Elbow bursitis: symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment methods.
Definition of elbow bursitis
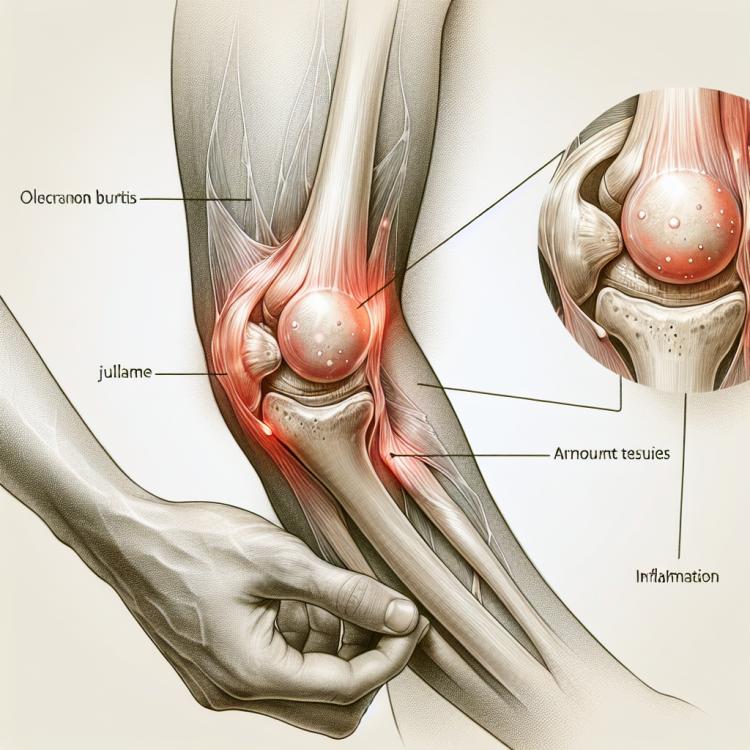
Elbow bursitis is an inflammatory disease characterized by inflammation of the mucous membrane (bursa) in the area of the elbow joint. This condition is often related to mechanical injuries, infections, or rheumatic processes. In elbow bursitis, pain, swelling, and redness in the elbow area can be observed, which may limit joint mobility. Diagnosis is based on clinical manifestations, medical history collection, and instrumental examination methods such as ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging.
Etiology of elbow bursitis
Elbow bursitis can be caused by various factors, including damage or injury to the elbow joint, improper positioning or loads on the elbow joint, as well as infections. One of the most common causes of elbow bursitis is damage to the mucous membrane, leading to inflammation of the bursa and the formation of exudate.
Other factors that contribute to the occurrence of elbow bursitis include regular monotonous movements of the arms and loads on the elbow joint, periodically recurring injuries, as well as infections that penetrate the bursa through various pathways. Understanding the etiology of the disease allows doctors to determine the best methods for treating and preventing elbow bursitis.
- Elbow joint injuries: injuries and trauma to the elbow joint can lead to inflammation of the bursa.
- Incorrect position of the elbow joint: constant load on the elbow joint or incorrect positioning of the arm while performing daily activities can contribute to the development of bursitis.
- Regular monotonous movements: repetitive monotonous movements of the arm or elbow can cause overload and irritation of the bursa.
- Repetitive injuries: frequent injuries to the elbow joint can be a cause of bursa inflammation.
- Infections: various infections, both bacterial and viral, can enter the bursa through different routes, causing the development of elbow bursitis.
The clinical picture of elbow bursitis
The clinical picture of elbow bursitis is usually characterized by swelling, tenderness, and redness around the elbow area. On palpation, the bursa may show signs of thickening and warmth. Patients may also experience limited movement in the elbow joint due to pain and stiffness. Some may note an increase in symptoms when bending or straightening the elbow, as well as when applying pressure to the bursa area.
In the case of acute elbow bursitis, external manifestations aid in establishing the correct diagnosis. The skin temperature over the bursa area may be elevated. A detailed examination considering clinical symptoms and additional diagnostic methods helps accurately determine the presence of elbow bursitis and take appropriate treatment measures.
- Swelling and thickening: elbow bursitis is often accompanied by swelling and thickening in the elbow area.
- Tenderness upon palpation: patients experience pain and discomfort when pressing on the bursa area.
- Skin redness: the area around the elbow may be characterized by redness and increased skin temperature.
- Limited movement: patients may experience difficulty bending or straightening the elbow due to pain and stiffness.
- Symptom intensification: symptoms of elbow bursitis may worsen when pressure is applied to the bursa or with certain elbow movements.
Expert opinion on the treatment of elbow bursitis
Expert opinions on the treatment of elbow bursitis emphasize the importance of a comprehensive approach, including conservative methods such as the use of anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and rehabilitation, as well as, in some cases, corticosteroid injections. Experts also recommend limiting physical activity during treatment to prevent further injuries and inflammation.
However, in the case of prolonged or chronic disease, specialists may decide on the necessity of surgical intervention to remove any possible formations in the bursa. Experts also highlight the importance of further monitoring of patients after treatment to prevent potential relapses and ensure full recovery of elbow joint functions.

Methods for diagnosing elbow bursitis
The diagnosis of elbow bursitis includes several methods aimed at establishing an accurate diagnosis and determining the causes of the disease. The doctor may conduct a physical examination, which includes palpation of the elbow area to identify swelling, tenderness, and thickening in the bursa area. X-rays may be used to rule out other possible causes of elbow pain, such as fractures or degenerative changes in the joint.
To confirm the diagnosis and identify the presence of fluid in the bursa, an aspiration procedure may be performed, in which fluid is extracted for subsequent analysis. Additional diagnostic methods, such as ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging, may be used for a more detailed examination of the condition of the elbow area and the bursa. The combination of results from various diagnostic methods helps determine the optimal treatment plan for a patient with elbow bursitis.
- Physical examination: The doctor performs palpation of the elbow area to identify swelling, tenderness, and thickening in the bursa.
- X-ray: A method that allows excluding other possible causes of elbow pain, such as a fracture or degenerative changes in the joint.
- Joint cavity aspiration: A procedure in which fluid from the bursa is extracted for subsequent analysis.
- Ultrasound examination: A method that allows for a more detailed study of the condition of the elbow area and the bursa.
- Magnetic resonance imaging: An additional diagnostic method used to obtain a more accurate picture of the condition of the tissues in the elbow area.
Methods for treating elbow bursitis
In cases of chronic or recurrent elbow bursitis, treatment may include corticosteroid injections or, in rare cases, surgical removal of the bursa. An individualized approach to treatment, taking into account the specifics of the case, is key to successful recovery from the condition and preventing potential complications.
- Use of anti-inflammatory medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs help reduce inflammation and relieve pain, which contributes to the improvement of the patient’s condition.
- Physical therapy and rehabilitation: Exercises and physical therapy procedures are aimed at restoring the functionality of the elbow joint and strengthening the muscles around it.
- Antibiotics: If a bacterial infection of the elbow bursitis is suspected, antibiotics may be prescribed to combat the pathogens.
- Corticosteroid injections: In some cases, a corticosteroid injection may be used directly into the bursa to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Surgical intervention: In severe and rare cases, when conservative treatment does not lead to improvement, the removal of the elbow bursa may be considered.
Preventive measures for elbow bursitis
For the prevention of elbow bursitis, it is also recommended to observe hygiene and protection measures when working with harmful substances or in conditions of increased trauma risk. An important aspect is the timely treatment of infections and injuries to prevent their spread to the elbow bursa. Adhering to a balanced diet, taking regular breaks, and monitoring physical activity also contribute to the prevention of elbow bursitis.
- Adherence to proper movement technique: avoid overstressing the elbow joint when performing daily tasks and exercises.
- Minimizing monotonous movements: avoid long, repetitive movements that can cause irritation of the bursa.
- Correct physical activity regimen: ensure a balanced load on the elbow joint, avoid excessive loads, and take breaks periodically.
- Observance of hygiene and protection measures: use protective equipment when working with harmful substances or in conditions of increased risk of injury.
- Timely treatment of infections and injuries: seek help at the first signs of infections and injuries to prevent complications.
Amazing aspects of elbow bursitis
Another fascinating fact is that elbow bursitis can be associated with work or hobbies that require constant repetitive hand movements and elbow bending. Understanding the possible causes and impacts on the development of this condition allows for more successful prevention and treatment of elbow bursitis, making it an intriguing subject of study in the medical field.