Paratonsillar abscess: diagnosis and treatment
- Definition of peritonsillar abscess
- Etiology of peritonsillar abscess
- Clinical picture of paratonsillar abscess
- Approaches to the treatment of paratonsillar abscess, expert recommendations
- Diagnosis of peritonsillar abscess
- Treatment of peritonsillar abscess
- Prevention of peritonsillar abscess
- Amazing features of peritonsillar abscess
- FAQ
Definition of peritonsillar abscess
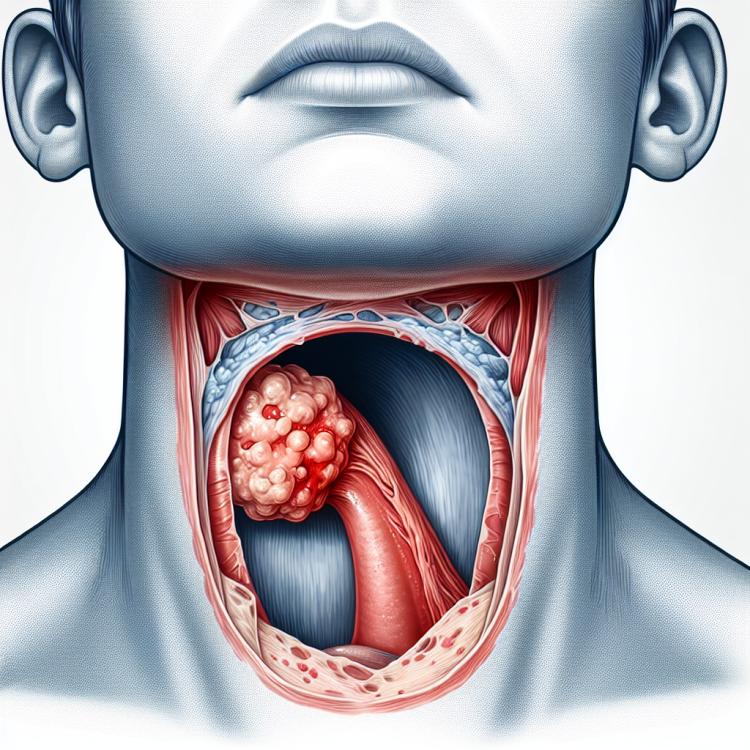
Paratonsillar abscess is an acute inflammatory disease characterized by the formation of a purulent cavity in the tissues located near the tonsils. It is a typical complication of pharyngitis or tonsillitis when the infection spreads beyond the tonsils, causing rapid accumulation of pus and swelling of the tissues, leading to the formation of an abscess.
Symptoms of a paratonsillar abscess include severe throat pain, difficulty swallowing, swelling of the soft tissues of the neck, fever, and general weakness. Diagnosis typically requires a physical examination where the doctor can identify the characteristic signs of the abscess and conduct necessary additional studies to confirm the diagnosis.
Etiology of peritonsillar abscess
Paratonzillar abscess usually develops as a complication of untreated tonsillitis or peritonsillar abscess. The main causes of this disease are infections caused by bacterial agents such as streptococci and staphylococci, which affect the tissues around the tonsils, leading to the formation of a purulent focus.
- Untimely treatment of tonsillitis: lack of adequate therapy for tonsillitis can lead to the formation of a peritonsillar abscess.
- Immunodeficient states: a weakened immune system can increase the risk of bacterial infections in the tonsil area.
- Throat injuries: damage to the mucous membrane of the throat can facilitate the entry of bacteria and the formation of an abscess.
- Disrupted drainage of the peritonsillar area: impaired lymph or exudate drainage from this area can contribute to the accumulation of purulent content.
- Decreased lysosomal activity: reduced activity of protective enzymes in the tissues of the tonsils can promote the proliferation and growth of bacteria.
Clinical picture of paratonsillar abscess
Paratonsillar abscess is characterized by various clinical manifestations, including severe pain and discomfort in the throat area, which intensifies during swallowing. Patients may also experience a sense of swelling or tension inside the mouth, an increase in body temperature, general weakness, and a deterioration in overall well-being.
Additionally, a paratonsillar abscess may be accompanied by swelling and redness of the tissues around the tonsils, difficulty opening the mouth, difficulty swallowing, and sometimes even breathing. Children and adolescents suffering from this condition may exhibit increased hostility when attempts are made to examine the mouth or throat, which should be taken into account during diagnosis and treatment.
- Severe sore throat: patients often complain of intense pain that worsens when swallowing.
- General malaise: patients feel weakness, fatigue, and sometimes an increase in body temperature.
- Swelling and redness of the tissues around the tonsils: there is significant swelling and redness in the area of the tonsils, which may be evident upon examination.
- Difficulties opening the mouth: patients may experience difficulty opening their mouths due to pain and swelling in the throat area.
- Difficulties swallowing and breathing: due to the formation of an abscess, there may be issues with swallowing food and breathing, leading to discomfort and anxiety.
Approaches to the treatment of paratonsillar abscess, expert recommendations
Expert opinion on the treatment of peritonsillar abscess highlights the importance of a comprehensive approach, including antibiotic therapy to combat bacterial infection, drainage of the purulent focus to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications, as well as mandatory observation and monitoring by medical professionals.
Experts recommend early detection and immediate treatment of peritonsillar abscess to prevent threats to the patient’s overall health. A combination of medication therapy, drainage procedures, and constant monitoring of the patient’s condition is considered the optimal strategy for managing this disease.

Diagnosis of peritonsillar abscess
The diagnosis of a peritonsillar abscess is usually based on clinical manifestations and physical examination. The doctor inspects the patient’s throat for swelling and redness, as well as assesses body temperature and lymph nodes. Additional diagnostic methods, such as ultrasound or computed tomography, may be used to more accurately determine the size of the abscess and its characteristics.
In cases of uncertain diagnosis or the need to confirm the diagnosis, aspiration of the abscess contents may be performed for laboratory analysis. Accurately identifying the microorganism that caused the infection can be important in choosing antibiotics for treatment.
- Clinical manifestations: the doctor examines the throat for swelling, redness, and enlarged lymph nodes.
- Instrumental methods: ultrasound or computed tomography may be used for more accurate diagnosis.
- Aspiration of abscess contents: may sometimes be required for laboratory analysis and identification of the infectious agent.
- Bacteriological studies: are conducted to determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics.
- Medical examination: an important part of diagnosis, allowing assessment of the patient’s condition and the adoption of correct treatment strategies.
Treatment of peritonsillar abscess
In cases of large abscesses that threaten breathing, surgical intervention may be required, such as drainage of the abscess to remove pus. This helps alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. Additionally, the use of analgesics and anti-inflammatory medications may be utilized to relieve pain and discomfort associated with this condition.
- Antibiotics: The use of antibiotics is a key component in the treatment of peritonsillar abscess to combat the infection and prevent its spread. It is recommended to prescribe antibiotics based on the sensitivity of the pathogen to them.
- Surgical intervention: In cases of large and life-threatening abscesses, drainage may be required to remove the purulent contents and prevent complications.
- Analgesics and anti-inflammatory agents: The use of these medications can help alleviate pain and discomfort associated with the peritonsillar abscess.
- Rest and regular monitoring: It is recommended to ensure rest and provide regular monitoring of the patient’s condition during treatment.
- Nutrition and hydration: It is important to provide the patient with adequate nutrition and fluids to support immunity and nourishment during treatment.
Prevention of peritonsillar abscess
To support tonsil health and prevent peritonsillar abscess, it is recommended to avoid contact with infectious patients, regularly ventilate the room, and support the body’s overall immunity through a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, and physical activity.
- Timely and adequate treatment of upper respiratory infections, such as tonsillitis, to prevent progression to peritonsillar abscess.
- Following oral and throat hygiene rules, including regular brushing of teeth and tongue, gargling, especially during viral epidemics.
- Avoiding contact with infected individuals and taking precautions when visiting crowded places, especially during the cold season.
- Regularly ventilating rooms and maintaining optimal humidity to prevent dryness of mucous membranes and reduce the likelihood of infections.
- Supporting the body’s overall immunity through a healthy lifestyle, nutritious diet, moderate physical activity, and adequate rest.
Amazing features of peritonsillar abscess
Interestingly, paratonsillar abscess is more common in children and young adults, although it can occur at any age. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to the symptoms of upper respiratory infections and seek medical help in a timely manner to prevent the development of extensive and complicated forms of this disease.