Warts: everything important to know about symptoms, causes, and treatment
Definition and main characteristics of papillomas
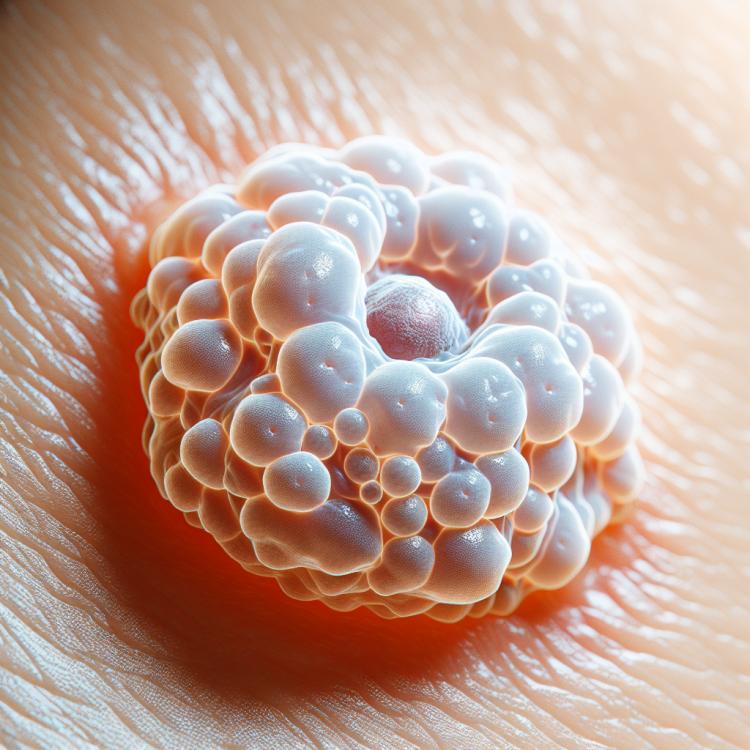
Papillomas are benign tumors caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They usually occur on the skin and mucous membranes of a person, appearing as tiny, protruding formations. They are characterized by slow growth and can be flat or raised, as well as have various shades, including colors ranging from pink to brown.
Papillomas are often diagnosed in individuals with weakened immune systems who are exposed to the human papillomavirus. Although they are generally not a health risk, in some cases, they can cause cosmetic discomfort or distress. Careful monitoring, consultation with a specialist, and timely treatment can effectively manage these formations and prevent their further spread.
Etiology of papillomas
Warts are benign growths on the skin and mucous membranes caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). The virus is transmitted through contact with infected skin or mucous membranes of a person, sometimes through contaminated household items. Some types of HPV are considered oncogenic and can lead to the development of malignant tumors, such as cervical cancer, anogenital cancers, and oral cancer.
Factors that contribute to the appearance of warts include a weakened immune system, frequent microtraumas to the skin, hormonal imbalances, and hereditary predisposition. Immunity plays a crucial role in controlling the reproduction of HPV and preventing the emergence of warts. Thus, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, regularly strengthening the immune system, and avoiding contact with potentially contaminated surfaces are important measures for the prevention of warts.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection: papillomas are caused by the activation of this virus, most often through contact with infected skin or mucous membranes.
- Reduced immunity: a weakened immune system poses a risk for the development of papillomas, as it limits the body’s ability to fight the virus.
- Micro-injuries to the skin: skin damage can facilitate the penetration and growth of the human papillomavirus.
- Hormonal changes: disruptions in hormonal balance, such as during pregnancy or puberty, can contribute to the appearance of papillomas.
- Hereditary factors: genetic predisposition may also play a role in the occurrence of papillomas, although specific genes associated with this are not always known.
Clinical picture of papillomas
Papillomas appear as growths on the skin or mucous membranes. Symptoms can vary depending on the location of the papilloma and its type. Common symptoms include the presence of small, firm, pigmented or colorless formations on the skin, which may have a rough or shiny surface. On mucous surfaces, papillomas may appear as soft, pink formations.
One of the characteristic symptoms is the possible appearance of itching, swelling, or even mild tenderness in the area of the papilloma. With multiple formations, cosmetic dissatisfaction may be observed. In some patients, papillomas can cause discomfort when in contact with clothing or while performing everyday activities.
- Appearance: Warts are usually pigmented or colorless growths on the skin or mucous membranes.
- Surface characteristics: Warts can have a rough or shiny surface, depending on their type and location.
- Skin symptoms: Growths on the skin can be firm, small, and rough to the touch.
- Mucous membrane symptoms: On mucous surfaces, warts may appear as soft, pinkish growths.
- Additional symptoms: Patients with warts may experience itching, swelling, discomfort when in contact with clothing, and mild tenderness in the area of the growths.
Expert opinion on the treatment of papillomas
The experts’ opinion on the treatment of papillomas is related to the choice of the optimal method depending on the type and location of the formations. One of the main methods of papilloma therapy is their removal. This can include both medications, such as cryotherapy, chemical solutions or topical agents, as well as surgical methods, such as surgical excision or electrocoagulation.
Experts also emphasize the importance of a comprehensive approach to papilloma treatment, which includes not only the removal of the formations themselves but also addressing the underlying causes that contribute to their occurrence. This may include correcting immune function, using antiviral agents in cases of viral etiology of papillomas, as well as regular examinations and monitoring of the patient to prevent recurrences.

Methods for diagnosing papilloma
The diagnosis of papillomas is based on a visual examination of the formations on the skin or mucous membranes. It is important to consider the characteristics of the papillomas – their size, shape, color, texture, and specific surface features. To clarify the diagnosis, a biopsy may sometimes be required for further microscopic analysis.
In addition to visual inspection and biopsy, methods such as dermatoscopy may also be used in the diagnosis of papillomas to study the structure of the formations on the skin in more detail. Additional methods, such as PCR to identify the human papillomavirus (HPV), may be used to confirm the diagnosis and determine the specific type of virus.
- Visual inspection: the main method of diagnosing papillomas, allowing assessment of the characteristics of lesions on the skin or mucous membranes.
- Biopsy collection: a procedure in which a small tissue sample of the papilloma is extracted for subsequent microscopic analysis.
- Dermatoscopy: a method that allows for a more detailed study of the structure and characteristics of papillomas using a dermatoscope.
- PCR diagnosis: a method that allows for the detection of human papillomavirus (HPV) in tissue samples to confirm the diagnosis and determine the specific type of virus.
- Immunodiagnostics: determining the level of antibodies to HPV in the blood to assess contact with the virus and possible activation of papillomatous lesions.
Methods of treating papilloma
In addition to physical removal methods, chemical agents may also be used, such as creams or solutions containing acids or other chemicals, for the direct treatment of papillomas. For patients with extensive manifestations of HPV infection, immunostimulatory drugs may be used to enhance the body’s defensive capabilities and reduce the frequency of papilloma recurrences.
- Cryodestruction: a method of removing papillomas based on freezing the formations using liquid nitrogen or other refrigerants.
- Electrocoagulation: a procedure in which the papilloma is removed using high-frequency electric current.
- Surgical removal: a method that can be used to remove large or incompatible formations through surgical intervention.
- Chemical agents: the use of creams, solutions, or patches containing acids or other chemicals for the treatment or removal of papillomas.
- Immunostimulation: the use of immunostimulatory drugs to activate the immune system and combat HPV infection, helping to prevent recurrences.
Prevention measures for papilloma: expert advice
Other effective prevention methods include using condoms during sexual contact and vaccination against HPV. Regular medical check-ups, timely identification, and removal of papillomas can also help in preventing further spread of the infection and development of the disease.
- Avoid close contact with skin lesions or mucous membranes of other people: precautions will help reduce the risk of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection.
- Practice personal hygiene: regular hand washing and avoiding contact with contaminated surfaces are also important in the prevention of papillomas.
- Use condoms during sexual contact: using condoms may reduce the risk of HPV transmission through sexual contact.
- Get vaccinated against HPV: the HPV vaccine can prevent infection with certain types of the virus and the development of papillomatous formations.
- Have regular medical check-ups: timely detection and removal of papillomas will help prevent further spread of the infection and disease progression.
Amazing features of papillomas
Another interesting aspect is that many individuals with HPV infection may remain asymptomatic or present with minimal symptoms, making early detection and treatment of warts difficult. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor when suspicious formations appear on the skin or mucous membranes, even if they do not cause discomfort.