Neurodermatitis: symptoms, causes, and treatment
- Understanding neurodermatitis
- Factors contributing to the development of neurodermatitis
- Manifestations of neurodermatitis
- Approaches to treating neurodermatitis: expert opinion
- Methods of diagnosing neurodermatitis
- Methods of treating neurodermatitis
- Measures for the prevention of neurodermatitis
- Interesting aspects of neurodermatitis
- FAQ
Understanding neurodermatitis
Neurodermatitis, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by itching, dryness, and inflammation. This pathology is often associated with allergic reactions and immunological disorders. The main factors contributing to the development of neurodermatitis are genetic predisposition, exposure to external allergens, and stressful situations. Defects in the skin barrier, imbalance in the immune response, and hyperreactivity of the nervous system play a role in the pathogenesis of the disease.
Factors contributing to the development of neurodermatitis
The development of neurodermatitis can be caused by various factors, including genetic predisposition, immune system disorders, and exposure to external irritants. For example, the presence of certain genes may increase the tendency toward autoimmune diseases, including neurodermatitis. Dysfunction of the immune system can also play a key role in the development of this disease, weakening the body’s protective functions and triggering inflammatory processes in the skin. Exposure to various allergens, stressful situations, and changes in the environment may also contribute to the worsening of neurodermatitis symptoms.
- Genetic predisposition: The presence of certain genes may increase the likelihood of developing neurodermatitis.
- Imbalance in the immune system: Disorders in the immune system can trigger inflammatory processes in the skin.
- Exposure to allergens: Contact with various allergens can provoke a worsening of neurodermatitis symptoms.
- Psychological stress: Stressful situations can exacerbate skin conditions and trigger the appearance of rashes.
- Impact of external irritants: Chemicals, dust, and animal fur can cause allergic skin reactions, intensifying neurodermatitis symptoms.
Manifestations of neurodermatitis
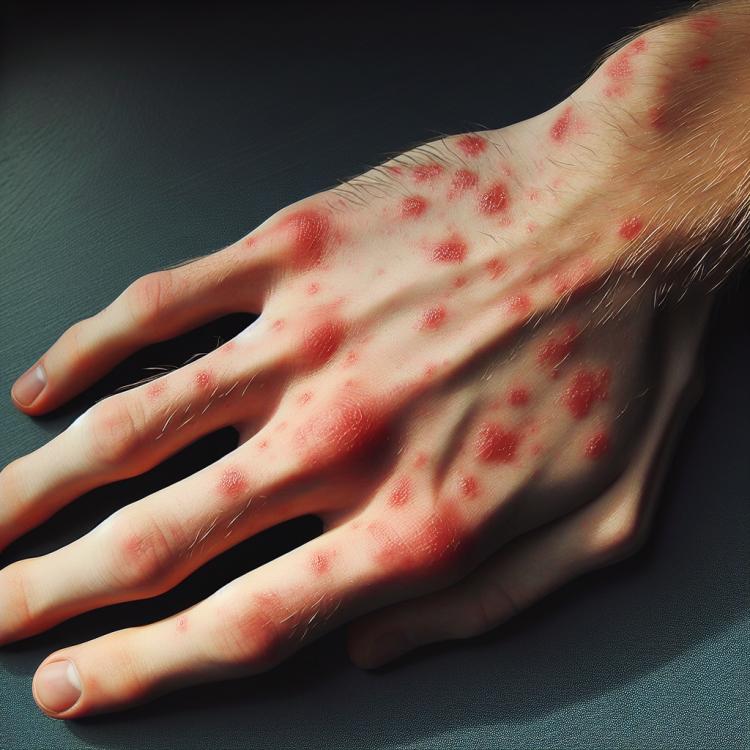
Neurodermatitis is characterized by a variety of symptoms, including itching, redness of the skin, dryness, flaking, and inflammation. Often, the external manifestations of neurodermatitis are accompanied by bouts of itching, especially when in contact with irritants or during stress. Skin rashes can vary in intensity and may range from small areas of skin to extensive zones, depending on the degree of disease manifestation. Other symptoms include the formation of yellow crusts on the skin, increased skin sensitivity, swelling, and possible appearance of blisters on the skin’s surface. It is important to consider the individuality of neurodermatitis manifestations in each patient and pay attention to changes in skin condition for timely diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
- Itching: one of the most characteristic symptoms of neurodermatitis is intense itching, often accompanied by the desire to scratch the skin for relief from discomfort.
- Skin redness: the skin in neurodermatitis often becomes red, which is associated with inflammatory processes in it and increased blood flow to the affected areas.
- Dryness and peeling: symptoms of neurodermatitis may be accompanied by skin dryness and the appearance of peeling, which may be caused by a disruption of the protective layer of the epidermis.
- Inflammation: the presence of inflammatory processes on the skin is a characteristic sign of neurodermatitis, manifested by swelling and redness of the skin.
- Formation of yellow crusts: patients with neurodermatitis may notice the formation of yellowish crusts on the skin, indicating a chronic inflammatory process and the accompanying healing of the skin covers.
Approaches to treating neurodermatitis: expert opinion
Experts believe that the treatment of neurodermatitis should be comprehensive and individually tailored for each patient. The basis of therapy usually consists of topical medications, such as anti-inflammatory creams, moisturizers, and gentle cleansing agents, which help to reduce inflammation, itching, and maintain the skin in good condition. Some experts also recommend the use of systemic medications, such as antihistamines or glucocorticosteroids, in cases of severe neurodermatitis symptoms. It is important to consider the needs and characteristics of each patient when choosing treatment methods and to coordinate the treatment plan with a qualified doctor to achieve optimal results.

Methods of diagnosing neurodermatitis
The diagnosis of neurodermatitis includes the medical history, analysis of clinical manifestations, skin examination, and assessment of the patient’s general condition. The doctor may perform special tests for allergic reactions to identify potential allergens that may contribute to the exacerbation of neurodermatitis. A skin biopsy may also be necessary for a more detailed analysis and to rule out other dermatological diseases. The diagnosis of neurodermatitis requires a comprehensive approach, taking into account all symptoms and characteristics of the patient to determine the most effective treatment plan.
- Medical history and examination: The doctor conducts a conversation with the patient to identify the nature of the symptoms, the time of their onset, possible provoking factors, and previous illnesses.
- Clinical examination of the skin: The doctor examines the patient’s skin, identifying characteristic signs of neurodermatitis, such as rashes, redness, peeling, and inflammation.
- Allergy tests: Special tests can help identify allergens that may exacerbate the symptoms of neurodermatitis, such as patch tests or skin tests.
- Skin biopsy: In case of ambiguous results or the need to rule out other diseases, the doctor may decide to perform a skin biopsy for histological analysis.
- Use of medical devices: Some specialized methods, such as dermatoscopy or microscopy, can complement the diagnosis of neurodermatitis, allowing for a more detailed study of the skin condition.
Methods of treating neurodermatitis
- Application of moisturizing creams and ointments: Moisturizing the skin helps reduce dryness and itching associated with neurodermatitis, as well as maintaining its protective barrier.
- Avoiding contact with allergens: Using hypoallergenic skin care products and household items can reduce the risk of flare-ups.
- Treatment with anti-inflammatory agents: Using topical anti-inflammatory creams or oral medications can help reduce inflammation on the skin.
- Phototherapy: Phototherapy procedures, including UVB therapy, may be prescribed by a doctor to improve skin condition and reduce inflammation.
- Antihistamines: Antihistamines may be prescribed by a doctor to reduce itching and discomfort associated with neurodermatitis.
Measures for the prevention of neurodermatitis
- Skin hygiene adherence: Regular cleansing and moisturizing of the skin helps prevent irritation and dryness, which can contribute to the prevention of neurodermatitis.
- Avoiding allergens: Identifying and avoiding potential allergens, such as dust, pollen, mold, or certain food products, helps reduce the risk of allergic reactions and exacerbations of neurodermatitis.
- Choosing hypoallergenic products: Using hypoallergenic cleansing and moisturizing products for the skin, as well as household chemicals and cosmetics, can help prevent skin irritation and allergic reactions.
- Moderation in skin care: Avoiding excessive use of soap, aggressive products, and rough friction on the skin helps maintain the natural protective barrier and skin health, which is important for the prevention of neurodermatitis.
- Stress management: Stress can be one of the triggering factors for exacerbating neurodermatitis. Therefore, it is important to manage stress, apply relaxation techniques, and find ways to reduce the impact of stress on the body.