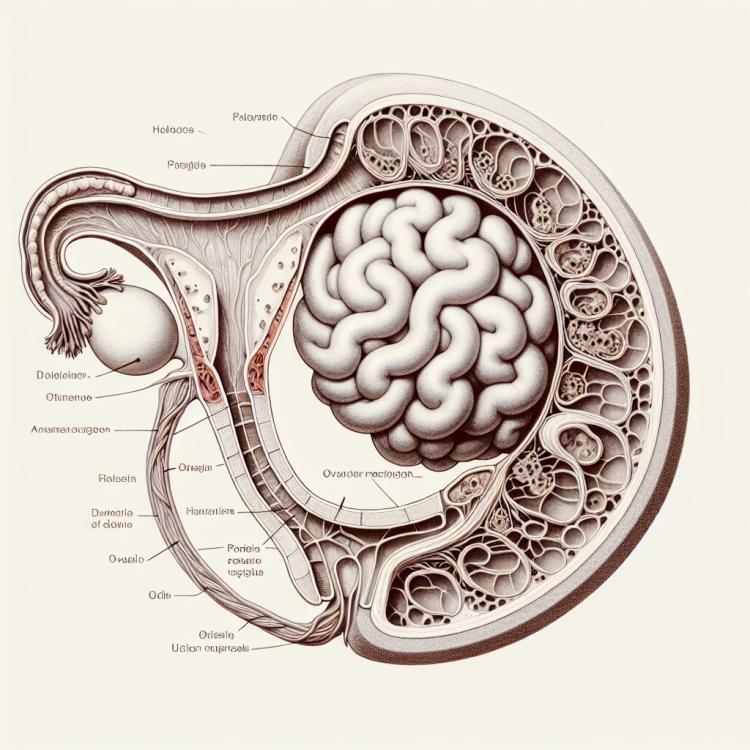
Ovarian cyst torsion: symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment
- Understanding the torsion of the ovarian cyst
- Etiology of ovarian cyst torsion
- Manifestations of ovarian cyst torsion
- Approaches of experts to the treatment of ovarian cyst torsion
- Methods for diagnosing ovarian cyst torsion
- Methods of treating ovarian cyst torsion
- Measures to prevent ovarian cyst torsion
- Amazing aspects of ovarian cyst torsion
- FAQ
Understanding the torsion of the ovarian cyst
Understanding ovarian torsion plays an important role in clinical gynecology practice. Ovarian torsion is an extremely serious complication that can lead to disruption of blood supply to ovarian tissues and necrosis. During this pathological process, severe pain in the lower abdomen, nausea, vomiting, and possible symptoms of general intoxication occur. Emergency medical intervention is required to prevent severe consequences, such as loss of the ovary and disruption of the woman’s reproductive function.
Etiology of ovarian cyst torsion
The etiology of ovarian torsion is usually associated with the formation of an ovarian cyst, which can be caused by an irregular menstrual cycle, hormonal disorders, or the presence of tumor formations. The twisting of the cyst on its base leads to impaired blood supply to the ovary, which can result in the formation of hemorrhages and tissue necrosis. Such changes often require urgent surgical intervention to prevent serious complications, such as ovarian sclerosis or loss of the ovary.
- Hormonal imbalances: changes in hormone levels, such as estrogen and progesterone, can contribute to the formation of cysts on the ovaries.
- Irregular menstrual cycle: improper hormone fluctuations and lack of ovulation can increase the likelihood of cyst formation.
- Genetic factors: a hereditary predisposition to the formation of ovarian cysts may play a role in their development.
- Tumor processes: the presence of tumors or neoplasms in the ovarian area can increase the risk of cyst occurrence and torsion.
- Inflammatory processes: infections and inflammations in the ovarian area can trigger cyst formation and contribute to their twisting.
Manifestations of ovarian cyst torsion
Manifestations of ovarian cyst torsion may include sharp pain in the lower abdomen, nausea and vomiting, as well as increased sensitivity in the pelvic area. Patients may also experience fever, increased heart rate, and changes in respiratory rate. In the event of ovarian cyst torsion, complications such as impaired blood flow to the ovary may develop, requiring urgent evaluation and treatment to prevent serious consequences.
- Sharp pain in the lower abdomen: Patients may experience sharp or severe pain in the abdominal area, often concentrated on one side.
- Nausea and vomiting: Symptoms of ovarian cyst torsion may include nausea and vomiting due to disrupted normal intestinal peristalsis and changes in internal pressure within the abdominal cavity.
- Increased sensitivity in the pelvic area: Patients may feel tenderness or discomfort in the pelvic area due to the involvement of the ovary.
- Fever: Fever may occur as a result of the inflammatory process associated with the torsion of the cyst and possible disruption of circulation.
- Increased heart rate and changes in respiratory rate: In response to stressful conditions, the patient may experience an accelerated heart rate and changes in respiratory rate.
Approaches of experts to the treatment of ovarian cyst torsion
Experts in gynecology typically recommend urgent surgical intervention when there is a suspicion of ovarian cyst torsion. Laparoscopic surgery is considered the preferred treatment method for cyst torsion, as it is less invasive, promotes faster recovery, and is generally associated with fewer postoperative complications. Experts also emphasize the need for an individualized approach to treatment, taking into account the specifics of each clinical case to reduce the risk of complications and ensure the best outcomes.

Methods for diagnosing ovarian cyst torsion
To determine the torsion of an ovarian cyst, doctors usually use various diagnostic methods, including ultrasound (ultrasound) and computed tomography (CT). Ultrasound allows visualization of the formation in the ovary and determination of its characteristics, including size and structure. Computed tomography provides a more detailed image of the affected area, helping to more accurately assess the condition of the ovary and potential complications.
In addition to imaging methods, laboratory tests may be used to diagnose ovarian cyst torsion to evaluate the levels of biochemical markers, such as blood and urine, as well as a complete blood count to identify possible inflammatory processes. Accurate diagnosis of ovarian cyst torsion plays an important role in making decisions about the best treatment for this condition and preventing potential complications.
- Ultrasound (ultrasonography): This method allows doctors to visualize the structure and characteristics of the ovarian cyst, determining its size and location.
- Computed tomography (CT): CT provides more detailed images of the ovarian area, which helps in diagnosing torsion and assessing the condition of the tissues.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): MRI is used to obtain detailed images of internal organs, aiding in the diagnosis of ovarian cyst torsion and assessing its characteristics.
- Laboratory blood and urine tests: Used to evaluate the levels of biochemical markers and identify inflammatory processes, aiding in the diagnosis of the condition of the ovary.
- Clinical examination: The doctor may perform a physical examination to identify symptoms and signs, as well as take a medical history for a more accurate diagnosis of ovarian cyst torsion.
Methods of treating ovarian cyst torsion
In some cases, medication may also be required to manage pain and prevent inflammation resulting from the surgical intervention. The postoperative period plays an important role in the successful recovery of the patient and the return to normal activity. Special attention is given to maintaining the health of the ovary and preventing recurrent cases of cyst torsion.
- Surgical intervention: Restoration of blood supply to the ovary by untwisting the twisted vessel and removing damaged tissue.
- Medication treatment: Use of medications to control pain, prevent inflammation, and maintain ovary health.
- Monitoring and control: After the surgery, patients are monitored by doctors to track recovery and prevent complications.
- Health maintenance: Special attention is given to restoring ovary health and preventing recurrence of cyst torsion.
- Rehabilitation activities: Restorative procedures and recommendations for successful recovery of the patient after surgery.
Measures to prevent ovarian cyst torsion
In order to prevent ovarian cyst torsion, it is recommended to eliminate factors that may contribute to cyst formation and changes in the ovaries, including active participation in preventive examination programs and following a diet that promotes ovarian health. Regular consultations with a gynecologist and seeking medical assistance at the first signs of any conditions, including ovarian cysts, also help prevent complications associated with their torsion.
- Regular check-ups: Women are advised to undergo regular gynecological examinations and ultrasound studies to detect changes in the ovaries at early stages.
- Following doctor’s recommendations: It is important to strictly adhere to doctors’ recommendations for monitoring reproductive health and using contraception methods.
- Healthy lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition, regular physical activity, and avoiding bad habits, can help prevent the occurrence of ovarian cysts.
- Timely consultation with a doctor: It is essential to consult a doctor at the first signs of ovarian dysfunction to conduct diagnostics and prescribe necessary treatment.
- Educational programs: Participation in educational programs related to women’s health helps raise awareness about ovarian issues and prevention methods.
Amazing aspects of ovarian cyst torsion
Another interesting fact is that ovarian cyst torsion can occur both spontaneously and as a result of physical activity or even during sleep. Understanding the possible provoking factors and timely seeking of medical help play an important role in preventing potential complications of this condition.