Pediculosis: prevention, symptoms, and treatment
- Understanding Pediculosis
- Factors contributing to the development of pediculosis
- The main signs of pediculosis
- Specialists’ perspective on lice treatment methods
- Identification of pediculosis
- Methods of treating pediculosis
- Measures for the prevention of pediculosis
- Amazing aspects of pediculosis
- FAQ
Understanding Pediculosis
Pediculosis is an infectious disease caused by the presence of head lice on human skin. The causative agents of pediculosis are the parasitic insects Pediculus humanus capitis, which infest the scalp. Transmission of the infection occurs through close contact between people or through shared household items. Pediculosis is accompanied by itching, skin irritation, and possible inflammation. Successful treatment of pediculosis requires the use of special lice medications, appropriate sanitization of clothing and bedding, as well as efforts to eliminate possible sources of infection.
Factors contributing to the development of pediculosis
Pediculosis, caused by lice infestation, is most commonly transmitted through direct contact with an infected person. Lice can also be transmitted through shared household items such as combs, hats, or clothing. Bad habits, poor hygiene, and close interactions in crowded places create favorable conditions for the spread of pediculosis.
- Direct contact: The transmission of lice most often occurs through direct contact with an infected person.
- Common household items: Pediculosis can also be transmitted through common household items such as combs, hats, or bed linens.
- Poor hygiene: Lack of hygiene practices can contribute to the development of pediculosis.
- Close interaction in crowds: Gathering of people in crowded places also facilitates the spread of pediculosis infection.
- Bad habits: Some bad habits, such as sharing hats or grooming in public places, can increase the risk of lice infestation.
The main signs of pediculosis
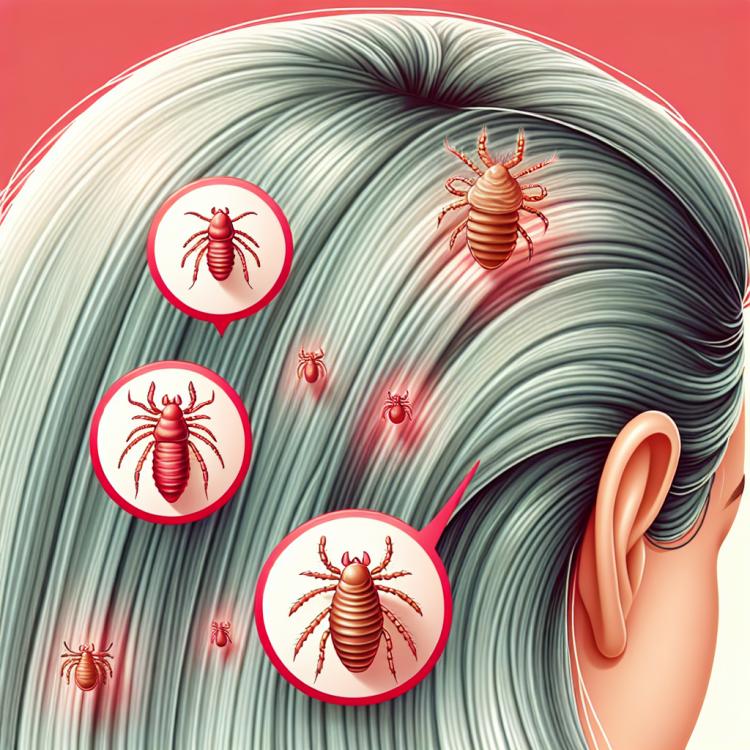
The main symptoms of pediculosis are itching of the skin caused by the activity of lice and the appearance of bites on the skin, often in the area of the head, neck, and behind the ears. Children may experience discomfort and skin irritation, which can lead to anxiety and sleep disturbances.
Other signs of pediculosis include the presence of lice eggs (nits) in the hair, which can be found at the roots of the hair. A definitive diagnosis is made through a visual examination of the hair and scalp by a specialist, and if lice or nits are identified, urgent treatment is required to prevent the spread of infection.
- Itching of the skin: the main symptom of pediculosis is intense itching of the skin caused by the activity of lice and their bites.
- Bites on the skin: patients may experience bites on the skin, especially in the area of the head, neck, and behind the ears, which is a sign of pediculosis.
- Presence of nits: nits, or lice eggs, may be seen at the roots of hair on the scalp, indicating a pediculosis infection.
- Discomfort and skin irritation: patients, especially children, may experience discomfort, a feeling of skin irritation, and unease, which can negatively affect their overall condition.
- Need for visual inspection: establishing a diagnosis of pediculosis requires a visual inspection by a specialist to identify lice and nits, followed by the appropriate treatment.
Specialists’ perspective on lice treatment methods
Experts in the field of pediculosis recommend a comprehensive approach to treating this condition, which includes the use of specialized products to eliminate lice and nits, as well as adherence to hygiene measures to prevent the spread of infection. It is noted that the choice of a specific product for treating pediculosis should be made taking into account the patient’s age, the presence of allergies, and other individual characteristics.
Experts also emphasize the importance of not only effective lice treatment but also thorough processing of the surrounding environment and household items. Regular washing of bed linen, clothing, and cleaning of premises helps eliminate lice and prevent their reappearance. Patients are also advised to inform their close contacts and acquaintances about the lice infestation to prevent further spread of the infection.

Identification of pediculosis
Diagnosis of pediculosis is usually carried out through a visual examination of the hair and scalp by a specialist. The discovery of live lice or eggs (nits) on the hair, especially at the roots, is the key sign of infection. To clarify the diagnosis, the specialist may use special tools, such as a magnifying glass or a special comb to search for lice and nits in the hair.
In addition to visual inspection, microscopic examination of samples of lice or nits may be conducted to establish the diagnosis of pediculosis. This helps confirm the presence of infection and determine the next steps for treatment. If lice or nits are found, treatment must be initiated immediately to eradicate the infection and prevent further spread of pediculosis.
- Visual inspection: Examination of hair and scalp by a specialist to look for live lice and nits.
- Use of special tools: Tools such as magnifying glasses and special combs are used to enhance the detection of lice and nits.
- Microscopic examination: Analysis of samples of lice or nits under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis.
- Consultation with a specialist: Consulting a healthcare professional for accurate identification of pediculosis.
- Personal observation: The patient may be trained to examine their hair and scalp for timely detection of signs of infection.
Methods of treating pediculosis
In addition to the use of pediculicides, an important part of pediculosis treatment is the additional processing of clothing, bedding, and household items, in order to destroy any potentially infested items. After treatment, it is recommended to carefully monitor the condition of the hair and scalp for several weeks to avoid recurrence of the infection.
- Use of pediculicides: special products containing pediculicides help to destroy lice and nits; it is essential to strictly follow the usage instructions.
- Additional treatment of household items: clothing, bedding, and other items that have come into contact with infected individuals require additional treatment to prevent reinfection.
- Re-treatments: in the case of pediculosis, it is important to conduct re-treatments with lice products for complete eradication of the infection.
- Monitoring the condition of the skin and hair: after treatment, it is necessary to closely monitor the condition of the skin and scalp to timely detect any possible reinfestation.
- Consultation with a specialist: in the case of pediculosis, it is recommended to consult a doctor or specialist for optimal treatment and monitoring of the recovery process.
Measures for the prevention of pediculosis
To prevent lice infestation, it is important to avoid close contact with people suffering from pediculosis and to check hair for lice and nits in a timely manner. It is also recommended to regularly inspect children’s heads, especially after contact with other children, to quickly identify and prevent the spread of infection.
- Regular hair washing: Clean hair helps to prevent pediculosis, so it is important to wash your hair regularly with shampoo.
- Avoiding contact with infected individuals: When cases of pediculosis are detected in the vicinity, it is essential to avoid close contact with infected individuals to prevent the transmission of the infection.
- Handling personal hygiene items: Using personal combs, hats, and other personal hygiene items will help avoid lice infestation through shared items.
- Regular checks for lice: Conducting regular inspections of the head to detect lice or nits helps to timely identify the infection and take measures for its treatment.
- Education on prevention: It is important to conduct educational activities for children and their parents on ways to prevent and spread pediculosis.
Amazing aspects of pediculosis
Moreover, studying the genetic structure and interaction mechanisms of lice with their host allows scientists to better understand the adaptation of these parasites and develop new methods to combat pediculosis. These intriguing aspects of pediculosis aid not only in the everyday struggle against the infection but also contribute to expanding our knowledge of the interaction between parasites and their hosts.