Panaritium: causes, symptoms, and treatment methods
- Clarification of the concept “Panariium
- Etiology of panaritium: main factors of occurrence
- Clinical manifestations of paronychia
- Expert opinion on the treatment of paronychia
- Methods for diagnosing panaritium
- Treatment of panaritium: methods and recommendations
- Prevention of panaritium
- Interesting aspects of panaritium
- FAQ
Clarification of the concept “Panariium
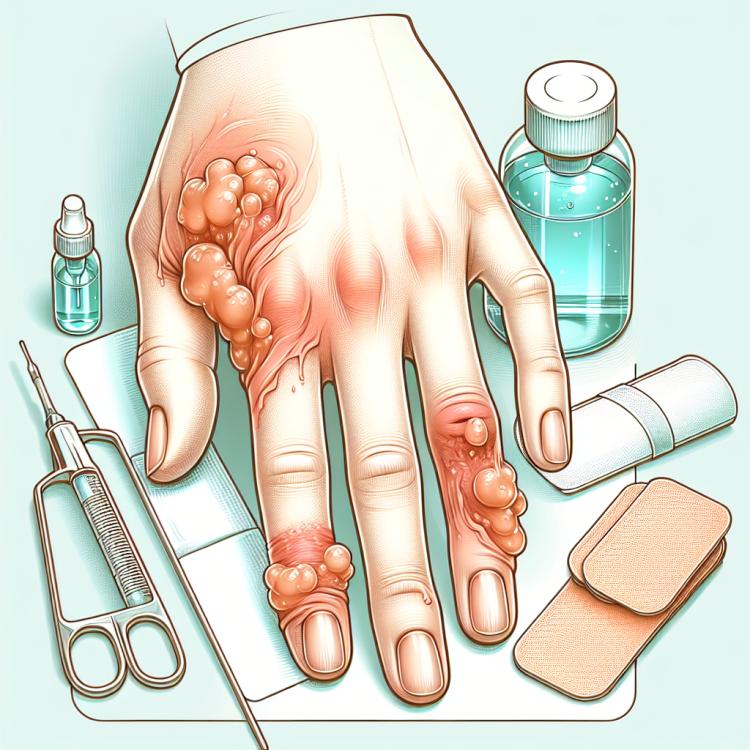
Panaritium is an inflammatory disease characterized by infection of the tissues around the nail. The main cause of the development of panaritium often becomes trauma to the nail or its surrounding tissues, creating conditions for bacteria to penetrate the soft tissues. Patients often complain of pain, swelling, redness, sometimes with purulent content. Successful treatment of panaritium requires timely diagnosis and comprehensive treatment, including antibiotics, drainage of purulent accumulations, as well as wound care and the use of anti-inflammatory agents.
Etiology of panaritium: main factors of occurrence
Panaritium is an inflammatory condition usually caused by a bacterial infection around the nail. The main cause of the development of panaritium is related to trauma or damage to the skin around the nail, which creates conditions for the invasion of pathogenic microorganisms leading to infection. Other contributing factors for the onset of panaritium may include improper handling of nail care tools, wearing uncomfortable shoes, as well as the presence of conditions that impair blood supply to the tissues around the nail.
- Injury or skin damage: even small cuts or scratches in the nail area can become entry points for bacteria.
- Improper use of nail care tools: poor-quality tools or incorrect techniques can damage the skin around the nail.
- Wearing uncomfortable or tight shoes: pressure or friction on the nail area can contribute to injuries and infections.
- Poor hand hygiene: insufficient hand washing and disinfection can lead to the transfer of bacteria to the skin around the nails.
- Frequent contact with water: constant exposure to a moist environment can weaken the skin barrier and promote infection.
Clinical manifestations of paronychia
In panaritium, patients usually experience localized pain, swelling, redness, and increased temperature in the area around the nail, often in combination with purulent discharge. An abscess may develop, which can lead to the formation of a purulent-inflammatory focus.
Also among the symptoms of panaritium, there may be a feeling of pulsation in the area of infection, sensitivity when pressing on the affected tissue, and sometimes a disruption of the nail’s mobility due to pain and swelling. It is important to consider that in the early stages, the symptoms of panaritium may be quite similar to the phenomena of other skin diseases, so differential diagnosis is necessary for accurate determination.
- Local pain: patients experience painful sensations in the area around the affected nail.
- Swelling and redness: the affected finger may be swollen and red due to inflammation and blood stagnation in the tissues.
- Increased temperature: the area around the nail may be hot to the touch due to the inflammatory process.
- Purulent discharge: the presence of pus in the affected area may be one of the key symptoms of paronychia.
- Abscess: the possible formation of an abscess, accompanied by tenderness and possible suppuration, indicates a serious course of the disease.
Expert opinion on the treatment of paronychia
Experts in the medical field recommend that the primary method for treating panaritium involves the opening and drainage of the purulent focus. This process helps to remove pus and reduce the pressure exerted on the tissues around the infected area. Antibiotic therapy may be required thereafter, especially in cases where there are signs of systemic infection or a risk of the infection spreading to deeper tissues.
Experts also emphasize the importance of adhering to aseptic rules when treating panaritium to prevent reinfection and encourage patients to seek medical attention at the first signs of infection around the nail area. Consulting a specialist and timely treatment can help prevent complications and accelerate the recovery process.

Methods for diagnosing panaritium
To diagnose a paronychia, the doctor usually conducts a physical examination of the affected area, assessing the presence of redness, swelling, and tenderness. It is also important to identify the presence of purulent discharge and evaluate the degree of inflammation in the tissues around the nail. In cases of suspected complicated or chronic paronychia, laboratory tests may sometimes be required, such as a bacteriological analysis of the purulent content.
For a more accurate determination of the nature of the infection and to make decisions regarding further treatment, additional examinations such as X-rays or ultrasound may be necessary. Differential diagnosis is crucial to rule out other conditions such as arthritis or other infectious processes, which helps determine the optimal treatment strategy for a patient with paronychia.
- Physical examination: the doctor assesses the presence of inflammation, swelling, redness, and tenderness around the nail.
- Laboratory tests: bacteriological examination of pus helps to identify the pathogen of the infection.
- Imaging methods: X-rays and ultrasound may be performed for a more detailed assessment of the condition of tissues and bones in the affected area.
- Differential diagnosis: ruling out other diseases, such as arthritis, allows for a more accurate diagnosis of panaritium.
- Clinical interview: information about medical history and any previous injuries may be an important component of the diagnosis of panaritium.
Treatment of panaritium: methods and recommendations
In addition, to prevent further complications and recurrences of panaritium, it is important to follow hygiene rules, properly care for the nails and the skin around them, and avoid injuries and mechanical damage that could become a source of infection. A specialist may recommend individual treatment guidelines based on the characteristics of each specific case of panaritium.
- Warm compresses: The use of warm compresses helps improve blood circulation, which can aid in the absorption of pus and relieve the symptoms of paronychia.
- Drainage of the abscess: In the case of abscess formation, drainage of the pus cavity may be necessary to remove the contents and speed up the recovery process.
- Antibiotic treatment: In some cases, especially with complicated or extensive infections, a course of antibiotics may be prescribed to combat the bacterial infection.
- Hygiene practices: One of the important aspects of treating and preventing paronychia is adherence to hygiene rules, including regular handwashing and proper nail care.
- Preventing injuries: To prevent the occurrence of paronychia, it is important to avoid injuries and mechanical damage to the skin around the nails, which can become a starting point for infection.
Prevention of panaritium
Special attention should be paid to hand hygiene, including frequent hand washing with soap and water, especially after contact with foreign bodies or substances. Avoiding tight or uncomfortable shoes, as well as promptly consulting a specialist at the first signs of infection around the nails, such as redness, swelling, or tenderness, will also help prevent the development of panaritium.
- Proper care for the skin around the nails: it is important to regularly trim the nails, avoiding injury, and to remove dead skin cells.
- Hand hygiene: regular hand washing with soap and water helps prevent infection in the area around the nails.
- Avoiding injuries: try to avoid injuring the skin around the nails, using protective gear when working with sharp objects.
- Wearing comfortable shoes: avoid tight or uncomfortable footwear to prevent pressure on the nails and the skin around them.
- Timely consultation with a doctor: if signs of infection appear, such as redness, swelling, or tenderness, it is important to see a specialist for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Interesting aspects of panaritium
Some cases of paronychia may be complicated by serious complications such as sepsis. Therefore, it is important to seek medical attention promptly at the first signs of infection around the nail area to prevent the development of acute paronychia and its possible complications.