Otosclerosis: causes, symptoms, and modern treatment methods
- Understanding otosclerosis: symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment
- Pathogenesis of otosclerosis
- The clinical picture of otosclerosis
- The specialists’ perspective on otosclerosis therapy
- Methods of diagnosing otosclerosis
- Modern methods of treating otosclerosis
- Preventive measures to prevent otosclerosis
- Amazing aspects of otosclerosis
- FAQ
Understanding otosclerosis: symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment
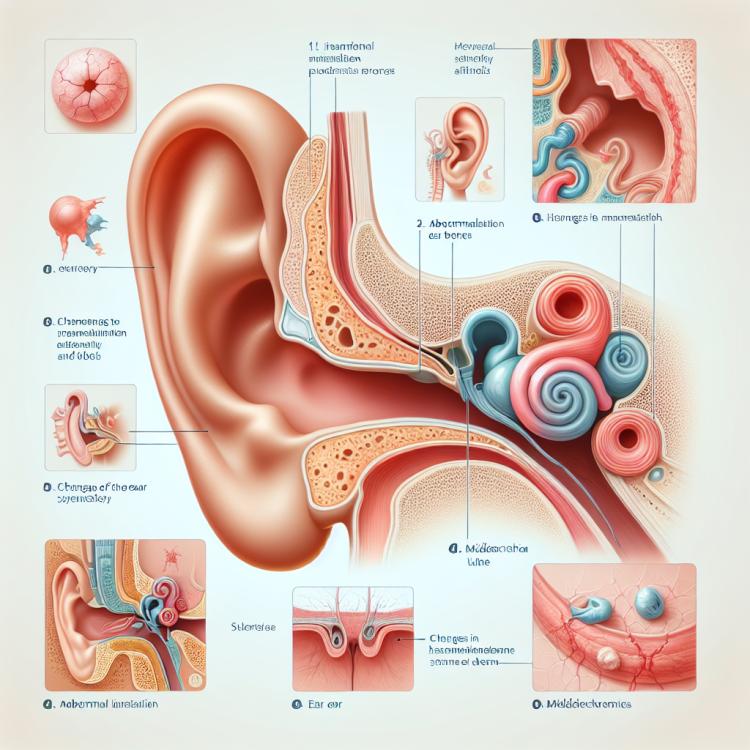
Otosklerosis is a chronic condition of the inner ear, characterized by abnormal bone growth in the cochlea. Patients with otosclerosis often complain of a constant decline in hearing, tinnitus, or echoing sounds. In diagnosing otosclerosis, audiometry is performed to assess hearing function, as well as imaging (such as CT or MRI) to visualize changes in the ear.
Treatment for otosclerosis may include observation, the use of hearing aids, or surgical intervention, such as stapedectomy. The goal of treatment is to restore hearing and improve the patient’s quality of life. However, each case of otosclerosis is individual, and the optimal treatment plan is determined after a thorough assessment of symptoms and the extent of the disease.
Pathogenesis of otosclerosis
Otosclerosis is a chronic disease characterized by abnormalities in the bone tissue of the anterior part of the labyrinth of the inner ear. The pathogenesis of otosclerosis is related to hyperostosis and resorption in the bone tissue around the cochlea, leading to impaired conduction of sound waves and, consequently, hearing loss in patients.
Studies also indicate a genetic predisposition to otosclerosis, as well as possible influences from external factors such as trauma and infections. Effective treatment for otosclerosis should consider the pathogenesis of the disease and aim to improve hearing and quality of life for patients.
- Hyperostosis of the bone around the cochlea
- Resorption of bone tissue in the anterior part of the labyrinth of the inner ear
- Genetic predisposition to otosclerosis
- Influence of external factors such as trauma and infections
- Disruptions in the transmission of sound waves due to abnormal bone tissue in the ear
The clinical picture of otosclerosis
The clinical picture of otosclerosis usually includes a gradual loss of hearing, which may begin in early adulthood. Patients may experience difficulties in perceiving low and high-frequency sounds, as well as the onset of noise or ringing in the ears. In addition, otosclerosis can lead to symptoms related to balance and coordination disturbances, such as dizziness and nausea.
In some patients, otosclerosis may also manifest symptoms related to vestibular function disturbances, such as vertigo and instability while walking. The clinical picture of otosclerosis can vary depending on the degree of damage and the individual’s characteristics, so it is important to conduct a comprehensive examination for an accurate diagnosis and to determine the treatment strategy.
- Gradual hearing loss: otosclerosis is often accompanied by progressive hearing loss, starting with low frequencies.
- Tinnitus or ringing in the ears: patients may experience a constant ringing or noise in the ears, known as tinnitus.
- Difficulties in sound perception: difficulties in perceiving high frequencies may occur, affecting the understanding of conversations and sound signals.
- Symptoms of balance disturbance: in some patients, otosclerosis may cause dizziness, unsteadiness, and other symptoms of coordination impairment.
- Vestibular symptoms: vertigo, nausea, and other symptoms related to vestibular function disorders may also be observed in some patients with otosclerosis.
The specialists’ perspective on otosclerosis therapy
The opinions of experts on the treatment of otosclerosis are based on extensive clinical research as well as the practical experience of specialists in this field. Modern methods of otosclerosis therapy include both conservative approaches, such as the use of hearing aids and rehabilitation measures, and surgical intervention, including stapedectomy or stapedoplasty.
Experts recommend a personalized approach to the treatment of otosclerosis, taking into account the individual characteristics of each patient and the degree of impairment. Monitoring the dynamics of the disease and regular consultations with specialists help to optimize treatment outcomes and improve the quality of life for patients suffering from otosclerosis.

Methods of diagnosing otosclerosis
To diagnose otosclerosis, a doctor may use various methods. The main methods include audiometry, which determines the level of hearing and identifies the presence of otosclerosis, as well as computed tomography for visualizing changes in the bony structure of the inner ear. Assessing audiometric indicators and detecting anomalies in computed tomography images play a key role in the accurate diagnosis of otosclerosis, allowing for the selection of the most effective treatment and improving the prognosis of the disease.
- Audiometry: This method allows the assessment of hearing at various sound frequencies, revealing changes characteristic of otosclerosis.
- Computed Tomography: This method can obtain detailed images of the inner ear and identify changes in the bone structure characteristic of otosclerosis.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): This method provides a more detailed study of soft tissues and organs, which can be useful for assessing the condition of the inner ear and surrounding structures.
- Oscillometry: This method allows the determination of measurable hearing parameters, such as the amplitude and frequency of sound vibrations, which can be useful for diagnosing otosclerosis.
- Vestibulometry: This method is used to assess vestibular function, allowing for the identification of possible balance and coordination disorders in patients with otosclerosis.
Modern methods of treating otosclerosis
- Stapedectomy: surgical removal of part of the stapes joint and replacement with a prosthesis to restore the transmission of sound vibrations in cases of otosclerosis.
- Use of hearing aids: utilization of hearing devices to compensate for hearing loss in patients with otosclerosis.
- Rehabilitation activities: conducting specialized training and classes to improve the quality of hearing and life for people with otosclerosis.
- Tympanomastoidectomy: surgical procedure used to correct anomalies in the structure of the ear and restore hearing in patients with otosclerosis.
- Tympanoplasty: surgical intervention aimed at restoring the integrity of the eardrum and improving hearing in patients with otosclerosis.
Preventive measures to prevent otosclerosis
- Avoid noise exposure: Continuous exposure to loud noise can lead to hearing damage, so it’s important to use protective headphones in noisy environments.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Healthy eating, regular physical exercise, and avoiding harmful habits can contribute to overall health and strengthen hearing.
- Regular medical check-ups: Conducting regular hearing tests can help identify problems at early stages and start treatment in a timely manner to prevent otosclerosis.
- Avoid injuries and infections: Taking precautions to prevent ear injuries and infections also helps in preventing the development of otosclerosis.
- Maintain ear hygiene: Regular hygienic care of the ears can help prevent infections and other issues that may lead to otosclerosis.
Amazing aspects of otosclerosis
Another remarkable aspect of otosclerosis is its impact on the quality of life of patients, as hearing loss can significantly affect their daily activities and social interactions. Studying the psychosocial aspects of the disease is important for a comprehensive approach to caring for patients with otosclerosis and enhancing their quality of life.