Leukoplakia of the bladder: diagnosis, treatment features, and prognosis
- Basics of bladder leukoplakia
- Factors contributing to the development of bladder leukoplakia
- Possible manifestations of bladder leukoplakia
- Approaches to the treatment of bladder leukoplakia: specialists’ opinions
- Main methods for diagnosing bladder leukoplakia
- Approaches to the treatment of bladder leukoplakia
- Measures for the prevention of bladder leukoplakia
- Amazing facts about bladder leukoplakia
- FAQ
Basics of bladder leukoplakia
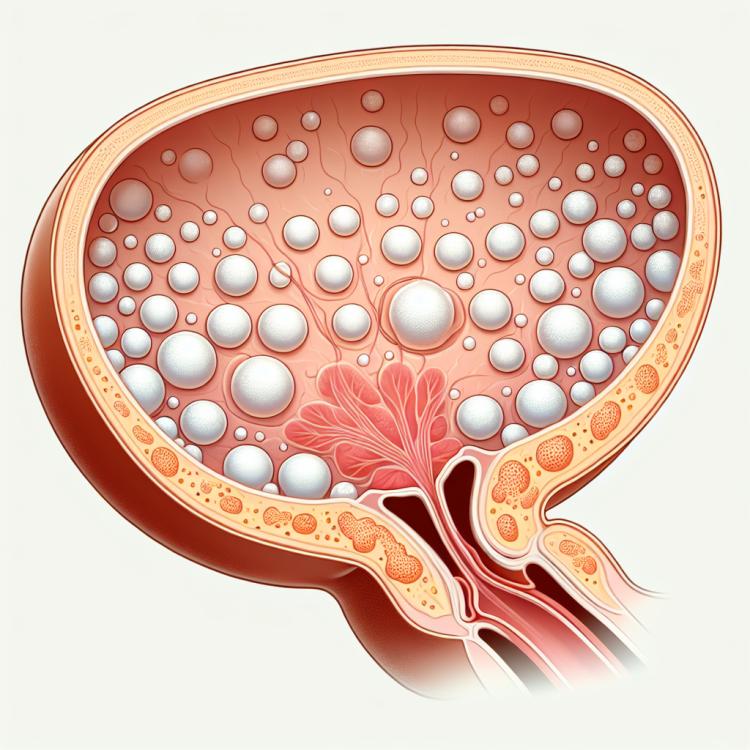
Bladder leukoplakia is a precancerous change in the bladder characterized by the formation of white spots or plaques on the inner surface of the mucous membrane. This condition can manifest with various clinical symptoms, such as bloody discharge from the urinary tract, painful urination, and a sharp decline in organ function. The diagnosis of bladder leukoplakia includes cystoscopy, biopsy, and mandatory exclusion biopsy to rule out bladder cancer.
Factors contributing to the development of bladder leukoplakia
Bladder leukoplakia is a rare condition, and its exact causes are not yet fully understood. However, factors that may contribute to the development of leukoplakia include prolonged exposure to carcinogens on the bladder mucosa, increased levels of inflammatory processes or trauma, as well as genetic characteristics affecting the susceptibility of cells to changes. Further research is needed for a deeper understanding of the causes of this disease and the development of effective treatment strategies.
- Prolonged exposure to carcinogens: An increased risk of leukoplakia may be due to prolonged exposure to carcinogenic substances on the mucous membrane of the bladder.
- Increased level of inflammatory processes: Chronic inflammation in the bladder area may contribute to the development of leukoplakia due to prolonged irritation of the tissues.
- Traumatization: Mechanical injuries or surgeries in the bladder area may increase the likelihood of developing leukoplakia.
- Genetic features: Hereditary factors may influence the increased tendency to develop changes in bladder cells, including leukoplakia.
- Immunodeficient conditions: A reduced immune response may make the body more vulnerable to various pathologies, including the possible development of bladder leukoplakia.
Possible manifestations of bladder leukoplakia
Bladder leukoplakia often proceeds asymptomatically in the early stages and may be incidentally found during examinations for other reasons. However, in the advanced stages of the disease, various manifestations may be observed, including frequent and painful urination, blood in the urine, pain in the lower abdomen or in the bladder area, general malaise, and deterioration of urination.
When such symptoms appear, it is important to seek medical assistance for diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Early detection of bladder leukoplakia allows for timely initiation of therapy and improves the prognosis of the disease.
- Frequent urination: there may be increased urination, especially in the advanced stages of the disease.
- Blood in urine: the presence of blood in urine can be one of the signs of bladder leukoplakia.
- Lower abdominal pain or bladder area pain: discomfort in the abdominal area may be related to bladder damage.
- General malaise: feelings of weakness, fatigue, or vague discomfort may also accompany bladder leukoplakia.
- Deterioration of urination: difficulty or pain during urination may be a sign of bladder problems.
Approaches to the treatment of bladder leukoplakia: specialists’ opinions
Experts in the fields of urology and oncology consider various approaches to the treatment of bladder leukoplakia, taking into account the individual characteristics of each patient. Depending on the stage of the disease and the nature of changes in the bladder, conservative treatment methods are possible, such as medication therapy or topical application of drugs.
Individuals with leukoplakia may also be subject to surgical intervention, including endoscopic removal of affected areas of the bladder mucosa or even radical cystectomy in the case of widespread changes or a high risk of malignant degeneration. The collective opinion of specialists emphasizes the necessity of a personalized approach to the treatment of bladder leukoplakia in order to ensure optimal results and maintain the patient’s health.

Main methods for diagnosing bladder leukoplakia
For the diagnosis of bladder leukoplakia, various methods are used, including the patient’s medical history, physical examination, urine laboratory tests, cystoscopy, and biopsy. The medical history and physical examination help assess the clinical picture and identify the initial symptoms of the disease, while urine laboratory tests may indicate the presence of inflammation, blood, or other pathological processes in the bladder. Cystoscopy is a procedure in which the doctor uses a special instrument to examine the internal walls of the bladder, allowing for the observation of potential changes and the collection of tissue samples for biopsy followed by cytological examination.
- Medical history: Analysis of past and present medical data of the patient to identify risk factors and preceding symptoms.
- Physical examination: Examination of the patient to detect possible signs or changes in the abdominal area related to bladder leukoplakia.
- Urine laboratory tests: Examination of urine for anomalies, including inflammation, blood, cells, and other pathological signs that may indicate leukoplakia.
- Cystoscopy: A procedure in which the doctor uses a special instrument to visually inspect the internal walls of the bladder for changes and to take biopsy samples.
- Biopsy followed by cytological examination: Examination of bladder tissue samples to determine the presence of pathological changes and the risk of developing leukoplakia.
Approaches to the treatment of bladder leukoplakia
- Surgical treatment: In cases of advanced leukoplakia, surgical removal of the affected areas of the bladder may be required to prevent further spread of the disease.
- Laser therapy: The use of lasers to remove tumors or affected areas can be an effective method for treating bladder leukoplakia, especially in cases where surgical intervention is not advisable.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: The prescription of medications to reduce inflammation in the bladder can help alleviate the negative symptoms associated with leukoplakia.
- Immunomodulatory therapy: Strengthening the immune system through medications or procedures may help improve resistance to potential complications of the disease.
- Screening and early detection: Regular medical examinations and screenings can help detect bladder leukoplakia at an early stage, allowing for timely treatment and increasing the chances of a successful outcome.
Measures for the prevention of bladder leukoplakia
Regular check-ups with a doctor, especially in the presence of risk factors, as well as careful monitoring of urinary tract conditions can help in the timely detection and treatment of bladder leukoplakia. It is also important to follow recommendations for the prevention of urinary tract infections, maintain hygiene levels, and consult a doctor at the first signs of illness.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: regular physical exercise, healthy eating, and refraining from harmful habits can reduce the risk of developing bladder leukoplakia.
- Maintaining an optimal weight: excess weight can increase the load on the bladder, which may contribute to the development of diseases.
- Regular medical examinations: timely visits to the doctor and undergoing recommended check-ups allow for early detection of changes in the condition of the bladder.
- Preventing urinary tract infections: drinking plenty of fluids, practicing proper hygiene, and timely treatment of urinary tract infections help reduce the risk of leukoplakia.
- Avoiding prolonged exposure to carcinogens: contact with carcinogens or toxic substances can increase the likelihood of developing bladder pathologies, so it is recommended to avoid such exposures.