Psoriasis: symptoms, causes, and treatment
Psoriasis: main aspects and characteristics
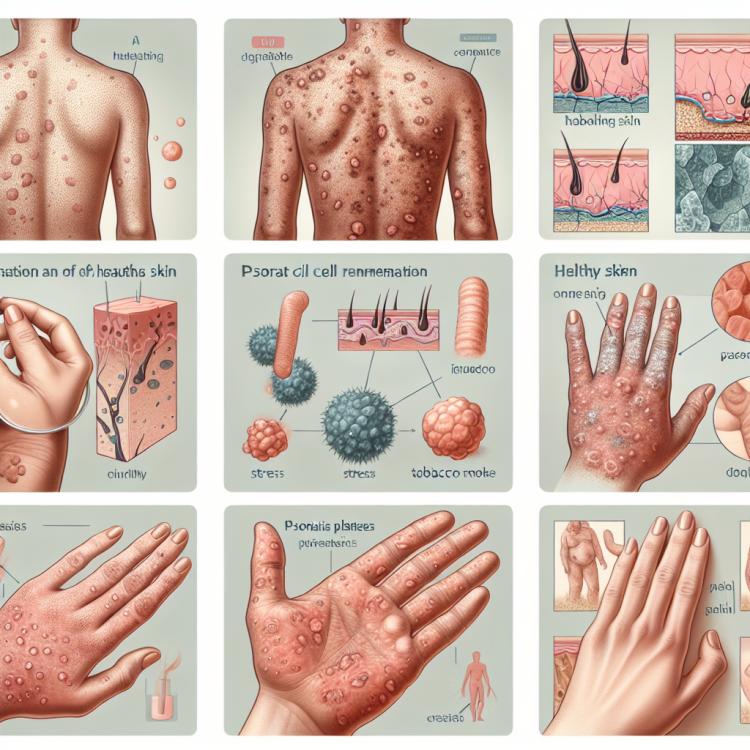
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by red patches and scaly areas of the epidermis. The cause of the disease is considered to be a disruption of the immune system, leading to accelerated skin cell renewal. Clinical manifestations of psoriasis can vary from mild forms with a small number of rashes to severe forms with numerous lesions and intense itching, which significantly impairs the patient’s quality of life.
Etiology of psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease, and its etiology is not fully understood. However, it is believed that psoriasis is caused by the interaction of genetic, immunological, and environmental factors. Genetic studies show a hereditary predisposition to the development of psoriasis, particularly associations with certain immune response genes. Furthermore, immunological changes, such as T-cell activation and cytokine production, play an important role in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Finally, the environment, including stresses, infections, and skin injuries, may also contribute to the development and exacerbation of psoriasis.
- Genetic predisposition: Hereditary factors play an important role in the development of psoriasis; a family history of the disease can increase the risk for offspring.
- Immunological changes: Activation of T-cells, disruptions in cytokine balance, and other immune alterations are considered key in the pathogenesis of psoriasis.
- Environmental factors: Environmental influences such as stress, infections, skin injuries, and even climatic conditions can trigger psoriasis flare-ups.
- Infections and skin injuries: Infections as well as mechanical damage to the skin can often provoke the onset of psoriasis or exacerbate its course.
- Psychological factors: Severe stress, depression, and other psychological issues can worsen psoriasis or contribute to its flare-ups.
Signs and symptoms of psoriasis
Psoriasis is characterized by the appearance of red, scaly patches or plaques on the skin, usually on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. These areas of skin often become inflamed, itchy, and may be painful. Some people may also experience changes in their nails, such as pitting or bumps, as well as joint inflammation known as psoriatic arthritis, which is accompanied by pain and stiffness in the joints.
- Red spots on the skin: Psoriasis manifests as red, inflamed areas of the skin, usually covered with silvery-white scales.
- Scaly plaques: The skin manifestations of psoriasis may have characteristic scaly covers that flake off when removed.
- Itching and discomfort: Patients often experience itching, burning, or discomfort in the affected area, which may be accompanied by unpleasant sensations.
- Nail abnormalities: Psoriasis can cause changes in the nails, such as pitting, thickening, or discoloration of the nail plate.
- Psoriatic arthritis: Some patients may also experience joint inflammation, manifested by pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joints.
Approaches to psoriasis treatment: expert opinions
In the treatment of psoriasis, experts often recommend a comprehensive approach that may include the use of topical agents, systemic medications, and phototherapy. Topical ointments and creams can help reduce inflammation and slow the formation of scales on the skin. Systemic drugs, such as retinoids and immunomodulators, are often used to control inflammation throughout the body. Phototherapy, or light therapy, can also be effective in reducing psoriasis symptoms, especially in cases where the use of medications may require a cautious approach.

Methods for diagnosing psoriasis
Diagnosis of psoriasis includes a visual examination of the skin, patient history, and sometimes a biopsy of the skin sample to confirm the diagnosis. The visual examination helps identify typical symptoms of psoriasis, such as red spots with silvery scales. Patient history helps uncover symptoms, duration of the disease, and factors that may trigger a flare-up of psoriasis. A biopsy of the skin sample may be used to confirm the diagnosis of psoriasis, although it is usually not required if the clinical signs are obvious.
- Visual inspection: the doctor examines the skin to identify typical symptoms of psoriasis, such as red spots with silver scales.
- Medical history: analyzing the patient’s medical history helps identify symptoms, the duration of the disease, and possible factors that triggered the exacerbation of psoriasis.
- Dermatoscopy: special equipment allows for a more detailed examination of skin changes and helps clarify the diagnosis of psoriasis.
- Skin biopsy: sometimes a skin sample may be required to confirm the diagnosis for further microscopic examination.
- Examination of nails and mucous membranes: additional studies may be necessary to assess the condition of the nails and check for the presence of psoriasis on the mucous membranes.
Approaches to the treatment of psoriasis
- Topical medications: Include ointments, creams, and lotions that are applied directly to the affected areas of the skin to reduce inflammation and itching.
- Systemic medications: Include oral drugs and injections of biological agents that affect the immune system to control inflammation and reduce symptoms.
- Phototherapy: Treatment with ultraviolet light can also be used to improve skin condition and reduce symptoms of psoriasis.
- Diet and lifestyle: Avoiding triggers such as stress and certain foods can help control psoriasis flare-ups. A healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and physical activity, can also have a positive impact.
- Psychotherapy: For patients experiencing psychological stress caused by psoriasis, psychotherapy or counseling from a psycho-emotional support specialist may be beneficial.
Preventive measures for psoriasis
- Healthy lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through balanced nutrition, regular physical exercise, and adequate rest contributes to strengthening the immune system and overall health.
- Avoiding stress: Emotional stress can trigger exacerbations of psoriasis, so it’s important to learn how to cope with stress and use relaxation techniques.
- Skin care: Regularly moisturizing the skin and avoiding trauma helps maintain its health and prevent the appearance of new psoriasis lesions.
- Avoiding risk factors: Quitting smoking and avoiding excessive exposure to sunlight or toxic substances can also help in preventing psoriasis flare-ups.
- Regular medical check-ups: Visiting a dermatologist for regular skin monitoring and consultations can help identify early signs of psoriasis and take timely treatment measures.