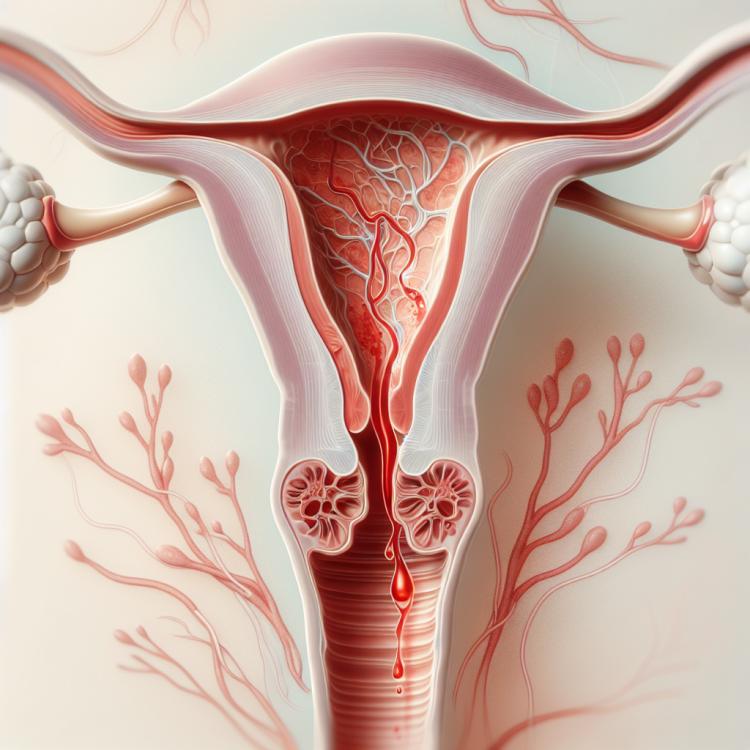
Uterine bleeding: causes, symptoms, and modern treatment methods
- Main aspects of uterine bleeding
- Factors that provoke uterine bleeding
- What manifestations accompany uterine bleeding?
- Expert opinion on the treatment of uterine bleeding
- Methods for diagnosing uterine bleeding
- Methods for treating uterine bleeding
- Measures to prevent uterine bleeding
- Amazing Aspects of Uterine Bleeding
- FAQ
Main aspects of uterine bleeding
Uterine bleeding is a condition characterized by excessive or unusually prolonged bleeding from the uterus. Causes include various pathologies such as cysts, fibroids, endometrial hyperplasia, or uterine cancer, as well as hormonal changes or blood coagulation disorders. Diagnosis is based on medical history, physical examination, and instrumental methods such as ultrasound and hysteroscopy, followed by the selection of the optimal treatment method, including conservative methods, surgical intervention, or angiohemostasis.
Factors that provoke uterine bleeding
Uterine bleeding can be caused by various factors, including hormonal balance disorders, abnormalities in the development of the uterus, uterine tumors, inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs, and blood coagulation disorders. Disturbances in the cyclical secretion of hormones, such as estrogens and progesterone, can lead to irregular and heavy menstruation, which contributes to the development of uterine bleeding.
Significant roles in the onset of bleeding can be played by diseases such as endometriosis, cervical polyps, uterine fibroids, malignant tumors, and thyroid gland dysfunction. Other factors contributing to uterine bleeding may include endocrine disorders, blood system pathologies, and the use of uncontrolled medications or contraceptives.
- Hormonal imbalance: Imbalance of estrogens and progesterones can lead to irregular and heavy menstruation.
- Uterine developmental anomalies: Structural changes in the uterus can be the cause of uterine bleeding.
- Uterine tumors: The presence of fibroids or cancerous tumors can cause disruptions in uterine bleeding.
- Blood system pathologies: Blood clotting disorders or other diseases of the blood system can be factors contributing to uterine bleeding.
- Inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs: Infections or inflammations in the pelvic organs can be the cause of uterine bleeding.
What manifestations accompany uterine bleeding?
Uterine bleeding can manifest with various symptoms, including heavy and prolonged menstruation, bleeding outside the menstrual cycle, the appearance of blood in urine or stool, as well as anemia due to excessive blood loss. Women suffering from uterine bleeding may experience severe lower abdominal pain, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, shortness of breath, and tachycardia due to anemia.
In addition, some patients may notice changes in the texture and odor of discharge, the presence of bloody discharge between cycles, as well as prolonged retention of menstrual blood in the uterus, which can lead to inflammatory processes. It is important to pay attention to these signs and seek medical help in a timely manner for the diagnosis and treatment of uterine bleeding.
- Heavy and prolonged menstruation: women with uterine bleeding often experience excessive bleeding during menstruation, which can lead to anemia and other issues.
- Bleeding outside the menstrual cycle: unexpected bleeding between periods can be a sign of uterine bleeding and requires medical intervention.
- Anemia: ongoing blood loss due to uterine bleeding can lead to iron deficiency and the development of anemia, accompanied by weakness and fatigue.
- Lower abdominal pain: women with uterine bleeding may experience severe pain in the lower abdomen related to changes in the uterus and the flow of blood.
- Other symptoms: blood in urine or stool, dizziness, shortness of breath, changes in the texture and odor of discharge can also accompany uterine bleeding and indicate the need for a doctor’s consultation.
Expert opinion on the treatment of uterine bleeding
The experts’ opinion on the treatment of uterine bleeding reflects the necessity for an individualized approach for each patient, taking into account the specifics of her condition and the causes of the bleeding. Experts recommend starting treatment with a consultation from a specialist for the correct diagnosis and selection of the optimal treatment strategy, which may include both medication therapy and surgical methods in severe cases.
Based on scientific data and clinical experience, experts emphasize the importance of regular monitoring of the patient’s condition during the treatment of uterine bleeding. Continuous monitoring helps assess the effectiveness of the chosen tactics and timely adjust the treatment if necessary, minimizing the risks of complications and ensuring the best outcome for the woman’s health.

Methods for diagnosing uterine bleeding
The diagnosis of uterine bleeding includes a variety of methods, starting with a thorough medical history and physical examination of the patient. Additional methods include laboratory tests, such as blood tests for hemoglobin and hormone levels, as well as ultrasound to assess the condition of the uterus, ovaries, and surrounding structures. Hysteroscopy, MRI, and CT scans may be used to obtain more detailed information about the structure of the organs and potential pathological changes.
For accurate diagnosis and determination of the cause of uterine bleeding, a histological analysis of endometrial biopsy may be required. These methods help establish a diagnosis, determine the nature of the bleeding, and select the most effective treatment plan for each specific case. It is important to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis to correctly identify the causes and optimize the management of uterine bleeding.
- Medical history and physical examination: The medical history and preceding symptoms are important for the initial assessment of uterine bleeding.
- Laboratory tests: Blood may be analyzed for hemoglobin levels, hormones, and other indicators that may suggest the causes of bleeding.
- Ultrasound examination: Ultrasound can be used to assess the condition of the uterus, ovaries, and other structures in the pelvic area.
- Hysteroscopy: This method allows for direct visualization of the inner surface of the uterus and the performance of an endometrial biopsy.
- MRI and CT: Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging can be used for a more detailed examination of structures in the area of the uterus and ovaries.
Methods for treating uterine bleeding
In cases where conservative methods do not yield the desired effect or when the bleeding is caused by other pathologies, surgical intervention may be required. Surgical treatment methods may include endometrial ablation, the removal of polyps or fibroids, and even hysterectomy in severe cases. When choosing a treatment method, it is necessary to consider the individual characteristics of each patient and strive for the best outcome for the woman’s health.
- Hormonal therapy: The use of hormonal medications, such as oral contraceptives or progesterone, can help balance hormonal levels and reduce heavy bleeding.
- Endometrial ablation: A procedure that involves removing or destroying the inner layer of the uterus can be effective in reducing bleeding for women who do not plan to become pregnant.
- Medication therapy: The use of medications, such as antifibrinolytics or drugs that enhance blood clotting, can help control bleeding.
- Surgical intervention: In some cases, surgery may be required to remove polyps, fibroids, tumors, or even the uterus if other treatment methods are ineffective.
- Uterine artery embolization: This process involves blocking the blood supply to the uterus, which can lead to reduced bleeding and decreased blood flow to the uterus.
Measures to prevent uterine bleeding
Monitoring hormonal levels, selecting appropriate contraception methods, as well as timely treatment of gynecological diseases contribute to reducing the likelihood of uterine bleeding. Educating women about their health, including identifying the first symptoms of menstrual cycle abnormalities, is also an important part of the prevention of uterine bleeding.
- Regular visits to the gynecologist: Conducting regular examinations and screenings allows for the early detection of potential reproductive health issues.
- Healthy lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including balanced nutrition, physical activity, and avoiding harmful habits, contributes to the overall strengthening of the body and reduces the risk of developing pathologies, including uterine bleeding.
- Monitoring hormonal background: Following specialists’ recommendations for the proper choice of contraception methods and maintaining hormone balance helps stabilize the menstrual cycle and prevents the development of uterine bleeding.
- Education on health awareness: Increasing gynecological literacy, including various aspects of women’s health and self-monitoring of the body’s condition, allows for quicker identification of changes and symptoms related to uterine bleeding.
- Timely treatment of diseases: Early detection and treatment of gynecological conditions, such as endometriosis, fibroids, and other pathologies, help prevent the development of uterine bleeding.
Amazing Aspects of Uterine Bleeding
Another interesting aspect of uterine bleeding is that modern medicine offers various diagnostic and treatment methods for this condition, allowing for the selection of the most effective strategies to address the problem. The use of advanced technologies and methods helps specialists accurately pinpoint the cause and effectively manage uterine bleeding, ensuring patients receive optimal health care.