can expect improvements in their condition regarding Coccygeal canal problems and further control over the disease.

Diagnosis of problems with the Coccygeal canal
Diagnosis of issues with the coccygeal canal includes a detailed clinical examination and patient’s history, as well as instrumental methods such as X-ray, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT). These medical methods allow for the identification of anomalies, injuries, infections, or tumors in the coccygeal area and determine the extent of pathology. After establishing an accurate diagnosis and assessing the patient’s condition, the specialist can prescribe appropriate treatment tailored to the specific case.
- Clinical examination: The doctor conducts a visual and tactile examination of the coccyx area to identify swelling, redness, tenderness, or other symptoms.
- X-ray: X-rays can help identify deformities, injuries, fractures, or tumors in the coccyx area.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI provides detailed images of soft tissues, allowing for the detection of inflammatory processes, infections, or other pathologies.
- Computed Tomography (CT): CT scanning can be used for a more precise determination of the sizes of tumors, cysts, and other formations in the coccyx area.
- Tests: A laboratory blood test may be conducted to identify inflammatory markers or infections that may be related to problems in the coccyx area.
Treatment of problems with the coccygeal passage
- Conservative treatment methods: Include the use of medications to relieve pain and inflammation, as well as physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Surgical intervention: In cases where conservative methods have not yielded results, operative treatment may be required to correct anomalies, remove tumors, or restore damaged tissues.
- Use of medications: The doctor may prescribe medications to reduce pain, inflammation, and improve the overall condition of the patient.
- Physical therapy and rehabilitation: Important components of comprehensive treatment aimed at strengthening the pelvic floor muscles and improving the functions of the coccygeal area.
- Individualized approach: Treatment should be tailored to the specific case, taking into account the patient’s characteristics and the nature of the manifestations of issues with the Coccygeal canal.
Prevention of problems with the Coccygeal canal
- Hygiene maintenance: Regular cleaning and care of the coccyx area can prevent the development of infections and other issues.
- Avoiding injuries: Exercising caution during sports, preventing falls or traumatic injuries in the coccyx area.
- Strengthening pelvic floor muscles: Regular exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles can enhance support and prevent issues in the coccyx area.
- Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in fiber promotes normal bowel function and may reduce the risk of problems in the coccyx area.
- Regular consultations with a specialist: Timely visits to a doctor at the first signs of discomfort or pain allow for the detection of pathologies in the coccyx area at early stages and prevent their progression.