Scaly lichen: causes of occurrence and treatment methods
- Description of ringworm: symptoms, causes, and treatment
- Factors contributing to the appearance of pityriasis versicolor
- The clinical picture of Tinea Versicolor
- Expert opinion on the treatment methods for tinea versicolor.
- Methods for diagnosing tinea versicolor
- Methods of treatment for tinea versicolor
- Prevention measures against tinea capitis
- Amazing aspects of pityriasis versicolor
- FAQ
Description of ringworm: symptoms, causes, and treatment
Pityriasis Versicolor, also known as an inflammatory dermatosis, is characterized by the appearance of round or oval spots on the skin, covered with fine scales resembling bran. The symptoms are caused by hyperpigmentation, dry skin, and itching. The infection is caused by fungi of the genus Malassezia, which normally inhabit human skin but can lead to the development of this disease under certain conditions.
Treatment of Pityriasis Versicolor includes the use of antifungal ointments and creams, as well as antihistamines to relieve itching. Comprehensive treatment involves not only eliminating symptoms but also correcting factors that contribute to the development of the disease. Consultation with a dermatologist and following the specialist’s recommendations are important components of successful therapy for Pityriasis Versicolor.
Factors contributing to the appearance of pityriasis versicolor
Pityriasis versicolor is a fungal skin disease caused by the fungus Malassezia furfur. Factors contributing to the appearance of this type of lichen may include immune system disorders, prolonged use of antibiotics, changes in hormone levels, as well as external agents affecting the skin. Other risk factors can include skin damage, excessive sweating, and a hot and humid environment that promotes the multiplication of the pathogen.
However, it is important to note that the appearance of pityriasis versicolor is not always associated with these factors, as the infection can occur in individuals without obvious predisposing conditions. Thus, a comprehensive approach to understanding the causes of pityriasis versicolor includes both congenital and acquired factors, requiring an in-depth study of the mechanisms underlying this dermatological disorder.
- Immunodeficient conditions: disturbances in the immune system can contribute to the development of tinea versicolor.
- Prolonged use of antibiotics: long-term antibiotic treatment can alter the balance of microorganisms on the skin, creating conditions for the development of tinea versicolor.
- Hormonal changes: changes in hormone levels in the body can affect the condition of the skin, increasing the risk of disease development.
- Skin damage: mechanical injuries, the formation of scratches or cracks can facilitate the penetration of the fungal agent causing tinea versicolor.
- Exposure to external agents: using aggressive cosmetic products, highly aggressive chemical exposure, or prolonged exposure to water can create a favorable environment for the proliferation of the tinea fungus.
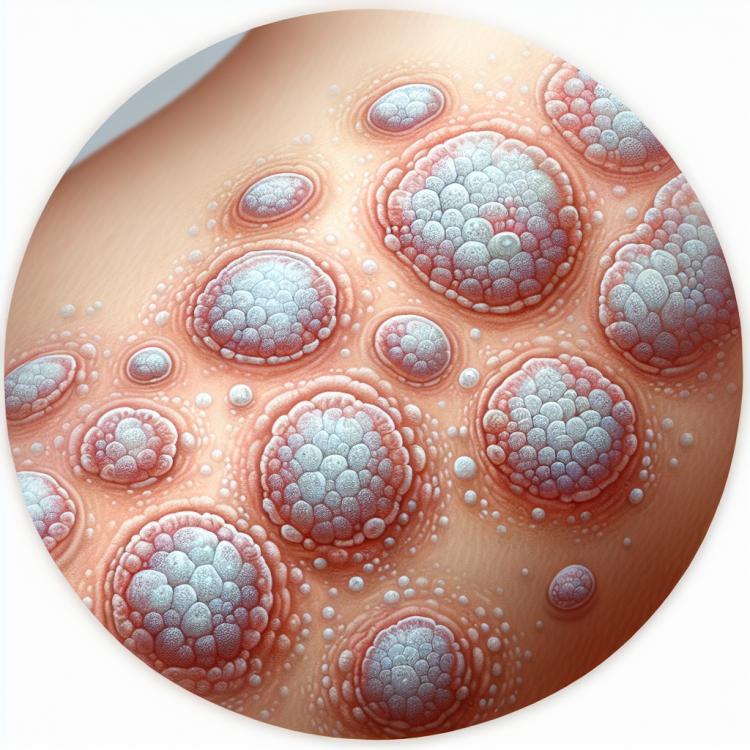
The clinical picture of Tinea Versicolor
Pityriasis versicolor is characterized by the appearance of yellowish or gray spots of small size, often merging into ring-shaped lesions with edges of scaly exfoliation of the skin at the periphery. The observed intense peeling can lead to the formation of visible scales, which gave the disease its name.
In addition, patients often experience itching and irritation in the affected skin area. Such symptoms may intensify in conditions of increased humidity or after physical activity. Often, the symptoms of pityriasis versicolor may resemble other dermatological conditions, highlighting the importance of consulting a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
- Appearance of yellowish or gray spots: initial manifestations of pityriasis may appear as yellowish or gray spots on the skin.
- Round patches with skin peeling: often these spots merge, forming ring-shaped patches with characteristic skin peeling at the edges.
- Peeling and formation of scales: patients may observe intense peeling in the affected skin area, which can lead to the formation of scales.
- Itching and irritation: skin affected by pityriasis often causes itching and discomfort for patients.
- Worsening of symptoms in conditions of high humidity: high humidity and physical activity can lead to an increase in itching and skin irritation in patients with pityriasis.
Expert opinion on the treatment methods for tinea versicolor.
Experts’ opinions on the treatment methods for tinea versicolor emphasize the importance of a comprehensive approach to this condition. The main therapy methods in dermatology include the use of antifungal ointments or creams containing active ingredients such as ketoconazole or clotrimazole. These medications help to eliminate the fungal pathogen and lead to the disappearance of rashes and symptoms of the disease.
In cases where tinea versicolor is complicated by severe itching or inflammation, the appointment of anti-inflammatory agents or antihistamines may be necessary. Experts also note that to prevent recurrences and maintain healthy skin, it is essential to follow hygiene measures, avoid skin trauma, and regularly consult a dermatologist for effective skin condition monitoring and prevention of further complications.

Methods for diagnosing tinea versicolor
The diagnosis of pityriasis versicolor is usually based on the clinical picture, which includes characteristic symptoms and features of the skin lesions. The dermatologist conducts a visual examination of the affected areas of the skin and may use a dermatoscope for additional evaluation. Skin samples may be taken for microscopic analysis, which helps identify fungal involvement and confirm the diagnosis of pityriasis versicolor.
If necessary, cultural diagnosis may be performed to clarify the diagnosis, which helps establish the type of fungus and its sensitivity to antifungal drugs. Additional diagnostic methods, such as standard fungal visualization techniques, may be applied in complex or ambiguous cases. Accurate and timely diagnosis is an important step in choosing the optimal treatment for pityriasis versicolor.
- Clinical examination: the dermatologist conducts a visual examination of the skin to determine the characteristics of lesions and identify characteristic symptoms.
- Dermatoscopy: use of a dermatoscope for additional visualization of affected areas of the skin, which aids in differential diagnosis.
- Microscopic analysis of skin samples: taking control skin samples for microscopic examination to detect fungal impact.
- Cultural diagnosis: performing analysis of skin samples to determine the type of fungus and its sensitivity to antifungal agents.
- Standard methods of fungal visualization: application of specialized methods for visualizing fungi to clarify the diagnosis in complex cases.
Methods of treatment for tinea versicolor
In addition to antifungal treatment, symptomatic relief of itching and irritation may be provided with antipruritic and anti-inflammatory agents. Furthermore, supporting hygiene and skin care measures can also play an important role in the recovery process and in preventing recurrences of the condition.
- Use of antifungal agents: Antifungals are prescribed to eliminate fungal infections on the skin.
- Local treatment: Topical application of creams, ointments, or lotions with antifungals helps combat the pathogen on the skin’s surface.
- Systemic treatment: The doctor may prescribe internal medications in cases of extensive lesions or ineffectiveness of topical agents.
- Symptomatic relief: Antipruritic and anti-inflammatory agents can help cope with itching and irritation on affected areas of the skin.
- Hygiene and skin care measures: Supportive measures may include preventing moisture on the skin, cleansing affected areas, and following hygiene rules that promote recovery and prevent recurrence of the disease.
Prevention measures against tinea capitis
Additional preventive measures may include using antiseptics for skin care, especially in the presence of micro-injuries or damage. Regular skin examinations and timely consultation with a doctor upon noticing suspicious changes are also important for preventing the development and spread of tinea versicolor.
-
– Skin hygiene compliance: Regular washing and using mild cleansing agents helps maintain skin cleanliness and reduce the risk of fungal infections.
– Avoiding close contact: Preventing close contact with infected individuals and personal hygiene items will help reduce the likelihood of transmission of tinea versicolor.
– Choosing natural and breathable fabrics: Preferring natural clothing materials can help prevent the creation of a suffocating environment on the skin, which promotes fungal growth.
– Conducting skin examinations: Regular skin examinations to identify suspicious changes, such as spots, irritations, or peeling, allow for timely consultation with a specialist for diagnosis and treatment.
– Using antiseptics: In the presence of microtraumas or redness on the skin, using antiseptics helps prevent the development of secondary infections and protects the skin from potential fungal infections.
Amazing aspects of pityriasis versicolor
Additionally, tinea versicolor is a recurring condition, meaning that even after treatment, recurrences may occur. This is due to the fact that the fungus can remain on the skin in doses insufficient to cause symptoms and can activate under certain conditions. This aspect necessitates strict control over skin hygiene and constant attention to the prevention of reinfection.