Effective treatment of nasolacrimal duct obstruction: symptoms and causes
- Understanding the obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct
- Etiology of nasolacrimal duct obstruction
- The clinical picture of nasolacrimal duct obstruction
- Expert recommendations for the treatment of nasal lacrimal duct obstruction
- Methods of diagnosing nasolacrimal duct obstruction
- Goals and methods of treating nasolacrimal duct obstruction
- Measures to prevent obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct
- Funny aspects of nasolacrimal duct obstruction
- FAQ
Understanding the obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct
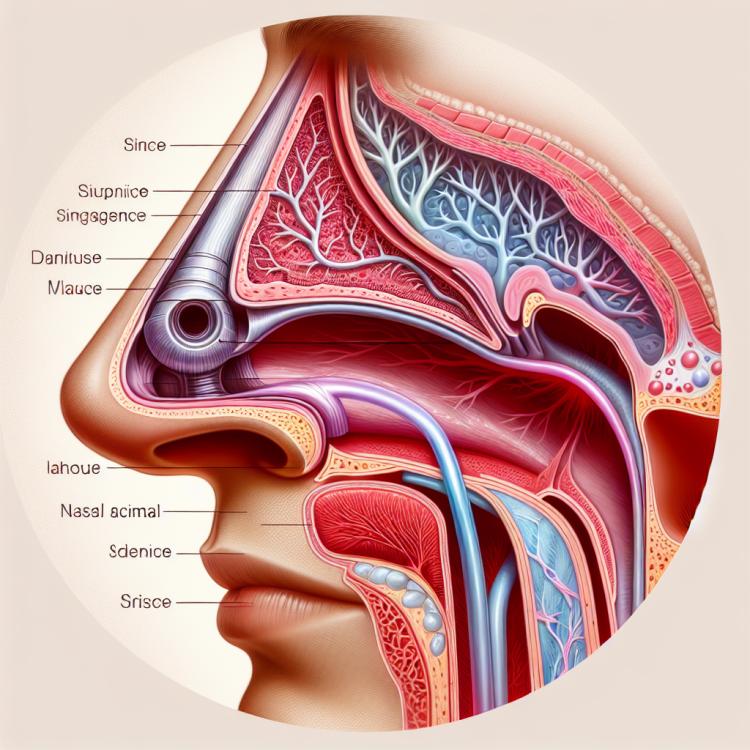
Nasolacrimal duct obstruction is a pathological condition characterized by the impairment of the anatomical structure that ensures the drainage of tear fluid from the eye socket to the nasal cavity. This can lead to the accumulation of tears in the eyes, the appearance of swelling and inflammation in the area of the tear sac, a condition known as dacryocystitis. The causes of nasolacrimal duct obstruction can be varied, including congenital anomalies, infections, injuries, tumors, or age-related changes in the tissues.
To diagnose nasolacrimal duct obstruction, methods such as retrograde dacryocystography, endoscopic examination, slow infusion of saline through the tear duct, and others may be used. Treatment may include conservative methods such as massage of the tear sac and irrigation of the duct, or surgical intervention, for example, dacryocystorhinostomy.
Etiology of nasolacrimal duct obstruction
Obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct can have various causes, including congenital anomalies in the structure of the nose, such as a blocked nasolacrimal duct or incomplete development of the lacrimal system. Other common causes may include inflammatory processes, such as rhinitis, sinusitis, as well as trauma, tumors, or even complications following surgical interventions. Understanding the specific cause of the obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct will not only aid in establishing an accurate diagnosis but also determine further treatment options, facilitating the successful restoration of lacrimal system function.
- Congenital anomalies: in some cases, the obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct may be due to developmental anomalies, such as blockage of the nasolacrimal duct.
- Inflammatory processes: rhinitis, sinusitis, and other inflammations in the nasal area and sinuses can lead to blockage of the nasolacrimal duct.
- Injuries: traumatic damage to the structures of the lacrimal system, for example, as a result of contusions or fractures in the nasal area, can contribute to the appearance of obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct.
- Tumors and neoplasms: tumors, sarcomas, cysts, or other neoplasms in the area of the nose or lacrimal gland can hinder the normal passage of tears to the nasolacrimal duct.
- Complications after surgeries or procedures: some surgical interventions in the area of the nose or eye may lead to temporary or permanent obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct due to scar formation or other complications.
The clinical picture of nasolacrimal duct obstruction
The clinical picture of nasolacrimal duct obstruction can manifest through various symptoms, including frequent tearing and eye irritation in bright light or wind. Patients may also experience a constant feeling of tension in the area of the nose, eyelid swelling, or a shiny sclera. Other common signs include persistent itching or burning in the eyes, as well as increased sensitivity to makeup and other cosmetic products around the eyes.
In addition, patients with nasolacrimal duct obstruction may experience a feeling of a foreign body in the eye, impaired sense of smell, swelling in the nasal area, as well as an increased tendency to develop inflammatory processes in the eyes and nose. If these symptoms are present, it is important to consult a doctor immediately for diagnosis and the necessary treatment aimed at restoring the patency of the nasolacrimal duct and improving the overall condition of the patient.
- Frequent tearing: obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct can lead to frequent episodes of tearing, especially in bright light or wind.
- Eye irritation: patients may experience irritation and discomfort in the eyes due to inadequate drainage of tears.
- Feeling of pressure in the nose area: the appearance of a constant feeling of pressure or tension in the area of the nose may be one of the signs of nasolacrimal duct obstruction.
- Persistent itching or burning in the eyes: symptoms of itching or burning in the eyes may indicate problems with the nasolacrimal duct.
- Swelling of the eyelids and scleral shine: obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct can cause swelling of the eyelids and changes in the appearance of the eye sclera, such as unusual shine or redness.
Expert recommendations for the treatment of nasal lacrimal duct obstruction
Experts in the field of otolaryngology recommend that the treatment of nasolacrimal duct obstruction should begin with a consultation with a specialist to establish an accurate diagnosis. Identifying the cause of the obstruction, whether due to congenital anomalies, inflammatory processes, or injuries, plays a key role in developing an individualized treatment plan.
Depending on the identified cause, various treatment methods may be offered by experts, including conservative approaches such as flushing the nasolacrimal duct or using medications, as well as surgical interventions aimed at restoring patency. Expert intervention and adherence to an individualized treatment plan contribute to the effective restoration of lacrimal system functions and improvement in the quality of life for patients.

Methods of diagnosing nasolacrimal duct obstruction
Various methods are used to diagnose obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct, including X-rays of the nasal region and paranasal sinuses, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), as well as lacrimal scintigraphy, which allows for the assessment of the patency of the tear ducts and lacrimal system. An analysis of the tear for the presence of infection or inflammation may also be conducted to confirm the diagnosis and determine the cause of obstruction.
Additionally, performing an endoscopic examination of the nasolacrimal duct allows the doctor to visualize the condition of the duct and identify any possible abnormalities or obstructions. The comprehensive application of these diagnostic methods enables the determination of an accurate diagnosis, identifies the causes of nasolacrimal duct obstruction, and develops an effective treatment plan to restore the function of the lacrimal system.
- X-ray: a method used to visualize the structures of the nose and paranasal sinuses, which can help identify anomalies or obstructions in the nasolacrimal duct.
- Computed Tomography (CT): an imaging method that provides a more detailed image of the structures of the nose and sinuses, assisting doctors in assessing the patency of the nasolacrimal duct.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): a medical method that allows for a more detailed image of the tissues and structures of the nose to identify the causes of nasolacrimal duct obstruction.
- Lacrimoscintigraphy: a procedure that assesses the patency of the tear pathways and lacrimal system by introducing a radioactive substance.
- Endoscopic examination: a visual examination method of the nasolacrimal duct using an endoscope to identify possible anomalies, obstructions, or changes in the structure of the duct.
Goals and methods of treating nasolacrimal duct obstruction
In cases where conservative methods do not yield the desired effect, surgical intervention may be required. Surgical treatment methods may include dilation of the nasolacrimal duct, irrigation of the tear pathways, removal of obstructions, or restoration of normal drainage. The primary goal of treatment is to ensure the normal function of the lacrimal system, prevent further complications, and enhance the quality of life of the patient.
- Conservative therapy: Includes the use of medicinal preparations, such as eye drops and ointments, to facilitate tear drainage and reduce inflammation.
- Physical therapy procedures: May include the application of heat compresses and massage of the area around the eyes to stimulate tear flow.
- Surgical intervention: In cases where conservative therapy is ineffective, surgical treatment may be required, such as dilation of the nasolacrimal duct or irrigation of the tear pathways.
- Removal of obstructions: Surgical removal of obstructions, such as polyps or tumors, can help restore normal tear drainage and function of the lacrimal system.
- Rehabilitation measures: After successful treatment, rehabilitation procedures are conducted to strengthen the lacrimal system and prevent possible recurrence of nasolacrimal duct obstruction.
Measures to prevent obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct
An important aspect of prevention is timely consultation with a doctor when symptoms indicating a disturbance in the drainage function of the tear pathways appear. Regular medical check-ups will help identify and prevent the development of pathologies related to nasolacrimal duct obstruction, contributing to the preservation of eye health and the lacrimal system.
- Regular hygiene procedures around the eyes and nose help prevent infections and inflammatory processes in the tear ducts.
- Avoiding trauma to the area around the eyes and nose will help prevent damage that may contribute to the development of nasolacrimal duct obstruction.
- Following individual recommendations from a doctor when initial signs of nasolacrimal duct obstruction are detected will help timely prevent the progression of the pathology.
- Regular check-ups with an ophthalmologist contribute to the detection and monitoring of the condition of the tear ducts, which helps prevent possible complications.
- Timely consultation with a doctor upon the appearance of symptoms indicating possible dysfunction of the lacrimal system contributes to the early detection of pathologies and the appointment of appropriate treatment.
Funny aspects of nasolacrimal duct obstruction
Moreover, in recent years, research has been conducted aimed at developing new technologies that can improve the diagnosis and treatment of nasolacrimal duct obstruction. This expands our knowledge of the functional and structural aspects of the lacrimal system, contributing to the search for more effective methods of prevention and therapy for diseases associated with this condition.