Bone panaritium: diagnosis and treatment methods
- Understanding bone paronychia
- Risk factors for the development of bone paronychia
- Main signs of bone panaritium
- The best approaches to treating bone panaritium
- Methods of diagnosing bone panaritium
- Methods for treating bone panaritium
- Preventive measures for bone panaritium
- Amazing aspects of bone panaritium
- FAQ
Understanding bone paronychia
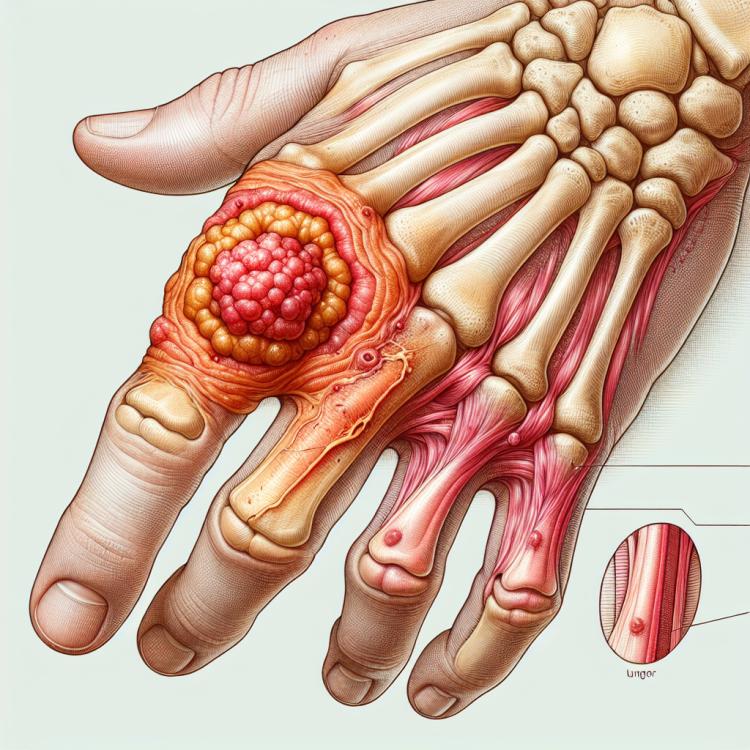
Bone panaritium is a surgical disease characterized by an inflammatory process in the bone tissue of the finger. It most often occurs due to infection penetrating through small wounds or cuts on the fingers. In cases of bone panaritium, tenderness, swelling, redness, and limited movement in the affected finger are often noted, making it important to promptly consult a specialist for an accurate diagnosis and treatment of this condition.
Risk factors for the development of bone paronychia
Risk factors for the development of bone paronychia include diabetes, obesity, a weakened immune system, skin injuries, and poor hygiene. Diabetes increases the likelihood of infection, as elevated blood sugar levels can impair blood circulation and weaken the immune system. Obesity is also a risk factor, as excess weight increases pressure on the foot, which can lead to injuries and raise the risk of infection. Therefore, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, regular medical check-ups, and following hygiene practices can help reduce the risk of developing bone paronychia.
- Diabetes: high blood sugar levels can worsen blood circulation and weaken the immune system, increasing the risk of infection.
- Obesity: excess weight increases the load on the foot, which can lead to damage and increase the likelihood of infection.
- Weakened immune system: a compromised body defense reduces the ability to fight infections, including paronychia.
- Skin injuries: the presence of wounds, burns, or other injuries on the skin can promote bacterial entry and the development of infection.
- Poor hygiene: improper care of nails or foot skin can create conditions for bacterial proliferation and the development of paronychia.
Main signs of bone panaritium
The main signs of bone panaritium include swelling, redness, pain, and increased sensitivity in the area of the affected bone joint. The skin over the affected area may be tense and hot to the touch. The affected joint may also have limited mobility due to pain and inflammation of the tissues. The diagnosis of bone panaritium is usually based on clinical signs, and additionally, x-rays or magnetic resonance imaging may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of involvement of the bones and joints.
- Swelling: Bone paronychia is often accompanied by swelling, which manifests as an increase in the volume of the affected joint and surrounding tissues.
- Redness: The inflamed areas of the affected bone joint usually acquire a bright red hue due to increased blood flow and inflammation.
- Pain: Under the influence of inflammation, patients feel pain in the area of the affected joint, which can be sharp or dull, intense or moderate.
- Sensitivity: The affected joint may have increased sensitivity to touch or when performing movements that cause discomfort.
- Limited mobility: Due to pain and tissue inflammation in the area of bone paronychia, patients may experience difficulty moving the affected joint, which can limit their ability to perform normal movements.
The best approaches to treating bone panaritium
Experts in the medical community agree that effective treatment of bone panaritium includes antibiotic therapy to combat infection and prevent its spread. Based on the results of the infection diagnosis, the appropriate antibiotic is prescribed depending on the sensitivity of the pathogen. Simultaneously, local treatment is carried out, including drainage of purulent content and disinfection of the affected area.
To reduce pain syndrome and inflammation, experts recommend using anti-inflammatory medications and local anesthetics. In cases where conservative treatment does not lead to improvement, as well as in the development of complications, surgical intervention may be required, such as the removal of necrotic tissue or even amputation of part of the affected limb.

Methods of diagnosing bone panaritium
For the diagnosis of bone panaritium, various methods are used, including clinical examination of the affected area, assessment of symptoms, and the patient’s history. In addition, diagnostic methods may include X-rays, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). These methods help determine the extent of damage to the bones and joints, as well as identify the presence of complications related to bone panaritium.
Additionally, laboratory tests, such as complete blood count and bacteriological studies, may be conducted to confirm the presence of infection and identify potential pathogens. A comprehensive approach to diagnosing bone panaritium allows for effective diagnosis, selection of the appropriate treatment method, and prevention of possible complications.
- Clinical examination: Conducted by a doctor to assess the condition of the affected area, identify signs of inflammation, swelling, and redness.
- X-ray: Used to evaluate the condition of the bones, identify bone changes, anomalies, and complications associated with bone panaritium.
- Computed tomography (CT): Allows for a more detailed visualization of the affected bones, joints, and surrounding tissues, clarifying the nature of the changes.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): Provides information about the structure of tissues, helping to identify possible complications related to bone panaritium.
- Laboratory studies: Include blood tests, bacteriological studies to identify infection, determine the pathogen, and choose the prescribed treatment.
Methods for treating bone panaritium
Physical therapy, rehabilitation, and adherence to hygiene measures may also be part of the comprehensive treatment of bone panaritium. These methods contribute to the restoration of function in the affected joint, strengthening of the muscles, and improving the overall well-being of the patient. Monitoring the course of the disease and support from specialists help ensure effective treatment and prevent potential complications.
- Use of antibiotics: Treatment of bone panaritium often includes a course of antibiotics to combat the infection and prevent its spread.
- Surgical intervention: In case of the formation of a purulent focus, surgical drainage and removal of necrotic tissues may be required.
- Physical therapy and rehabilitation: The use of physical therapy methods aids in restoring functions of the affected joint and strengthening muscles.
- Adhering to hygiene measures: Maintaining cleanliness and dryness of the affected area contributes to the quick healing of wounds and prevents new infections.
- Consultation with specialists: Following the recommendations of doctors, regular monitoring of the condition, and timely treatment help achieve the best results in treating bone panaritium.
Preventive measures for bone panaritium
Regular medical check-ups and consultations with a doctor can help identify potential issues in a timely manner and prevent the development of bone panaritium. Education on hygiene rules and preventative measures is a key component of the prevention of bone panaritium, especially for people at higher risk of developing this condition.
- Compliance with hygiene rules: Regular washing and disinfecting of wounds and injuries helps prevent the risk of infection and the development of bone panaritium.
- Examination and care of the skin: It is important to carefully monitor the condition of the skin, avoid injuries and cuts, and promptly consult a doctor if any changes occur on the skin.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: A balanced diet, physical activity, and avoiding harmful habits contribute to strengthening the immune system and the health of the skin.
- Regular medical check-ups: Routine examinations and consultations with a doctor can help detect early signs of disease and take necessary preventive measures.
- Training in preventive measures: Educating about hygiene rules, seeking medical help early in cases of skin lesions, and knowing risk factors can help prevent the occurrence of bone panaritium.
Amazing aspects of bone panaritium
An interesting fact is that bone panaritium can arise both from the effects of external microorganisms and from the spread of infection from adjacent tissues or vessels. Understanding the causes of this disease, its symptoms, and treatment methods plays a crucial role in the effective prevention and combat against bone panaritium.